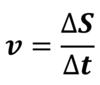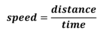Mega Deck Flashcards
State two conditions for any object to be in equilibrium
Resultant force zero
Resultant moment about any point zero
State three vector quantities
Any 3 of the following:
Velocity
Acceleration
Force
Displacement
Weight
Momentum
State three scalar quantities
Any 3 of the following:
Speed
Distance
Mass
Energy
Power
Temperature
How can force vectors be arranged to show that an object has constant velocity?
- Vectors make a closed shape when rearranged (by scale drawing)
- Or resolve into components and show
- Total up forces = Total Down forces
- Total left forces = Total right forces
What is the difference between a vector quantity and a scalar quantity?
Vector has a direction
Scalar does not
What is meant by centre of mass?
The point in a body where the weight of the object appears to act
Also the resultant moment about this point = 0
Define the moment of a force
Product of the force and the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the point

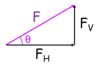
Resolve F into its vertical and horizontal components…

FH = FcosØ
Fv = FsinØ
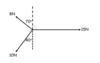
What mistake has been made in rearranging the vectors for a scale drawing?

6N vector has been translated (moved) but also rotated
Should be:

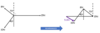
What are the steps in working out the resultant force using a tip-tail scale drawing?
- Set a scale
- Draw the horizontal or vertical vector first (if there is one)
- Move each vector in turn to the end of the previous one (DO NOT ROTATE THE VECTORS)
- Resultant vector goes from the very start to the very end
How is the balancing force different from the resultant force?
The balancing force brings the object into equilibrium so makes the resultant force = 0
For a scale drawing, it is the vector that closes the shape

If vectors are parallel they can be resolved by…
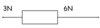
Adding or subtracting the values

If vectors are perpendicular they can be resolved by…
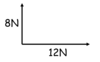
Making a right angled triangle and using trigonometry and pythagoras
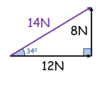
What is wrong with this?

Vectors of different types can’t be combined
(Here, force and velocity cannot be combined)
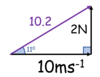
How do you solve this if the object is in equilibrium?
(3 vectors with 2 unknown sizes)
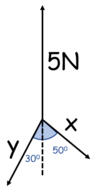
- The vectors must form a closed shape
- Start as you would with a scale drawing
- But draw the third vector meeting for where it connects to the start of the first
- Draws vectors as dotted lines
(x=2.54N, y=3.89N)

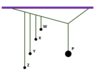
The box is in equilibrium with no external forces applied
Label the forces acting on the box
Notice the angle between weight and perpendicular is also Ø
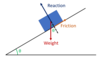
How do you calculate the resultant moment? (2 ways)

- Multiply perpendicular component of force by distance
- Multiply perpendicular component of distance by force
(First method is shown)

What’s wrong with this?
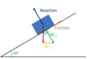
Weight must form the hypotenuse of the triangle
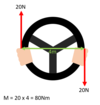
What is a couple?
A pair of equal and opposite coplanar forces which do not act along the same line of action
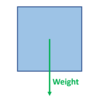
What does it mean if an object is uniform?
It has an constant density so its centre of mass acts from the physical centre point of the object
(Weight vector starts from middle of object)
When should you use moments?
Any situation that has two unknown forces acting on an object
Take moments about one of the unknown forces to find the other
Then use total up force = total down force to find the other
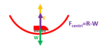
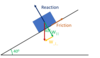
If this box is in equilibrium how would you go about calculating the frictional force and the reaction force?
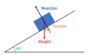
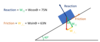
State the principle of moments
Sum of the clockwise moments about a point is equal to the sum of the anticlockwise moments for a system in equilibrium
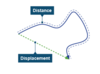
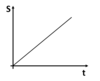
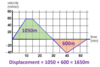
What is displacement and how is it different to distance?
Displacement is a measure of the line connecting the starting point to the finishing point.
Distance is a measure of the total length of the path travelled.
Also distance is a scalar and displacement is a vector.