MBB Pathology/Imaging Flashcards
Describe what you see here; what condition is this

rounded atrophic fibers and lymphocytic infiltrate; top right is macrophages attacking muscle fiber; polymyositis
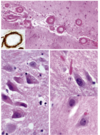
describe the constellation of findings seen and for what disease

a) balooning neuron
b and c) neurofibrillary tau tangles
d) astrocytic plaques
corticobasal degeneration
Describe the difference between hemorrhagic infarct and a intraparenchymal hemorrhage and how they would look micro/macroscopically
Hemorrhagic infarct has brain tissue with blood infiltrating, tissue is becoming necrotic, wil lsee petechiae and neutrophils etc.
intraparenchymal hemorrhage is when blood spills out and pushes brain tissue out of the way and takes up space, so microscopically you would only see blood and fibrin

what is this

medulloblastoma
What is going on here, what is causing it

central herniation of temporal lobes, brainstem bein displaced downward, severing basilar pontine arteries, fatal (overall cause is edema)
What is going on in this image? what condition is this common in

asymmetrical atrophy; corticobasil degeneration
What is this? What conditions is this common in

lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia
What is this, what is the most common cause, is it fast or slow growing

subdural hemorrhage, trauma, slow growing
describe what you see; what condition is this common in

ballooned neuron; corticobasil degeneration
Name 3 possible causes of this

high grade glioma (GBM)
cns lymphoma
rlly bad MS
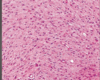
describe what you see; what type of cancer is this; what age group is involved

dense eosinophilic rosenthal fibers; pilocytic astrocytoma children
Describe the process going on here from left to right and what kind of process is this?

myopathic process
1) left most: muscle fiber necrosis
2) middle: attempts at regeneration
3) fibrosis
What is going on here; what condition would this be seen in

alpha synnuclein cytoplasmic inclusions in GLIAL cells; multiple system atrophy
What are yo ustaining for here; what disease is this common in

staining for ubiquitin/huntington protein inclusions ; huntington disese
describe what you see; what disease is this

neuronal loss, reactive (alzheimers type 2 ) astrocytes; metabolic gliosis (thing in the center) –> wilson’s disease
what cancer is this
what demographic is it common in

medulloblastoma children
describe the symptoms; what syndrome do they belong to

plexiform neurofibroma on peripheral nervous sytem
cafe au lait spot
neurofibromatosis 1
What is this? Name some causes?

interparenchymal hemorrhage, htn most common, also arteriovenous malformation, lesion, amyloid
describe the two images; what condition is this

swollen neuron aka pick cell
status spongiosis aka vacuolization of the cortex
pick’s disease
what is this, where does it come off of

vestibular schwannoma/acoustic neuroma; nerve VIII at the cerebellopontine angle
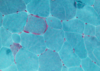
describe what yo usee; what cancer is this

vascular tumor, vacuolated stroma, hemangioblastoma from von hippel lindau
Describe these findings; what condition is this associated with

different manifestations of tau protein accumulations
left is neurfibrillatory tangles
bottom left is tufted astrocytes
right (c shpaed) is glial inclusions (also neuronal inclusions)
PROGRESSIVE SUPRANUCLEAR PALSY
Describe what is happening here: what condition is this

perifascicular atrophy; dermatomyositis
describe each of the three images; what disease is this
top- cerebral amyloid angiopathy (amyloid depositing in leptomeningeal and intraparenchymal arteries)
bottom left- granulovaculoar degeneration (clear cytoplasmic inclusions with basophilic granules)
bottom right- hirano bodies, glassy eosinophilic bodies made of actin
alzheimers
What virus is responsible for this? what is happening

polio virus; microglia are surrounding a dying neuron and trying to eat it (neuronophagia, microglial nodule)
what are these; what condition is it common in

glial cytoplasmic inclusions, multiple system atrophy
describe what you see; what condition is this

rounded atrophic fibers, lymphocytic infiltrate; purple cytoplasmic vacuolar inclusions; inclusion body myositis
what do you see; what is it called; what conditions is this associated with

acellular region then pallisating region, verrucay bodies; schwannoma and neurofibromatosis 2
describe what you see on the left and bottom right image; what are they called; what condition are they common in

left: dense eosinophilic center with clearing around it, lewy body
right: lewy neurites
What process is going on here for what disease

in parkinsons alpha synnuclein can accumulate so much that the neuron dies and then this image shows microglia coming in to eat the dead neuron
What type of astrocytoma is this ? how do yo uknow
diffuse, only hypercellcularity and atypia
describe what you see

diffuse enhancing lesion; lymphoid cells
cns lymphoma
What neuropathy causes this? why does this happen

radial nerve neuropathy; loss of extension of the fingers and wrist
what is going on here; what condition is this

atrophic muscle fibers and a few normal/hypertrophic fibers; werdnig hoffman disease/spinal muscular atrophy
What is happening here; what condition is this

onion bulb; attempt at remyelination after demyelination (right pick has schwann celsl surrounding); chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
can also happen in charcot marie tooth
Describe what you see; what cancer is this and what condition can this occur

large astrocytes in sheaths, subepyndemal lgiant cell astrocytoma (SEGA); tuberous sclerosis
what is the arrow pointing to? wha is it made of what condition is this

bunina body, tdp43, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
describe what you see; what is this

