MCB - Exam 3 Flashcards
(321 cards)
What differenciates cell types?
Cell - Structure and Function
- All cells contain the same genetic material.
- Differentiation depends on differences of gene expression.
What are some differences in the ways cells express proteins?
Different Cell Types - Different Proteins
- Common proteins (housekeeping proteins), i.e. glucose metabolism.
- Specifically limited proteins, i.e. hemoglobin.
- Typical human cell expresses 30-60% of its 21,000 structural genes (protein coding) but level of gene expression varies - fingerprint expression profiles e.g. microarrays or RNA Seq.
- Other factors post transcription include: alternative splicing (dystrophin gene), post translational modification.
What are the 6 locations where gene expression is controlled?
Gene Expression - Locations of Control
- Transcriptional control
- RNA processing control
- RNA transport and localization control
- Translation control
- mRNA degradation control
- Protein activity control

Describe DNA binding motifs.
DNA Binding Motifs
- Gene regulation requires:
- Short stretches of DNA of defined sequence - recognition sites for DNA binding proteins.
- Gene regulatory proteins - transcription factors that will bind and activate gene.
- Recognition sequences for regulatory proteins e.g. GATA1: TGATAG
- Logo: ex. TAATTGC
- Recognition sequences can be proximal or distal to first exon (few base pairs - 50kb away).
Describe DNA motif recognition.
DNA Motif - Recognition
- Regulatory proteins associate with, recognize specific DNA sequence, and bind to bases in the major groove.
- Major groove presents a specific face for each of the specific base pairs.
- Surface of protein is extensively complementary to the surface of the DNA region to which it binds.
- Contacts made with the DNA involve 4 possible configurations:
- Possible H-bond donors.
- Possible H-bond acceptors.
- Methyl groups.
- H atom.

How many interactions are involved in a typical gene regulatory protein - DNA interaction?
10-20 interactions.
Describe how sequence specific transcription factors are modular.
Sequence Specific Transcription Factors - Modularity
- May have different modules such as:
- DNA-binding module
- Dimerization module - forms dimer with other subunits.
- Activation module - turns on gene.
- Regulatory module - regulates transcription factor.

How was the modular nature of transcription factors proven?
Evidence for Modular Transcription Factors
- Used a series of plasmids making mutant GAL4 protein and measured binding to UAS (upstream activation sequence) and expression activity.

What are the various DNA-binding domain structural motifs?
DNA-Binding Domain Structural Motifs
- Helix-turn-helix
- Zinc finger motif
- Leucine zipper
- Helix-loop-helix
- Homeodomain
- Beta-sheet
Describe the helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif.
DNA-Binding Motifs - Helix-Turn-Helix
- Most simple and common DNA-binding motif.
- 2 alpa-helices connected by short chain of AA that make the “turn” (turned at fixed angle).
- Longer helix = recognition module - DNA-binding module - fits in major groove.
- Side chains of AA recognize DNA motif.
- Symmetric dimers: bind DNA as dimers.

Describe the zinc finger domain DNA-binding motif.
DNA-Binding Motifs - Zinc Finger Module
- DNA-binding motif includes Zn atom.
- Binds to major groove.
- Zn finger domains found in tandem clusters.
- Multiple contact points.

Describe the Leucine zipper DNA-binding motif.
DNA-Binding Motif - Leucine Zipper
- 2 motifs:
- Type I:
- 2 alpha helical DNA binding domain.
- Grabs DNA like clothes pin.
- Activation domain overlaps dimer domain.
- Interactions between hydrophobic AA side chains (leucines)
- Type II:
- Dimerizes through leucine zipper region (homo- / hetero-).
- Interactions between hydrophobic AA side chains (leucines).
- Leucine residue every 7 AA down one side of alpha-helix in dimerization domain: forms zipper structure.
- Type I:

