Menopause Flashcards
What are the four theories around why we have Menopause?
- Blessings of Modern Life
- Most animals reproduce as long as they live
- We live longer now, this wasn’t an issue in the past!
- Fixed # follicles
- Senescence
- Deterioration of reprod. precesses with age
- Protects aging women from hazards of childbirth.
- Group Selection***
- Menopause protects the human genepool against birth defects due to the age-related increase in chromosomal abnormalities
- Only confirmed theory!!
- Good-mother/grandmother
- Pause from reproduction to provide extended maternal care of offspring

1,2 and 3 may just be an incidental finding
How was the timing of Menopause determined?
What signifies the end of a woman’s reproductive life?
- Under intense evolutionary pressure, consequence of the ovaries running out of follicles
- Occurs between 50 and 52 yrs (45-55)
- End of Reproductive Life: last epsidoe of natural menstrual bleeding men- month, pauo- to stop
- Atresia and ovulation (only ~400 follicles) lead to exhaustion of follicular reserve

POF and EM?
Premature Ovarian Failure: ovarian failure <40yrs
- Affects 1% of women and 0.1% by age 30yr
- Increasing issue as women delay childbearing
Early Menopause: 40-45yr

The age of menopause can be correlated with the age of _____ by a ____year gap
The age of menopause can be correlated with the age of last birth by a 10 year gap of last time of fertility.
This shows us that is a woman gets menopause at 48 she was probably infertile at 38

How do follicle numbers change throughout life?
- peak in fetal development of ~7mill
- Down to 1mill by birth
- steady ddecline to ~400, 000 by puberty
- Menopause: <1000 follicles

What’s the ‘popcorn Hypothesis’?
Describes how the quality of follicles also decrease over time, as well as the quantity
- The best follicles go early (20’s)
- As you get close to 40, the ovary “turns up the heat” by increasing the levels of FSH to try get the last few follicle ‘kernels’ to grow and ovulate.
- But as you age the amount of chromsomal abnormalities decrease.
When are you ‘most fertile?
Optimal Fertility: 20’s
declines
End of fertility: starts around 40’s

University students knowledge quiz
- Chance of a women getting pregnant from unprotected intercourse around ovulation
- Real answer:
- Students answer: overestimated fertility by 10-20%
- Chance of a women getting pregnant via IVF
- Real answer
- Students answer: overestimated older years by 20-30%, medical students convinced technology could save fertility

What influences timing of Menopause
- Independent from race, parity, marital status and age of menarche
- Mothers and daughters have similar menopausal age strong genetic correlation/prediction
- Pourly nourished and/or smoking women have an earlier menopause
- Repro. system the first to shut down
- smoking is earlier by 1-2 yrs; mainly from atresia of primordial follicles

Does ‘male menopause’ exist?
“andropause”
- Thought to affect men 40-55yr
- Due to testosterone decline
- Body changes occur very rapidly: mood change, fatigue, loss of sex drive and physical agility
- Not much strong evidence; and you’d need a really low level to have an effect
- Probably just to sell male products
Draw the female reproductive phases leading upto
Pre-menopause: 40 to age of irregular menstrual cycles (~46 yrs)
Menopausal Transition: from start of irregular cycles to menopause (Last menstrual bleed)
Post-menopause: after last menstrual bleed.
Peri-menopause: when all the symptoms and clinical features are noted
Ovarian senescence: as ovary is active for ~1yr after last menstrual bleed.

What does STRAW show us.
We can measure the stges of menopause BUT
Its the peri-menopause where we see the clinical symptoms, the longer and more irregular menstrual cycles
When do we have irregular menstrual cycles?
At the beginning and end of a womens reproductive life.
- Takes until around 20-30 to begin having regular cycles
- THis gets irregular again ~40yr as cycles begin to length (transitioning into menopause begins)
- Where a follicle begins to grow, nothing happen/goes wrong, undergoes atresia and we have to wait for the next cycle to get another follicle

The longer the cycle length, the less like it is ________
The longer the cycle length, the less like it is ovulatory

<40 days: ovulatory
>40 days: not likely to develop and ovulate
Older women are more likely to have _______ cycles
Older women are more likely to have anovulatory cycles
26-40 yrs: ~5 % anovulatory
41-50yrs : ~15% anovulatory

THe Perimenopausal phase is a time of?
Erratic hormone fluctuations which starts at the begnning of the menopausal transition and continues through to ovarian senescence.
~5-10% of women don’t experiance a transition phase and just abruptly cease menstrual activity
Climacteric: Physical and emotional symptoms associated with the perimenopause
Dogma around accelerated decline of events just prior to perimenopause
- Follicle levels reduce below a critical threshold (~25,000 follicles)
-
Inhibin B levels begin to decline
- Inhibin B is produced by the granulosa cells of primary follicles, and these cells are decreasing along with the follicles
- Release on inhibin negative feedback on FSH
- FSH levels rise (popcorn hypothesis)
- Acceleration of last few Follicle loss by:
- Shortened follicular phase
- Increased early follicular oestrogen

How much does the increased FSH deplete the follicuar pool just prior to perimenoopause?
- Increased FSh stimulates a greater proportion of primordial follicles to enter the growing pool
- Accelerates depletion of primordial reserve from ~20-40/day to ~80/day
Also increases “twinning” as you age because of this!! Two dominant follicles have been able to survive
What are feautures of perimenopause?
- Irregular cycles
- Annovulatory cycles comon (bad follicles)
- Gonadotrophs elevated (especially FSH)
- remains high post-menopause
- clinical indicator
- Oestrogen levels are often high early peri-MP, but then low late peri-MP
- Unpredictable hormone patterns
- Ovulation is still possible
- but Contraception is difficult


FSH: loss of negative feedback from inhibin, begins to rise ~7-8 yr prior to menopause. Remains high after (clinical diagnostic indicator)
LH: only rises a little as not affected by inhibin
Estrodial: Produced by granulosa and thecal cells in follicles, high up till 2 years prior to menopause, then comes crashing down
Estrone: relatively unaffected as the adrenal glands are the main producer. This becomes the main sources of oestrogen most menopause


Testosterone: loss of libido
Post-menopause?
From the last menstrual bleed, this doesn’t truly reflect what’s happening in the ovary.
There’s no simple test to confirm menopause, and it’s usually defined retrospectively.
Woman >45yrs, who’s had amenorrhoea for at least 12 months is highly unlikely to ovulate again, and is probably post-menopausal.
Fluctuations in hormones (esp. oestrogen) can continue >6months
Are there any follicles left post-menopause?
Some may be left, but they are non-responsive
(POPCORN HYPOTHESIS)
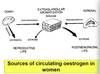
Post-menopausal oestrogen production
- By around 1yr post menopause, the ovary has essentially ceased producing hormones: “ovarian senescence”
- Estrogen produced daily is less then 1/10th what she used to
- Circulating estrodial levels are very low and don’t fluctuate
- Pre-MP: changes 10-fold
- Post-MP: very little variation
- Main Estrogen source: Oestrone
- still reduced post MP