cystic; pilocytic astrocytoma
describe what you see; what hiv associated condition is this

calcifications; toxoplasmosis
what type of hemorrhage is this
what condition is commonly associated with this and what age group

lobar hemorrhage, amyloidosis, old people
what neurodegenerative disease is this? what are these called

pick’s disease; pick bodies made up of tau 3r
Describe what you see, what is this called, what can cause this

optic disc borders aren’t sharp, blood vessels runcated; papilledema; increse intercanial pressure due to brain tumor
What type of astrocytoma is this ? how do yo uknow

gbm; has pseudopalisating necrosis and endothelial proliferation
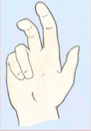
What neuropathy causes this? Why do the fingers look like this

ulnar nerve neuropathy; inability to flex MCP (lumbricals) and inability to extend IP (interossei)
what is this called? what group of disorders is this common in
ragged red fibers (accumulation of abnormal mitochondria), mitochondrial myopathies
Describe what you see
what tumor is this
what population is affected
what symptoms would yo uexpect

small blue cells, high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, can be arranged n lines, can have homer wright rosettes; can have drop mets
medulloblastoma; homer wright rosettes
What are the signs of what the arrows are pointing to; what is it indicative of

insular ribbon sign and hyperdense MCA sign; infarct of MCA
what is this called? What condition is this common in

hummingbird sign (midbrain atrophy), progressive supranuclear palsy
What kind of rash is this; what is this common in? what else can concomittantly happen with this

maculopapular rash, neisseria meningitidis, DIC and thrombocytopenia
what do you see; what cancer is this

basiloid cells surrounding a cyst
wet keratin (pink)
purle= calcifications
carniopharyngioma
Describe each of the three images, what staining it is and whether they belong to a certain condition

top left= normal staining for dystrophin (brown)
top right: staining for duchenne muscular dystrophy; no dystrophin is present
bottom right: staining for becker muscular dystrophy, reduced dystrophin is present
what are the triangular shaped blobs; what is wrong with this pic; what condition is this

neurons; loss of neurons; als
what type of tumor is this
how can you tell

meningioma, dural tail, hyperostosis
what type of astrocytoma is this? how do you know?

anaplastic, has mitoses
Describe whaty you see; what condition is this seen in? what else coudl you stain for

neuronal loss and subsequent astrocytosis (small purple things); huntington’s disease; can also stain ubiquitin to look for huntington protein inclusions, but not really necessary
What part of the body is this? what is happening

muscle, angulated atrophic fibers on the left, nuclear cluster on the right (due to atrophy of the muscle, nuclei are now closer together); denervation injury
what are C and U; what is different about them, what condition is this

lateral and anterior corticospinal tracts; demyelinated; ALS
what is going on here; what condition is this

lipid accumulation in the muscle fibers: carnityl palmitoyl transferase deficiency
What is this? what most commonly causes this? is it fast or slowly growing?

epidural hematoma, trauma to middle meningeal artery, fast growing
describe what you see ; What type of cancer is this?

cuboidal to elongated ependymal cells surrounding a stromal core; myxopappilary ependymoma
describe what you see; what hiv associated condition is this

enahncement of basal ganglia with sparing of thalamus; cryptococcus meningitis
what is this called; what imaging modality is this; what condition is this common in

hot cross bun sign (in pons); mri; multiple system atrophy
describe the two pictures, which cancer is this, what population is it most common in

whorling pattern and psamomma bodies; meningioma, older women (can be associated in chidlren if NF2 Chromosome 22q)
What i happening here; what condition is this

glycogen filled muscle fibers; myophosphorylase deficiency, can stain with PAS; mcardle’s
describe the muscle on the left vs the muscle on the right. what condition is this

left is mroe normal, right is atrophic; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
What are the two types of pathology in this image nd for what disease

diffuse plaque top (no neurites around)
neuritic plaque bottom (amyloid center with dystorphic neurites around)
alzheimers
what is this? what is the most common cause

subarachnoid hemorrhage, aneurysm (a. comm artery and p comm artery most common)
What neuropathy causes this and why?
median nerve neuropathy; inability to flex 1 and 2 fingers (lumbricals)
describe the abnormality seen here
what cancer is this

perivascular pseudorosette
ependymoma
Describe what is happening; what is the condition
what age group is this common in

arteries and veins in clsoe proximity with brian tissue in between; arteriovenous malformation, dangerou
young women
What is this before and after pictures showing?

loss of axons in diabetic neuropathy
what do you see
what is this
fried egg= oligocytes
oligodendroglioma
What do you see; what is this

loss of grey white matter interface, edema, mass effect; hSV encephalitis
what is this

meningioma
what type of neurodegenerative disease is this associated with

alzheimers, neurfibrillatory tangles
What part of the brain is this? what is change d from the normal view; what disease is this implicated in

dark= locus ceruleus, right picture it is less, parkinson’s disease
What is happening here; what condition is this common in

atrophy of the caudate; huntingtons
describe the constellation of findings; what disease is this

decreased substantia nigra, discoloration of putamen; multiple system atrophy
describe this; what is the only condition this can be
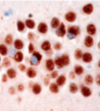
cytoplasmic tdp 43 accumulations (should be nuclear)- frontotemporal dementia with tdp43 pathology


