manufacturing_advanced edit Flashcards
How does a harmonic drive work?
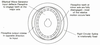
How does a lead screw work?

What are the equations for a rack and pinion systems?

What are the different acuator controls?

Electric motors bascis

Series wound DC motors

Shunt wound DC motors

Compound wound DC motors

Permant magnet DC motors
Built in tachometer for velocity feedback
Flux remains constant at all motor speeds so speed torque curve is linear
Avaliable in fractional and low horsepower designs

Advantages of permant magnet motors over conventional DC motors

What are AVG guidance systems?
Wire-guided: • An energized wire is rooted along the guide path. • The antenna of the AGV follows the rooted wire.
Optical: • Colourless florescent particles are painted on the concrete/tiled floor. • Photo-sensors are used to track these particles.
Inertial: • The guide path is programmed on a microprocessor which is fixed on the AGV • Sonar system is incorporated for finding obstacles.
Infrared: • Infrared light transmitters are used to detect the position of the vehicle. • Reflectors are affixed on the top of vehicle to reflect the light.
Laser: • Laser beam is used to scan wall-mounted bar-coded reflectors. • Accurate positioning can be obtained.
Teaching type: • AGV learns the guide path by moving the required route. • Sends the information to the host computer.
What is an AVG?
Driverless Vehicle
Electric motors, battery powered
Programming capabilities
Destination
Path selection
Positioning
Collision avoidance
• System Discipline
AGVs as assembley line opperators.
• Applications include assembly lines where the production rate is relatively low (e.g. 4 to 10 minutes per station), and variety of different models are made on the production line.
- Between workstations components are placed on the vehicle for the assembly operations on the partially completed product at the next workstation.
- Workstations are generally configured in parallel configurations to allow flexibility to the line.
- Unit load carriers and light load vehicles are used in this system.
AGVs in flexiable manufactuing systems
• Components are transferred from storage area to various work stations as part of FMS environment.
Once parts are processed (e.g. machined, etc.) at each station, they are transported to the next station for further manufacturing processing.
• AGVs provide added flexibility to the entire FMS.
What are some of the good things about guidance systems for AGVs?
- One of the major advantage of AGV is ease in modification given by the guidance system for changing the guide path at low cost compare to conveyors, chains, etc.
- Another benefit is: guide path is flexible which means intersection of path is possible.
- Generally, guide path does not obstruct another systems.
What is AGV routing?
• A routing system is used to select the vehicle which is positioned with the optimum path. • A network controller gives the destination, while the onboard controller navigates the vehicle.
Frequency select Method • At the junction of more than one paths (decision point), the vehicle reads a code on the floor in the form of metal plate, or coded device. • The vehicle selects one of the frequencies as per the direction required. • The frequencies are always active. • A continuous wire is used to loop the frequencies.
Path-Switch Select Method • Path is divided into segments. • One frequency is used. • Segments are switched On/Off by separate floor controls according to the path to be followed. • Less preferred over Frequency select method.
What is the definition of AS/RS?
Automatics storage and retrieval system
Combination of equipment and controls which, Handles, Stores and Retrieves materials with Precision Accuracy and Speed with a defined degree of automation
Function of AS/RS
- Automatic removal of items from a storage location.
- Transportation of items to a specific processing or interface point.
- Automatic storage of items in a predetermined location.
- Automatic reception and processing of items from a processing or interface point.
Advantages of AS/RS
High space efficiency
Improved inventory management and control
Reduction in labor costs
Better security
Flexibility in design to accommodate various loads
Increased productivity when interfaced with other manufacturing systems
Helps JIT implementation
Unit load AS/RS

Mini load AS/RS

Person on Board AS/RS
Allows storage of items in less than load quantities
Person performs tasks of selection and picking
Flexibility and time reduction
Definition of a robot
- Must be produced by manufacturing not by biology.
- Able to move physical objects or be mobile itself.
- Capable of some sustained actions without intervention by an external agent – programmable, multi-functional.
- Be possible to modify its behavior in response to its environmental changes (sensor equipped).
An industrial robot is a reprogrammable device to both manipulate and transport parts, tools or specialized manufacturing implementation through variable programmed motions for the performance of specific manufacturing tasks
Why are robots used?
Do not tire or grumble – no health claims (except some maintenance).
Higher quality (consistency).
Repeatable performance.
Stronger, faster, more accurate.
More productive.
Work 24 hours each day.
Immune to dangerous environment .
Reduction of labor cost.
















