midterm III (helminthology) (trematodes) Flashcards
(60 cards)
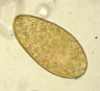
non-embryonated egg of Fasciola
(in fresh faeces sample)

native Cercaria of fascola hepatica

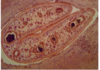
Fasciola hepatica
(liver fluke)
- see yellow mass of eggs behind the ventral sucker
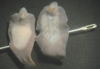
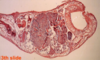
Fasciola hepatica (preserved sample)
- see the darker branches of intestines filled with blood

Paramphistomidosis
(rumen flukes)
- in europe Paramphistomum and calicophoron genres

unembryonated egg of rumen fluke
- eccentric zygote surrounded by course yolk

rumen fluke attached to a papillae

Dicrocolium dendriticum
(lancet fluke)
- transparent whitish body with a string of eggs seen throughout the tissue

the egg of dicrocoelium (lancet fluke)
- note the two eye-like excretory cells of the miracidium inside

Ants act as a sencond intermediate host for the lancet fluke
(they become infected from feeding on the ejected mucus from the landsnail)

chronic Dicrocoeliosis
- thick walled bile ducts in the cut surface of a sheeps liver
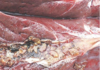
chronic fasciolosis
- adult flukes in enlarged and opened bile ducts of cattle

Rumen fluke (histology)

miracidium
-hatches and swims to find a freshwater snail

Trematoda: Miracidium inside the egg

Trematoda: miracidia

Trematoda: sporocyst

Trematoda: sporocyst containing rediae

Trematoda: sporocyst containing rediae

Trematoda: Redia

trematoda: cercaria

trematoda: full cecaria
- typical of blood flukes

trematoda: metacercariae

Trematoda: metacercariae
(notice the sucker in the middle)