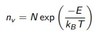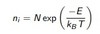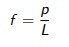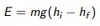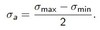Mechanical testing Flashcards
(98 cards)
What type of test is used for brittle materials and why?
3 point bend test clamping would damage the specimen reducing the measured specimens

Define stiffness
How much a material deflects under a given load
Define strength
a measure of how much force is needed to permanently deform or break a material
Define toughness
the ability of a material to resist fracture or to withstand impact
Define hardness
the ability of a material to resist local plastic deformation
Define true stress
It is defined as the force divided by the instantaneous cross sectional area true strain differs due to the change in cross sectional area of the specimen during the test
True strain equation
equation

True stress and true strain graph

Magneto- striction
materials strained by magnetic fields
Piezo-electric materials(uses)
materials which respond to electric fields Uses: piezoelectric actuators fuel injectors tyre pressure sensors engine knock sensors keyless door entry
Thermal strain
Thermal strain can cause stress in a constrained object

Isotropic mechanical properties
properties the same in the each direction regardless of the load applied
Number of properties of composites can be understood using the rule of mixtures. The density is given by…
equation

Electrical conductivity of a fibre reinforced composite along the fibres
equation

Thermal conductivity
equation

Modulus of elasticity along the fibres (Rule of mixtures)
equation the equation generally overestimates the yield strength as the matrix will not be fully extended when the fibres fail

Modulus of elasticity perpendicular to the fibres
equation

Define cohesive energy
It is defined as the energy per atom when solid bonds together
As the cohesive energy increases, the bond strength between the atoms increases
Cohesive energy is a quadratic around the minimum

Stress caused by an atom when a force is applied
equation

Types of point defects

Interstitial point defects
an extra atom is wedged into the crystal causing structural expansion
Substitutional point defects
a different atom i aadded into the crystal replacing an original atom
Self-interstitial point defects
an atom from the crystal jumps from its original position to elsewhere-remains close to a vacancy
Calculating number of vacancies
equation