Med Chem Final Exam Deck Flashcards
The Kefauver-Harris Amendments mandate…
efficacy as well as safety must be established before a drug can be marketed
and required the FDA to assess the efficacy of all drugs introduced since 1938.
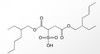
Identify the drug shown in the picture.

Lansoprazole (Prevacid) – PPI
Give examples of noncyclic SNRIs
Venlafaxine
Duloxetine
Milnacipran
Avagacestat is what type of drug
Gamma-secretase inhibitor
it is not selective for APP (amyloid precursor protein) and has other substrates
Drugs that are directed against tumor DNA have 3 different MOAs. List them and give an example.
- break the helix itself (cross-linkers)
- interfere with DNA-related proteins (topoisomerase inhibitors)
- modify the expression of genes (alkylating and methylating agents)
Identify the class of drug depicted in the photo.
Bonus: name each drug.

First generation beta blockers (non-selective)
Propranolol, Pindolol, Timolol
what are the two main considerations when making a prodrug?
effective conversion to active drug in the blood stream
the prodrug “shield” group is not toxic when released
What must all intercalators have in their structure?
Need large (usually multiple rings) planar (flat) surfaces so they can fit between pairs of DNA
What change occurs once a local anesthetic travels from the ECF to the ICF?
Because local anesthetics are basic aminds at pH 7.4, once they travel inside the cell into the more acidic environment, they become protonated
- once it’s protonated, it can bind to a sodium channel and prevent influx
NMR stands for
nuclear magnetic resonance
What drug is used to treat hypothyroidism?
Levothyroxine - synthetic T4 (thyroxine)
True or false: branched chain groups are more lipophilic than straight chain groups.
False - branched chain groups are less lipophilic than straight chain groups.
phenotypic screening is a whole organism (or cell) approach that speeds up ______________.
physicochemical property optimization
Define medicinal chemistry.
the science that deals with the discovery/design of new therapeutic agents and their development into useful medicines.
What structural modifications can be made to increase BBB penetration?
- reduce Pgp efflux
- reduce hydrogen bond donors
- increase lipophilicity
- reduce molecular weight
- replace carboxylic acid groups
- add conformational rigidity
- try to hitch a ride on uptake transporters
List and describe some of the methods that are available for target validation.
- Check peer reviewed papers
- Modern techniques allow us to check things in the lab in more efficient ways
- Gene Knockout (removal of the gene that encodes for the biomolecule of interest - does it result in death of the pathogen, would inhibiting have same effect?)
RNAi - dsRNA interfering with expression of genes with sequences complementary to it (results in reduction of production of protein)
Small Molecule Probe
Animal Models
Computation Docking
describe the function of ester prodrugs
carboxylic acids are excellent HBA and HBD, but they ionize too easily which can be a problem in crossing membranes a prodrug is used to protect the acid function by making it an ester. the less polar ester can cross the membrane and be hydrolyzed to the acid by an esterase enzyme
Which alkylating agent’s toxicity can be treated using an adjunct therapy of mesna?
Cyclophosphamide. It’s main toxicity comes from acrolein and CAA.
Acrolein can be counted with mesna because mesna (injected in the active form and selectively reduced in the kidney) will concentrate in the bladder and scavenge acrolein.
What is the actual alkylating agent made from the prodrug ifosfamide?
Aziridine
What is the MOA of SGLT2 inhibitors?
SGLT2 (sodium glucose co-transporter 2) normally facilitates glucose reabsorption in the kidney
–so, SGLT2 inhibitors block the reabsorption of glucose in the kidney, thus increasing excretion and lowering blood glucose levels.
Identify the class of drug depicted in the photo
What is it indicated for?
Bonus: identify the drug.

H2 receptor antagonist (competitive inhibitor of histamine H2 receptors)
Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcer, treatment of GERD
Pepside (Famotidine)
What type of drug is buproprion?
- selective inhibitor of DA reuptake at the DA presynaptic neuronal membrane and an NRI (induces the release of both DA and NE)
- also a selective inhibitor of neuronal nAChRs (gives it the ability to help reduce withdrawal symptoms following smoking cessation)
describe theranostics
the combination of diagnostics and therapeutics using the same molecular scaffold
To which class of drug do ranitidine (Zantac) and famotidine (pepside) belong?
H2-receptor antagonist.
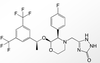
Identify the drug in the picture. What class does it belong to?
Describe its MOA.

