Measures of Variability Flashcards
What does variance measure?
How far each number in the set is from the mean - the difference is called deviation
Why does measuring the variability of a data give a better description about a set of data compared to measures of central tendency?
Measure of variability describes the spread or dispersion of the set of data
What is the range?
Difference between the lowest and highest values in the data set
What are the advantages of using range?
- Simplest measure of variability to calculate and interpret
- Useful for comparing spread between similar data sets
What are the disadvantages of using range?
- Only uses 2 of the values in the data set
- Affected by extreme values as they’re included in calculation
When will a variance be small?
When the values in the data set are tightly bunched around the mean
When will a variance be big?
When the values in a data set are spread apart from the mean
What is the advanatge of using variance?
The calculation uses all of the data values
What is the disadvantage of using variance?
It is not very easy to interpret
What is always the sum of deviations?
zero
the totals of the positive and negative deviations - caused by data values larger and smaller than the mean - will exactly cancel each other out because mean is the measure of the centre of the set
How do you calculate the variance?
Square each variation
Add them up
Divide by the number of data values
What is the formula for sample variance when there is raw data?
S2 = 1/n-1 [∑ x2 - (∑x)2/n]
What is the formula for sample variation when the data is presented as frequency distribution?
S2 = 1/n-1 [∑ fx2 - (∑ fx)2/n]
How do you calculate standard deviation?
Square root the variance
What is coefficient of variation?
It is a relative comparison of a standard deviation to its mena often expressed as a percentage
What do you use coeffiecient of variation for?
Use it to compare 2 samples of data with different scales of measurement
What does a larger co-efficient of variation mean?
The data has higher variability
How do you calculate coefficient of variation?
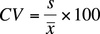
What is the disadvantage of using standard deviation and variance?
Influenced by extreme values


