LUMBAR SPINE Flashcards
(131 cards)
Lumbar Spine
L3 dermatome
distal anterior medial thigh
Local muscles of the trunk control what?
Inter-segmental motion
(Multifidus, intertransversari, interspinalis, transversus abdominus, internal
oblique, deep Erector spinae)
50-75% slippage=

Grade 3
name of muscle

quadratus lumburum
in the lumbar spine, passive range of motion examination is done by
two parts:
- Osteokinematic PROM: good reliability
-
Arthrokinematic (segmental) motion tests: poor reliability:
- PAIVM (Passive accessory intervertebral motion: joint glides to determine end-feel (hyper, hypo, normal) and pain/no-pain
- PIVM (Passive intervertebral motion): move the spine osteokinematically and
palpate motion of a single segment
what is the main function of the interspinales and intertransversarii muscles

- Primary function may be as motion indicators
- Small muscles with small moment arms and loaded with proprioceptors
The multifidus attaches to the spinous processes and, therefore, has an excellent moment arm for _________ . It also has a compressive element and contributes to sacral nutation.
spinal extension
Right Rotation of the lumbar spine is associated with posterior rotation of the right ilium. The right ASIS will move ________ as L5 rotates right relative to the sacrum.
In this position the right SI joint is _______ .
- superiorly
- “gapping.”
what it is for?
name of test?

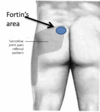
Gaenslens test
- SI pain provocation test
>95% of lumbar disc herniations occur at
L4-5 or L5-S1
Right Rotation of the lumbar spine is associated with posterior rotation of the right ilium. The right ASIS will move superiorly as L5 rotates right relative to the sacrum. In this position the right SI joint is “gapping.” Given the ___________ ligaments this makes sense. As the ilium moves posterior it “drags” the ipsilateral transverse process with it. Or conversely, as L5 rotates right it provides “slack” in the iliolumbar ligament “allowing” posterior rotation of the ilium.

iliolumbar

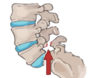
SPONDYLOLYSIS
Fx of pars inter-articularis
what are the 5 predictors that has been validated to thrust the spine?
- No symptoms distal to the knee
- Recent onset < 16 days
- FABQW < 19
- Hypomobility of at least 1 segment
- At least 35 degrees one hip IR
💡during AROM
Reproduction of symptoms when the pelvis was stabilized implicates a dysfunction originating primarily from the _____ .
spine
The psoas and DES provide opposite tensions to the spine, thereby ________ it, similar to “guy wires” for a tent pole.

stabilizing
zygapophyseal joints.
facet joint
“main goal of the examination of the lumbar spine is….
reproduction of pain.”
(Dr. )
👉🏻what is the cut off time for pt with LBP?
name of test
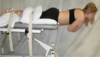
Sorensen Test (Sn: 92%, -LR 0.08; Sp: 94%, +LR 15.4)
- Patient presentation: younger age < 40 years, hypermobility in SLR, aberrant movements during, lumbar flexion and extension, Positive prone instability test.
- normal 2-3 minutes
- Cut off for patients with LBP is > 28-29 sec (Arab et al, 2009)
“a predictor for who may develop LBP” (Dr. M)
Sorensen test
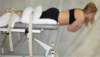

Slump Test (Sn: 84%, -LR 0.19; Sp: 83%
- lumbar radiculapathy
- Patient slumps as far as possible producing full trunk flexion; examiner adds firm overpressure
- +ve test is reproduction of patient’s symptoms
Nutation (meaning to nod) is defined as the relative _______ of the base (top) of the sacrum relative to the ilium.
anterior tilt

name of manipulation

LUMBOPELVIC THRUST MANIPULATION
______% of patients with LBP will have non-specific mechanical LBP
85%
💡can develop into which pathology?
Clinical significance of the ligamentum flavum

- It is located inside the spinal canal
- With age, the ligament flavum will degenerate and may hypertrophied (becoming fibrotic) → spinal stenosis