Pantoprazole (Protonix) – Proton Pump Inhibitor
- inhibits the final step in gastric acid production (in the gastric parietal cell of the stomach)
What was the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD and C Act) of 1938 signed in response to? What did it mandate?
Death of over 100 people, many of whom were children, due to the addition of diethylene glycol (antifreeze) in a marketed form of sulfanilamide.
It established that manufacturers must prove the safety of their products prior to marketing.
Why don’t peptides usually make good drug candidates?
- rapidly proteolyzed in GIT and serum
- poorly bioavailable
- rapidly excreted
- bind to multiple receptors
Why are menotropins used to induce ovulation?
Menotropins are prepared from the urine of post-menopausal women. hCG is naturally occurring in post-menopausal women, and hCG induces ovulation.
What criteria is in place when making a lead from a hit molecule?
- potency must be in the nanomoles (100nM); - must have some bioavailability (>10%) - must not bind too much to proteins (<99.5%) - solubility (>10ug/mL) - C log P < 3 (not too lipophilic) - log D < 3 - molecular weight < 450 - P450 IC50 > 10 uM for the 5 major isozymes (cannot be lower because then it potently inhibits CYP450) - HERG screening (look for toxicity)
Define ED50, TD50, and LD50.
ED50- dose at which 50% of subjects exhibit a therapeutic response to a drug.
TD50 - dose at which 50% of subjects experience a toxic response
LD50 - dose at which 50% of subjects die
How are metaglinides different from sulfonylureas?
Metaglinides have a weaker binding affinity and faster dissociation from the SUR1 binding site that results in a much shorter duration of action
___________ provides a link between the genetic alterations and a disease phenotype.
What is identified when using this method? What are the downsides?
Phenotypic screening
Genes (and thus proteins) identified this way are more likely to cause the disease, rather than be a consequence of the disease
The downside is that we don’t know the MoA of the drug; it’s typically a way to discover the first compound and cost of a drug (like the first antibiotic)
What is the single most important factor in the approval or disapproval for a new drug?
Safety and effectiveness studies done in clinical trials - particularly the safety aspect
What is pitocin used for?
It’s indicated for initiation or improvement of uterine contractions, as well in controlling postpartum bleeding
What suffix is associated with DPP-4 inhibitors?
Give at least 1 example of a DPP-4 inhibitor drug.
—Gliptin
Sitagliptin
Vildagliptin
The use of a _________ is common in scientific presentations as the conclusion of a SAR study.
Molecular Activity Map
To make a biosimilar of a biologic, you must have:
- proof of quality and similarity
- PK bioequivalence
- clinical safety and efficacy data
Which kind of topoisomerase inhibitor is able to bind to either the topo-DNA complex or the topoisomerase itself?
Topoisomerase 2 inhibitors
_____ can be differentiated into neurons (or other cell types) that harbor the same genetic mutation as the patient
iPSCs
What is the purpose of the two tri-fluoro methyl groups in NK1 antagonists?
Enhance the activity and improves the metabolism
what is a prodrug?
an inactive compound that is converted (either chemically or enzymatically) to the active form (once in the body)
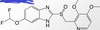
Identify the class of the drug depicted in the photo.
What is it indicated for?
Bonus: name the drug.

