Medical-Surgical Equipment Flashcards
How does oxygen move across the alveolar-capillary membrane?
Diffusion from a higher pressure to lower pressure
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in inspired air?
160 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli?
104 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in blood leaving the tissues and entering the lungs?
40 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in blood leaving the lungs and entering the tissue capillaries?
100 mmHg
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the tissues?
less than 40 mmHg
True or false: Hypoxemia is defined as SaO2 to less than 80% corresponding to an arterial blood O2 partial pressure less than 60 mmHg.
False; arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation is less than 90%
How does oxygen therapy improve diffusion?
By increasing the fraction of inspired O2 (FiO2) with supplemental O2
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the pulmonary veins?
100 mmHg
For every increase in liter per minute of oxygen, how much FiO2 does the Nasal Cannula increase?
3-4%
How much supplemental oxygen does the nasal cannula deliver?
1 to 6 liters per minute
What is a benefit for the patient having a nasal cannula?
Provides mobile patients with adequate lengths of extension tubing or a portable O2 tank
What is the approximate FiO2 of the Open Face Tent?
~ 30 to 55%
How much FiO2 is provided with a Closed Face Mask?
40% FiO2 with 5-6 lpm 50% FiO2 with 6-7 lpm 60% FiO2 with 7-8 lpm
How does the Transtracheal Oxygen Catheter work?
Small-bore catheter surgically inserted between 2nd and 3rd tracheal inter spaces to provide oxygen and supplemental oxygen mixed with RA is continuously provided.

How much FiO2 is increased with every lpm of supplemental O2 with Transtracheal Oxygen Catheter?
8% FiO2
How does a tracheostomy mask or collar work?
Mask is placed over tracheostomy site and secured with an elastic strap. Humidified supplemental O2 is provided through the mask/ collar.

How much FiO2 is provided with the tracheostomy mask or collar?
28% to 100%
Would you find humidified, supplemental O2 in a partial non-rebreather mask or in a tracheostomy mask?
Tracheostomy mask
Which provides more supplemental O2, the non-rebreather mask or the partial non-rebreather mask?
Non-rebreather mask. Non-rebreather mask provides 60-80% of FiO2 and partial NRB provides 40-60% of FiO2.
True or false: Physical Therapy is only deferred if a patient requires a partial non-rebreather mask to maintain oxygenation.
False, physical therapy is usually deferred if a patient requires a non-rebreather mask.
True or false: Extra lengths of oxygen extension tubing should be provided if the patient is 7-8 feet from the bedside.
True, at least 5-6 feet.
How does an air entrainment mask work?
It is a closed face mask that uses a high flow system and a jet mixing device to force 100% of oxygen past an entrainment.

True or False: It is okay for the patients to remove an air entrainment mask periodically from time to time.
False; the entrainment mask should be kept on for as long as possible to provide the specific concentration of supplemental O2
How does the BiPAP device work?
The BiPAP uses a mask and tubing to augment inspiratory and expiratory flow depending on what the device senses to decrease the patient’s work on breathing.

What are some benefits of using the BiPAP?
Used to avoid intubation and mechanical ventilation
True or False: A blue label designates the O2 supply in the hospital
False; it is a green label
What are clinical signs of hypoxemia?
Shortness of Breath, use of accessory muscles, confusion, pallor, cyanosis
True or False: An Arterial Line, also known as an A-line, is used as a guideline to assess overall fluid balance for patients with significant fluid volume deficit.
False; it is a central venous catheter (CVC)
True or False: A clinician should not use a BP cuff on an extremity with a central venous catheter in place in a patient.
True
What is the normal range for central venous pressure?
2-5 mmHg
What is the normal range for pulmonary arterial systolic pressure?
20-30 mmHg
What is the normal range for pulmonary arterial diastolic pressure?
5-10 mmHg
What is the Cerebral Perfusion Pressure range?
60-80 mmHg
How do you calculate CPP?
CPP = MAP - ICP
What is the normal range for intracranial pressure?
7-15 mmHg
How do you calculate the mean arterial pressure?
(SBP + 2XDBP)/3
True or False: Early stage of intracranial bleeding will have a stable blood pressure and heart rate.
True
How is an epidural sensor inserted into the epidural space?
Using a burr hole to monitor intracranial pressure
What is a subarachnoid bolt?
Hollow screw placed into the skull and dura to monitor ICP
Where is the intraventricular catheter placed?
In the 3rd ventricle
What is an arteriovenous fistula?
Surgical joining of a periphery artery and vein using an artificial blood vessel to provide access for long-term hemodialysis
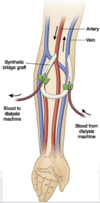
What are some complications of the arteriovenous fistula?
Thrombosis, infection, vascular steal syndrome
How does a chest tube work?
Removes and prevents the reentry of air/fluid from the pleural or mediastinal space and it is connected to a drainage system.
What is an example of an abnormal ICP waveform?
P2 (cerebral compliance) has a higher peak than P1 (arterial pulse) and P3 (aortic valve closure)
What are some complications of the intraventricular catheter?
Infection, meningitis, ventricular collapse, catheter occlusion by blood or brain tissue
What is the purpose of the nasogastric tube?
Keeps the stomach empty after surgery and rests the bowel by limiting the passage of gastric contents
What is the purpose of the nebulizer?
Delivers aerosolized water or medications to the respiratory tract
What is the purpose of the percutaneuous endoscopic gastrotomy (PEG)/ jejunostomy (PEJ) tube?
Provides long-term access for nourishment to patients who are unable to tolerate food by mouth or have a nasoenteral obstruction, or for a patient with confusion/ agitation at risk for nasoenteral tube dislodgement

What is the purpose of a peripheral IV line?
Provides temporary access for delivery of medications, fluids, electrolytes, nutrients, or blood product transfusions
What is the purpose of the peripherally inserted central catheter?
Intravenous access for administration of total parenteral nutrition (TPN), medications, fluid, blood products, or chemotherapy. Generally placed for midterm access (weeks to months) Placed via the basilic, cephalic or brachial vein, terminating in the superior vena cava. Exterior tubing is taped to the arm and covered with a transparent dressing.
What is the purpose of the rectal pouch/tube?
Collects bowel drainage, protects fragile skin from contact with feces.

What is the purpose of Sequential Compression Device?
Intermittent pressure to the lower extremities via gradual and sequential inflation and deflation of the air-filled sleeves. Promotes venous return and prevents deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) secondary to prolonged or postoperative bed rest or inactivity
What is the purpose of the suprapubic catheter?
Surgically placed catheter to drain the bladder temporarily or permanently after some bladder or gynecologic surgeries in cases of urinary retention or a severe voiding dysfunction
What is the purpose of the Surgical Drain (Penrose, Jackson-Pratt, Hemovac)?
Removes excess air, blood, or fluid (serum, lymph, bile, pus, or intestinal secretions) from a surgical site that would otherwise collect internally
How should the surgical drain be placed if the device drains by gravity?
Should be placed lower than the incision site.
What is the normal range for pulmonary artery systolic pressure?
20-30 mmHg
What is the normal range for pulmonary artery diastolic pressure?
5-10 mmHg
What is the normal range for pulmonary arterial occlusion pressure?
5-12 mmHg
What is the normal range for central venous pressure?
2-5 mmHg


