Lymphoid System Histology Flashcards
Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs)
- APCs survey the body, recognize and phagocytose Ags
- Peptide fragments of Ags bind to MHC molecules and are displayed on cell surface.
- Class I MHC – expressed by all nucleated cells
- Class II MHC–expressed mainly by APCs
T cells – cellular immune responses
Detect cell bound Ags presented by MHC molecules:
- T helper cells- CD4+, helper functions via contacts with APCs and other lymphocytes
- T cytotoxic cells – CD8+, cytotoxic functions–recognition & lysis of virally infected cells
- T regulatory cells – CD4+, FoxP3, limit the immune response, produce inhibitory cytokines
B cells- humoral immune responses
- Detect soluble (unlike T cells!) or cell- bound Ags
- B cells differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells

Lymphoid Tissue
- Lymphocytes
- Supporting cells
–Macrophages
–Dendritic cells
–Granulocytes
–Reticulocytes (Except thymus!)

What is depicted in the image

Stroma: the framework of cells subdivide parenchyma into ‘subdivisions’ & support parenchymal cells
What is depicted in the image

Parenchyma: Lymphoid cells
What is depicted in the image

Diffuse Lymphoid Tissue

What is depicted in the image


What is depicted in the image

Lymphoid nodules B cell area
•Primary & secondary follicles
–B cells
–Follicular dendritic cells(mesenchymal origin, NOT bone marrow-derived!)
- Primary follicle- naïve recirculating B cells
- Secondary follicle contains germinal center established by
activated B cells.
–Germinal center B cells undergo somatic hypermutations
–B cells with mutations that improve affinity for Ag are selected and exit a germinal center
Central (Primary) Lymphoid Organs
- Bone Marrow
- Thymus
- Fetal liver
Peripheral (Secondary) Lymphoid Organs
- Lymph nodes
- Spleen
- MALT
Tonsils
Peyer’s patches
Appendix
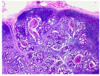
what is depicted by the image
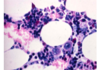
Bone marrow
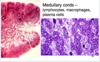
what is depicted by the image

Thymus
Secondary lymphoid organs:
•Facilitate the induction of adaptive immune responses
–Capture pathogens
–Facilitate encounters between APCs & lymphocytes
–Provide niches for the differentiation of immune effector cells
what is depicted in the image

MALT
- T cells (CD8 + intraepithelial, CD8 + & CD4 + lymphocytes in lamina propria)
- IgA- secreting plasma cells (after forming in germinal centers remain in the MALT)
- Granulocytes (Neutrophils are RARE in the healthy MALT)
- APCs
- M cells in Peyer’s patches and tonsils
What is depicted in the image

BALT
(bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue)
Lingual
stratified squamous, single crypt. On the base of a tongue (distal one third).
Pharyngeal (Adenoids)
pseudostratified ciliated columnar with some stratified squamous; no crypts but shallow pleats. In the posterior wall of nasopharynx
Palatine
covered with stratified squamous non- keratinizing epithelium. In the palatine fossa
- Many (10-12) deep crypts
- Capsule underneath
- Skeletal muscle deep to capsule
What is depicted in the image

Palatine Tonsil
What is depicted in the image


Peyer’s Patches Microfold (M) cells
M cells:
- Have a folded luminal surface
- Do not have a brush border
- Are not covered by glycocalyx
What is depicted in the image

Peyer’s Patches Microfold (M) cells
Appendix
lack of villi, lymphoid tissue in lamina propria and submucosa