Proton Pump Inhibitor.
Treatment in adults of duodenal ulcer and gastric ulcer, treatment of adults and children with GERD, and maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis
Omeprazole (Prilosec)
What is the pharmacophore of morphines?
Describe the SAR of mu-opioid ligands.
Pharmacophore: 4-phenylpiperidine moiety SAR:
- pKa of the N is 8.0-10.0; the protonated form is required
- phenolic OH is mostly unionized and participates as H+ donor
- is REQUIRED (an OR group works too)
- activity will increase if E ring is eliminated
- only tertiary amines provide clinically significant activity
- agonists - R1 is methyl group or longer than 3 C
- 7,8 double bond is responsible for action
- 6alpha-OH is responsible for mast cell degranulation
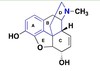
How do anthracyclines cause cardiotoxicity? How can it be mitigated?
They form superoxide radicals and hydroxide radicals.
The hydroxide radicals are formed through the Fenton reaction, and cardiac tissues don’t have enough catalases or cytoprotective enzymes.
The solution is to co-administer an antioxidant and an iron chelator.
Define bioisostere.
Substituents or functional groups that have similar chemical and/or physical properties and which produce broadly similar biological properties.
Sulphonamide formation involves ___________.
combination of a secondary amine and sulphanyl chloride
the nitrogen is still connected to the original 2 R groups, but the hydrogen from the scondary amine is replaced with the sulphonyl group (s double bonded to 2 O’s (each with a double bond) and another R group)

when is the overall benefit-risk relationship of the drug evaluated during clinical studies?
Phase 3
Define the function of DPP-4.
DPP-4 inhibitors block dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4), thus blocking the inactivation of incretins.
- the incretin is then able to stimulate the increase of insulin secretion and inhibit the release of glucagon
- -> this lowers blood glucose
Explain the process of SPOS (solid-phase organic synthesis)
It is provided by a solid support known as beads (or resins), thereby rendering the reactions heterogenous and conferring a simpler workup and purification
- the resin is cross-linked polystyrene

What are the important points to remember about platinum compounds?
- Platinum is electron deficient
- must be stabilized by amino acids to prevent it from reacting with everything
- NH3 act as stabilizing groups and chloride ions make for good leaving groups
- when it cross-links the DNA in the cis configuration it cannot be repaired by the cells
- side effects include nephrotoxicity, emetogenesis, and neurotoxicity (limiting factor in use)
Explain the biological basis of depression.
The levels of 3 different small molecules are involved:
1 - serotonin: anxiety, panic, phobia, and obsessive-compulsion
2 - dopamine: cognitive slowing, hypersomnia, anhedonia
3 - norepinephrine/noradrenaline: decreased concentration, decreased working memory, decreased information processing, fatigue
Define priviledged structures.
Certain scaffolds are capable of binding to multiple receptor targets.
- the core scaffolds (molecular master keys) are viable starting poitns in library generation
The common site of attack for DNA cross linking is
the 7-position N of guanine
Describe the SAR of flexible opioids (anilidopiperidines like fentanyl)
- no phenolic OH group
- highly lipophilic, so rapidly crosses the BBB; fast and potent
- SAR on R1 (nitrogen) = arylalkyl - high lipophilicity
What provides the framework for how to conduct well-controlled studies?
Good Laboratory Practices
- assures quality and integrity of data
- provides overall accountability
- facilitates study reconstruction
what is chemical biology (chemical genetics)
using a chemical to probe to learn about biological functions (usually a signaling pathway)
What class of drug is depicted in the photo?
Bonus: identify each drug.

NRIs (norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors)
Left to right: protriptyline, nortriptyline, desipramine, maprotiline

How is rapid acting insulin different than regular insulin therapy?
Rapid acting insulin has had its amino acid sequence modified, allowing for the rapid action.
When insulin is dimerized or hexamerized, it is not active. The monomeric formation is the active formation.
Rapid acting insulin works because it has been modified to decrease the formation of dimers and hexamers, allowing it to absorb more quickly.
What is the MOA of prolia?
It is a RANKL receptor inhibitor
– binds to the receptor to inhibit osteoclast activation and formation
–> this is because when RANKL binds to its receptor on the surface of osteoclasts and osteoclast precursors, it stimulates formation and activation
What effect does conformational regidity have on potency of CNS agents?
Increased rigidity (rings) locks the molecule into the bioactive conformation and increases potency
What are some particular things to watch out for with monoamine oxidase inhibitors?
- rarely first choice; mostly used in atypical depression and bulemia (off-label)
- common side effects: insomnia, agitation, dizziness, dry mouth, headache, confusion
- certain foods will cause hypertensive crisis because of the release and potentiation of catecholamines (no milk!)
Identify the drug class shown in the picture.
List the specific drugs left to right (if you can)

