Mathematical relationships in anaesthesia and ICU Flashcards
(19 cards)
What is a logarithm?
An inverse function, which is the inverse of the exponential function
What is a linear function?
y = mx + c
m is the gradient of the line and c represents the y-axis intercept
Give an example of a linear relationship.
- the polarographic Clark electrode produces an oxygen-dependent current and calibration is the process of relating this output of a transducer to what is to be measured
- the measured current (y) should vary linearly with blood O2 partial pressure (x)
- the best fit straight line can be determined from the calibration and gives values for m and c
- c is called the intercept and respresents the “zero-offset” of the electrode
- the sensitivity of the electrode to O2 determines the gradient of the calibration line given by m
- increasing the value of m steepens the line
What is the advantage and disadvantage of two point calibration?
It’s fast but may be error prone and full calibration usually uses more points
What is a parameter?
A number which completely describes a relationship
What is a hyperbolic function?
WHen two variables are oppositely related - as one increases the other decreases
y = 1 / x
This will make a rectangular hyperbola
Give an example of a hyperbolic relationship
Boyle’s Law - the pressure (P) and volume (V) of a quantity of ideal gas varies reciprocally if the pressure is constant.
P = constant / V
The constant depends on the absolute temperature and number of gas particles.
The curves approach the axes but never cross them. These are called “asymptotes”
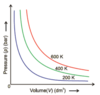
Name some important hyperbolic relationships
- Boyle’s Law - pressure and volume vary reciprocally
- serum creatinine and GFR
- alveolar CO2/end tidal CO2 and alveolar ventilation (for constant PaCO2 and CO)
What is an exponential function?
Exponentials are functions where a number, b, (called the base) is raised to a power:
y = bx
The curves pass through the y-axis but the x-axis is another example of an asymptote
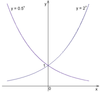
What is the number e?
2.7182…
It’s an important base because exponentials with base e are common in problems where the rate at which a quantity changes itself depending on that quantity
(eg radioactive decay, drug kinetics, oscillation, damping)
What is a decaying exponential?
It’s when -x is substituted for x in the exponential relationship
y = b-x
Eg wash out of drug from a single compartment
What is the elimination rate constant?
It’s the rate of decay (k)

What is the time constant?
The time taken for the concentration to decrease to ~37% (1/e) of the starting value
What is the half life?
The time taken for the concentration to halve.
What is a logarithm?
It is the exponential function reflected in the 45 degree line y = x.
So if the exponential ( y = bx)crosses the vertical axis y = 1, the logarithm ( y = logb(x) ) will cross the horizonal axis at x = 1
What is log (AB) equivalent to?
Log (AB) = log A + log B
What is log (A/B) equal to?
Log (A/B) = log (A) - log (B)
What is the equation for first order kinetics?
Rate at which drug is eliminated is directly proportional to plasma concentration, C
rate of elimination of drug (<u>Mass eliminated</u>) = ßC
time
Where ß is the rate constant we have seen before.
What is the equation for zero-order kinetics?
This is where the elimination mechanism becomes saturated so elimination is independent of C (plasma concentration)
rate of elimination of drug (mass eliminated / time) = γ
Where γ is a constant. Since rate of change is constant, the concentration will decrease linearly rather than exponentially.


