Lungs Flashcards
Causes of pulmonary granulomas?
Post-infection/inflammatory(eg TB, vasculitides, fungal disease)
Benign vs Malignant calcifications?
-benign(central, diffuse, popcorn, laminates) -malignant(eccentric, speckled, amorphous)
Typical age of round pneumonia?
Paediatric < 8 yrs
Association of multiple pulmonary AVMs?
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome(90%) = Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia -epistaxis -telangiectasia of skin/mucous membrane -GI bleed
Communications of pulmonary AVMs?
Between pulmonary/system artery with a pulmonary vein
Acquired causes of pulmonary AVMs?
Cirrhosis, trauma, infections
Is it reliable to evaluate pulmonary harmatomas by HU?
No, as may be falsely low by averaging with air, it should instead rely on visible fat
Ddx of feeding vessel sign(a distinct vessel leading directly to a nodule or mass)?
Infarction
Embolism
Angioinvasive
pulmonary aspergillosis
Vasculitis
AVMs
Metastases
Ddx of multiple lung nodules?
metastases, lymphoma, Ca lung with synchronous primary tutors, infections, granulomatous diseases, sarcoidosis, GPA, rheumatoid lung disease, amyloidosis, septic embolism
Predilection of pulmonary metastases?
peripheral and subpleural
Associated findings of pulmonary metastases?
-surrounding haemorrhage(ill defined or halo sign) -cavitation -calcification -feeding vessel sign(reflect their embolic nature)
Prognosis of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma(IMA)?
poor
CT features of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma(IMA)?
-diffuse/patchy lung consolidation -GGO -multiple lung nodules in centrilobular location -CT angiogram sign(visible opacified arteries within consolidative areas on contrast-chanced CT)
Tumour behaviour of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma(IMA)?
-lepidic growth(tumor cells proliferating along the surface of intact alveolar walls without stromal or vascular invasion pathologically) -they secrete mucin to fill the alveoli so consolidation can be seen as well
Old terms for invasive mucinous adenoCA?
diffuse or multifocal broncioloalveolar carcinoma
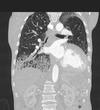
Features?

- Large arrows: focal areas of consolidation
- Small arrows: multiple nodules in centri-lobular location reflecting endobronchial spread of tumour
- Dx: invasive IMA with consolidaiotn and multiple nodules
Common fungal organism giving lung infection in immunocompromised patients?
Aspergillus
Differences in CT features of pulmonary infections in immunocompetent vs immunocompromised patients?
- Immunocompetent: focal consolidation/solitary nodule/solitary mass more common except massive inoculation of organism(e.g. histoplasmosis in a cave explorer)
- Immunocompromised: multiple nodules +/- halo sign +/- cavitation
What is granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
- multisystem disease of unknown cause
associated with upper, lower resp tract and kidney
- 90% ANCA +ve
Typical locations of lung nodules in amyloidosis?
peripheral or subpleural
CT features of granulomatosis with polyangiitis?
- typical multiple lung masses/cavities 2-4cm
- less commonly solitary nodule/mass
- +/- pulmonary hemorrhage
- with treatment, cavitatory nodules and masses become thin walled and decrease in size/complete resolution
Massive PE vs Submassive PE?
(1) Massive PE
- systemic hypotension
- drop in systolic arterial pressure >= 40mmHg for at leasts 15 minutes not caused by new-onset arrhythmias
- shock
(2) Submassive PE
- haemodymically stable but with RV dysfunction or hypokinesis confirmed by echocardiography
What is saddle embolus?
- large pulmonary embolism that straddles the birfurcation of the pulmonary trunk extending into left and right pulmonary arteries
- right heart strain signs usually present
(1) RV width > LV width
(2) straightening/leftward bulging of IV septum
(3) enlarged pulmonary trunk - contrast reflux into azygos vein(via SVC)/hepatic veins(via IVC) is controversial as it often occurs in the absence of raised RV pressure
Contrast density < ___ HU implied non-diagnostic study in CTPA?
300-350 HU