Tricyclic SNRIs
Impiramine
Amitriptyline
Chlomipramine
Trimipramine
Doxepin
HGH is used to treat…
What is the MOA?
short stature of unknown cause
MOA - mimics natural growth hormone to stimulate growth and cellular reproduction
Examples: genotropin, norditropin, humatrope
a vast majority of imaging agents have a _______ that acts as a delivery vehicle to deliver the _______ to the site of action you want to image
organic scaffold
inorganic element
The average time it takes to bring a drug to market is
12-15 years
iPSC stands for
induced pluripotent stem cells
The active site of renin contains…
two aspartyl residues
Why were noncyclic SNRIs developed? How do they compare?
To remove unwanted adverse effects of tricyclic inhibitors
They are as efficacious as tricyclic inhibitors and produce a faster and greater antidepressant response than an SSRI alone
What is the MOA of statins?
Competititive inhibitor of HMGR
What is ovidrel and what is it used for?
recombinant hCG
induces ovulation by stimulating late phase follicular maturation and resumption of oocyte meiosis
How is Forteo able to work as a bone forming agent?
It increases the number of osteoblasts
Why is salmon the preferable source of calcitonin?
It has greater receptor affinity and a longer half-life than human calcitonin.
What is the MOA of sulfonylureas?
Bind to and close ATP sensitive K channels on the cell membrane of pancreatic beta cells
- this impacts the cell membrane structure and increases insulin secretion
Which stage of the cell cycle are anthracyclines specific to?
G2
Identify some drugs that function as cholinesterase inhibitors. What effect do they have when treating Alzheimer’s?
Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine
improves attention, thinking memory, language comprehension, and communication
Describe the SAR of local anesthetics.
- lipophilic portion is essential for activity
- lipid solubility increases with extent of substitution (# of carbons) on the aromatic ring and/or amino group (ex. tetracaine is more lipid soluble and thus has a higher potency than procaine; it also has way more carbons attached off the aromatic ring)
- the lower the pKa, the more rapid onset of action (more uncharged form, faster diffusion inside the cell)
- the clinically relevant pKa is 7.0-9.0
What treatment strategies are used for Parkinson’s Disease?
- increase synthesis of DA in the brain (L-dopa)
- activate DA receptors (D2 agonists)
- decrease reuptake of DA at presynaptic space (MAO inhibitors)
- decrease metabolism of DA (or its precursor L-dopa)
_________ was the first non-platinum based chemotherapeutic approved since the approval of platinum
velcade
Identify the class of drug depicted in the photo.
What is it indicated for?
Bonus: Which drug is it?

5-HT3 Antagonist
Indicated for prevention of nausea and/or vomiting.
KYTRIL (Granisetron)
Why can statins be considered transition state analogues?
They imitate the transition state of the first step of the reaction mechanism of HMG-CoA reductase
Define biomarker.
A biomarker is a marker of biological or physiological states that can be easily measured (ideally on a scale allowing determination of effective treatment)
Ex. Lactic acid buildup during exercise; WBC levels in HIV; etc
Which clinical phase takes the longest?
Phase 3 (2-6 years)
Phase 4 is continuous
Identify the type of drug shown in the photo. How does it compare to an SSRI?

Non-tricyclic secondary amine NRIs (nisoxetine)
- the bulky 2-OMe group restricts the conformation of the phenyl ring, which aligns the HBA (methoxy) with the HBD of the binding site on the NET
- The SERT binding site does not have the same alignment, so the methoxy group in the meta position is what gives the non-tricyclic NRIs their selectivity for NET!
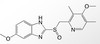
Which drug is shown in the picture?
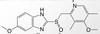
Omeprazole (Prilosec) - PPI
What is the MOA of BACE1?
Beta-secretase inhibitor
What is unique about the MOA of PPIs?
They’re one of the only drug classes that actually form covalent bonds with their target receptors