Describe the helix-loop-helix DNA-binding motif.
DNA-Binding Motifs - Helix-Loop-Helix
- Consists of a short and a long alpha-chain connected by a loop.
- Can occur as homodimers or heterodimers.
- Three domains or modules to this protein:
- DNA binding
- Dimerization
- Activation

What is a homeodomain protein?
Homeodomain Protein
- Homeodomain - 3 alpha helices.
- Helix-turn-helix motif.
Describe beta-sheet DNA recognition proteins.
Beta-Sheet DNA Recognition Proteins
- 2 stranded beta-sheet
- Beta-sheets consist of beta-strands.
- Connected laterally by 2-3 backbone H-bonds.
- Forms twisted, pleated sheet.
- Binds to major groove of DNA.
What is an example of a mutation in a Zn finger transcription factor leading to disease?
Zn Finger Transcription Factor Mutation
- Hereditary spherocytosis.
- Klf1 is a Zn finger protein that binds to promotor for all EMS proteins.
- Mutation in Klf1 = no EMS proteins.
- HS mutation: GAA to GAT or Glu to Asp in exon 3 (Zn finger domain 2).

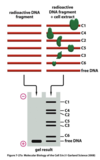
Describe the use of an electrophoretic mobility shift assay to identify transcription factors.
Transcription Factor Identification - Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
- Detection of sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins.
- Uses radioactive DNA fragment (regulatory DNA sequence) with protein extract from cell.
- DNA with proteins attached migrate according to size of protein.
- Isolate protein to identify.
Describe the use of affinity chromatography for the identification of transcription factors.
Transcription Factor Identification - Affinity Chromatography
- 2 Steps:
- Isolate DNA-binding protein.
- Purification of sequence-specific binding proteins.

How is chromatin immuno-precipitation used to identify DNA-binding sequences?
DNA-Binding Sequence Identificaiton - Chromatin Immuno-Precipitation (CHIP)
- Allows identification of the sites in the genome that a known regulatory protein binds to.
- Done in living cells.
- End product can be run through PCR and used to identify sequence.

Describe the gene control region of a typical eukaryotic gene.
Gene Control Region - Eukaryote
- DNA region involved in regulating and initiating transcription of a gene.
- Includes:
- Promoter (where transcription factors and RNA polymerase II assembles).
- Regulatory sequences to which regulatory proteins bind to control rate of assembly process at the promotor.
- 9% of the 21,000 human genes (2,000) encode gene regulatory proteins.
- Expression of mammalian genes is governed by an extremeley complex network of controls (very few generalities can be made).
- RNA polymerase and general transcription factors assemble at the promoter.
- Other gene regulatory proteins (activators or repressors) bind to regulatory sequences which can be adjacent, far upstream or in introns downstream of the promotor.

How does DNA looping and a mediator complex affect activation?
Transcriptional Activation
- DNA looping and a mediator complex allow the gene regulatory proteins to interact with the proteins that assemble at the promoter.
- Mediator serves as an intermediary between gene regulatory proteins and RNA polymerase II.

What effects the affinity between gene activator proteins and naked DNA vs DNA in nucleosomes and how can it be overcome?
Gene Activator Proteins
- Binds with lower affinity to DNA in nucleosomes.
- Binds with higher affinity to naked DNA.
- Possibly due to the surface of the nucleotide recognition sequence facing inward.
- 4 methods to overcome difference in affinity:
- Nucleosome remodeling
- Nucleosome removal
- Histone replacement.
- Histone modification (e.g. histone acetylation)

How do gene repressor proteins inhibit transcription?
Gene Repressor Proteins - Inhibiting Transcription
- Competitive DNA binding.
- Masking the activation surface.
- Direct interaction with the general transcription factors.
- Recruitment of chromatin remodeling complexes.
- Recruitment of histone deacetylases.
- Recruitment of histone methyl transferase.
Describe transcription inhibition by competitive DNA binding.
Transcription Inhibition - Competitive DNA Binding
- Binding sites for receptor and activator overlap or are the same site.