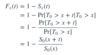LTAM 1 - Survival Models Flashcards
Pass LTAM Exam (42 cards)
Define life insurance.
pays a lump-sum benefit either on the death of the insured or on survival to a predetermined maturity date
Define life annuity.
ontract makes a regular series of payments while the recipient (called the annuitant) is alive
Define insurable interest.
An insurable interest exists if the death of the insured would cause the policyholder to suffer a financial loss
What is the difference between the policy owner, the insured and the beneficiary?
Insured: Must die in order for lump sum payment to occur. Beneficiary: Receives the payment when the insured dies. Policy owner: May be the insured, the beneficiary or a third party but must have an insurable interest in the insured.
Life insurance products have undergone radical changes since they first appeared. The reasons for the changes include:
Increased interest in products that combine savings and insurance More powerful computers Policyholders have become more sophisticated investors More competition among the insurers Increasingly complex risk management techniques
List 4 types of traditional insurance contracts
- Whole life insurance 2. Term insurance 3. Endowments 4. Participating insurance
Define term insurance and describe 4 types of term insurance.
Term insurance - benefit payable as long as death occurs during fixed term. 1. Level term insurance: premiums and benefit level through term 2. Decreasing term insurance: death benefits (and often premiums) decrease during term 3. Convertible term insurance: on maturity insurance can be converted to endowment or whole life without evidence of health. 4. Renewable term insurance and yearly renewable term insurance (YRT): on maturity insurance can be renewed (usually with increased premiums) without evidence of health.
Define endowment and micro insurance.
Endowment: Benefit is paid on death or at fixed maturity date (whichever comes first). Microinsurance: Endowment with small benefits used in developing countries.
Define whole life insurance
Benefit is payable on death whenever it occurs. Premiums are often payable only to a set date (ie. age 80)
Define participating insurance and describe how it differs in North America vs. UK/Austalia
Insureds share in profits of invested premiums. In North America profits are paid out usually in the form of cash dividends or reduced premiums. In UK/Australia benefits are paid toward increasing the death benefit through bonuses (reversionary or terminal). Reversionary bonuses are paid throughout the life of the policy to increase the sum insured and are guaranteed to be paid at maturity. Terminal bonuses are not guaranteed and are applied only at maturity to the sum insured.
What are the characteristics of modern insurance contracts?
- Flexible 2. Combine insurance and investment elements.
Describe universal life insurance.
They allow policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefits as long as the accumulated value of the premiums is sufficient to pay for the death benefits.
Name 3 types of modern insurance contracts.
- Universal Life Insurance 2. Unitized-with-profit 3. Equity-Linked Insurance
Describe unitized with-profit.
- Sold in UK until early 2000’s - Premiums are used to purchase shares in an investment fund called “With-profit fund” - Increases in the value of the fund increase the death benefit in the form of reversionary bonuses. - If fund performance is favourable, a terminal bonus may be payable on death or maturity.
Equity-Indexed Insurance
- Variable Annuity Contract - 20 year term - premiums to investment fund - death benefits are based on performance of fund at maturity -guaranteed minimum death benefit if paid before maturity -death benefit paid as lump sum but can be converted to annuity 2. Equity-Indexed Annuity (EIA) -EIA policyholders can earn returns based on the external stock index with protection downside through guaranteed minimum return on premiums - At maturity, the policyholders receive a proportion of the return of the index, if that is greater than the guaranteed minimum return. - EIA contracts usually have a maturity of 7 years. - death benefit paid as lump sum but can be converted to annuity
Describe 2 distribution methods insurance companies use to sell products.
- Commission - insurance company hires brokers/advisors to sell product in exchange for a commission (% of premium paid) - Front-end load: % paid on first premium is usually higher than subsequent 2. Direct marketing - Policies sold through this method typically have a smaller benefit than those sold through commission
Define underwriting
the process by which insurance companies collect and evaluate information on applicants of life insurance/life annuity contracts
List 3 forms of underwriting methods.
- Questionnaires 2. Medical history 3. Medical examination
List 3 things that the level or strictness of underwriting depends on.
- Type of insurance being purchased (term stricter) 2. Amount of benefit (higher benefit stricter) 3. Distribution method (commission stricter)
Describe the 4 classes of underwriting.
- Preferred - low mortality risk 2. Normal/standard lives - some increased risk factors, but still insurable at higher premium 3. Rated lives - one or more risk factors at raised levels but can be insured at higher levels. 4. Uninsurable - risk is so significant that insurer won’t cover.
The underwriting process can lower the risk of adverse selection. Define adverse selection.
Individuals with very high risk buy disproportionately high amounts of insurance, leading to excessive losses to the insurer.
Describe 2 types of premiums. When are all premiums paid?
- Single premiums paid at outset of contract 2. Regular premiums paid at intervals - all premiums are paid at the start of the contract
Define life annuities.
Life annuities are annuities that depend on the survival of the recipient, known as the annuitant.
Define whole life annuity contract.
A whole life annuity contract makes payments until the death of the annuitant.