Midterm Flashcards
(434 cards)
active transport
process which molecules move against the concentration gradient - energy is needed for this process
medical history r/t nutrition
- birth
- weight, length, head circumference, gestational age up to 2-3 yo (unless more pertinent)
- tollder - adolesence
- weight, height
- all ages
- previous dx states, comorbidities, hospitalizations, treatments, surgeries
- developmental history, growth history
- any issues r/t nutrition
bacterial infectious agents
- TB and haemophilus
- pertussis
- strep
- staph
- meningococcal
pediatric respiratory rate

CF overview pathophysiology
- CFTR (transmembrane conductance regulator) gene causes abnormal chloride-ion transport, reducing flow of water across cell membranes
- thick, dehydration mucous affects respiratory, GI, genitourinary systems
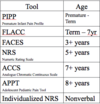
CRIES
- pain measurement scale
- crying
- requires oxygen
- increased vital signs
- expression
- sleeplessness
venous access for parenteral nutrition
- CVL
- PPN - peripheral parenteral nutrition
- consider reason
- consider fluid osmolality - lower than through CVL
- consider ability to optimize PN peripherally - enough nutrients
common side effects of opioids
- sedation/sleepiness
- mental confusion
- N/V
- pruritis (usually on face)
- urinary retention
- constipation
sepsis: “seeding” systemic circulation
- infection seeds sytemic circulation
- decreased tissue perfusion
- can’t get proper oxygen into and CO2 and toxins out of tissues
- leads to septic picture (decreased perfusion)
- severe sepsis, septic shock, death
- if you can interject with appropriate antibiotics, fluids in time you can mitigate and stop in its tracks
- potential is there once you’ve hit the inflammatory and decreased perfusion state
incision of artificial airway
- inferior border of cricoid cartilage
- de-cannulating
- pull trach out
- cover 5-7 days with gauze
- NO ibuprofen - inhibits stoma healing
- natural healing
nursing management of sepsis
- early recognition - get help
- IV access
- two working peripheral IVs is best practice
- aggressive fluid resuscitation
- early accurate antibiotic therapy; other meds
- ongoing VS assessment
- monitor urinary output
- labs
- blood culture, urine culture prior to antibiotics
- communicate with team and family
- accurately document
sepsis and decreased blood return to heart
- periphery not as tight as normal
- breakdown in ability of body to maintain peripheral contractility
- more pooling in extremities and periphery
- decreases blood flow back to heart
- decrease in CO
- decrease blood flow to organs
- vicious cycle
- increase SV to compensate for low blood flow causes tachycardia
response to disturbance in acid-base equilibirum
- acid-base buffer systems
- bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffers, intracellular protein buffers, phosphate buffers
- immediate regulation
- lungs alter rate of ventilate for CO2 removal
- minutes, hours
- kindeys alter excretion of H+ or bicarbonate
- hours, days
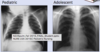
pnuemonia physical exam findings
- decreased/absent breath sounds
- accessory muscles
- adventitious breath sounds
- wheeze, crackles, partial breath sounds on one side vs other
- +/- abdominal pain
- children can’t discern exactly where pain is
parenteral nutrition
- when patients cannot meet nutritional needs PO or enteral
- sole of adjuntive therapy
- inadequate GI fxn
- inadequate oral/enteral take
- oncologic malignancies
- extensive burns
- pre/post op nutrition support
- severe malnutrition
functional residual capacity (FRC)
- volume in lung after passive expiration
- decreased in respiratory distress
- can cause precipitous desaturation
meckel’s diverticulum defined
- outpouching or bulge in lower small intestine
- congenital and leftover from unbilical cord
- most common congenital defect of GI tract
- may contain cells from stomach and pancreas
- cells from stomach secrete acid, causing ulcers and bleeding
all that wheezes is not asthma
- other diagnoses
- foreign body aspiration
- lower airway disease
- GE reflux
- GERD
- OSA
- response to bronchodilators, CXR may help with diagnosis

- “steeple sign” of croup seen on CXR
- narrowing at the top of the trachea
- usually treated symptomatically, not with X-ray
types of bleeds occurring in GI
- trauma
- 85% blunt
- meckels diverticulitis
- food related?
UTI treatment
- less than 3 mo - IV gent and amp, despite deafness risk with gent
- older children - oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- renal/bladder ultrasound to rule out anomalies
- voiding cystourethrogram
hypotonic IVF
- osmolarity is less than 300
- more water, less solute
- fluid moves from intravascular space into ECF into ICF
- cerebral edema (cell lysis)
- .45% NaCl (150 mOsm)
pertussis immunity
- should gain immunity in a pure world, but not everyone has the vaccination and we don’t have heard immunity
- speculation that the DNA has changed - may not have lifelong immunity
diet history
- usual mode of intake (PO, enteral, parenteral)
- age-appropriateness of diet
- food allergies/intolerances
- vitamin/mineral supplements
- herbal/natural supplements