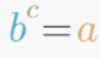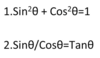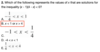Math Notes Flashcards
Pythagorean theorem not true for any triangle. Only applies to right triangles.
If a2 + b2 < c2, then the triangle would be an obtuse-angled triangle.
If a2 + b2 > c2, then the triangle would be an acute-angled triangle.
An expression is said to a perfect square trinomial if it takes the form ax^2 + bx + c and satisfies the condition
b^2 = 4ac
Factoring a Sum of Cubes:
Factoring a Difference of Cubes:
Factoring a Sum of Cubes:
a^3 + b^3 = (a + b)(a^2 – ab + b^2)
Factoring a Difference of Cubes:
a^3 – b^3 = (a – b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)
i imaginary number table
4 possible values

“AAS” is when we know two angles and one side (which is not between the angles).
“ASA” This means we are given two angles of a triangle and one side, which is the side adjacent to the two given angles.
The quotient of each side measure divided by opposite angle’s sin is the same for all sides.
Use degrees seen from Radians when calculating sin or cos
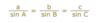
“SAS” This means we are given two sides and the included angle.
Cosine of the side you’re looking for
Use degrees seen from Radians when calculating sin or cos

Radian equal to
57.2958 degrees
180/3.141592
360/ 2PI
Only Right Triangles
“Hypotenuse” is the long one
“Opposite” is opposite to the angle θ (looking for)
“Adjacent” is adjacent (next to) to the angle θ
SOH CAH TOA

logarithm
a quantity representing the power to which a fixed number (the base) must be raised to produce a given number.


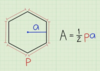
Sphere Volume
(4/3)*3.141592*r^3
Units of Length

Quadratic Formula
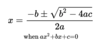
Common Logarithms
The common log of a number N is expressed as; log 10 N or log N. Common logarithms are also known as decadic logarithm and decimal logarithm
Formula to know number of solutions

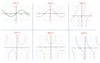
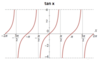
Sin Graph

Cos graph

Tan graph
“Pythagorean” trigonometric identities
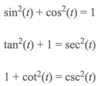
Basic Trigonometric Identities

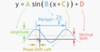
Period of a function
A function f will be periodic with period m, so if we have
f (a + m) = f (a), For every m > 0
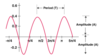
Period of Trig Functions
sin cos sec csc = 2PI/b
tan cot = PI/b
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable X, denoted E(X) or E[X], is a generalization of the weighted average, and is intuitively the arithmetic mean
Operations with matrixes
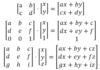
Multiplication and Determinant
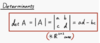
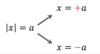
Two solutions, solving functions with absolutes