Midterm 1 Flashcards
What is the optimal distance for Van der Waals interactions?
Occurs at a distance slightly greater than the length of the covalent bond.
1 nm = 10-9 m
1 Aº = ?
10-10 m
Order bond strength from strongest to weakest
- Covalent
- Ionic
- Hydrogen Bond
- Van Der Walls
Given the Second Law of Thermodynamics, how can reactions that create order (which are entropically unfavorable) occur?
- A favorable enthalpy change overcomes entropic penalty.
- The unfavorable reaction is coupled to a favorable one.
Plant cell shape is determined by the amount of water stored in the central vacuole. What is directly responsible for maintaining turgor pressure in a leaf?
osmotic pressure
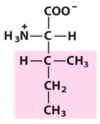
What are amino acids and how do they differ from one another?
Differ by the R group attached to central carbon

What 3 components make up a nucleotide?
- Nitrogen Base
- Pentose (5-ringed) Sugar
- Phosphate (1-3 groups)
Sugars contains what 3 atoms and what is the base molecular formula?
C, O, H
CH2O (Glucose is C6H12O6)
What does it mean if a molecule is amphipathic and which molecules usually exhibit this feature?
Has both hydrophobic and hydophilic parts.

Fatty acids
Compare saturated, polyunsaturated, and monounsaturated fats.
Saturated - No C=C double bonds
Polyunsaturated - Multiple C=C double bonds
Monounsaturated - One C=C double bond
Amino acids are _______ linked through _______ bonds.
covalently
peptide

Monosaccharides are _______ linked thorough _______ bonds.
covalently
glycosidic
What is supramolecular assembly?
NO covalent bonds involved
ex. membranes, DNA + Histones
What is the Organizational Heirarchy in Biochemistry?

What are the 3 unique properties of water?
- Solid water less dense than liquid water
- Liquid over wide range of Earth’s temperature
- Universal Solvent
What is a cofactor?
Any element required in conjuction with an enzyme to perorm a reaction.
When forming a hydrogen bond, there is always a H-bond ______ and H-bond _______.
donor
acceptor

In liquid, water makes about ____ H-Bonds
In ice, water makes about ____ H-Bonds.
3.4
4

What happens when a crystal of NaCl is dropped in water?
A hyrdation layer forms around the ions, preventing them from rejoining the crystal.

What exactly is a hydrogen bond?
A noncovalent weak bond that occurs between a hydrogen atom on an electronegative atom (N,O,) and a different electronegative atom.

What are Van Der Waals interactions?
Occur when temporary dipoles interact

What is the Van Der Waals radius?
Perfect distance between two atoms in order for Van Der Waals interaction to occur.
*Note: If atoms are too close, they will repel. If they are too far, they will not interact*

What are hydrophobic effects?
Weak noncovalent interactions between non-polar molecules in which the molecules clump together to reduce the size of the hydration layer.

Cell membranes are made of __________ bilayers.
phospholipid