Lots of Pictures Flashcards
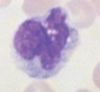
These cells with decreased nuclear segmentation are a characteristic of_______, more specifically __________.

Pelger-Huet abnormality; heterozygous
These cells with decreased nuclear segmentation are a characteristic of_______, more specifically __________.

Pelger-Huet abnormality; homozygous
These cells are hypersegmented neutrophils. Name the 3 conditions that cause this and their distinguishing features

Hereditary neutrophil hypersegmentation: large majority are hypersegmented, no macrocytic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia: 50% or fewer hypersegmented w/ macrocytic anemia
Myelokathexis: Increased apoptosis, Hypersegmented and pyknotic neutrophil nuclei, Intrasegmental filaments are longer than normal
The granules in the cells are the result of the incomplete breakdown of mucopolysaccharides. What are these granules called?

Alder-Reilly bodies
This neutrophil has giant granules caused by enlarged lysosomal vesicles. It is genetic and fatal. What is the cause?

Chediak-Higashi syndrome
This lymphocyte has a giant granule caused by enlarged lysosomal vesicles. It is genetic and fatal. What is the cause?

Chediak-Higashi syndrome
This disease is characterized by rod shaped inclusions in Eos, Bas, Neu, Mono. Giant platelets are also commonly seen.

May-Hellin Anomaly
This disease is autosomal recessive and results in a build up of glucocerebroside in macrophages.

Gauchers Disease
This macrophage appears foamy because of excess storage of lipids in lysosomes.
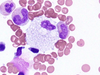
Niemann-Pick disease
This disease is a Myloproliferative Disorder characterized by chronic white cell production with maturation. It often terminates in acute leukemia, and sufferers a prone to frequent infections. It is the result of reciprocal translation on the Philadelphia chromosome.

Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML)
This is a MPD characterized by an overproduction of red blood cells. Sufferes tend to have splenomegaly (with distanded abdomins), an RBC mass > 36 mL/kg, and are treated with theraputic phlebotomy.

Polycythemia vera
This is a MPD disease characterized by chronic overproduction of platelets. It generally occurs after age 60, and has a platelet count of > 600x109 (commonly > 1000 x109), and causes thromboembolic events (mini blood clots which cause a block) in the brain and heart. Over time is can cause memory issues, and is treated with 32P.

Essential Thrombocytemia
This is a MPD disease which chronically overproduces hematopoietic stem cells (that are ineffective). Patients tend to have splenomegaly, weight loss, an altered humoral response, autoantibodies to RBCs, and occurs in patients over 60. Patients tend to be weak and usually die of infection. Identify the cells in the boxes.

Chronic Idiopathic Myelofibrosis
Platelets
Nucleus: Round to oval, reddish blue, 1-3 nucleoli, finely reticular chromatin with no clumping
Cytoplasm: Scant, basophilic, NO GRANULES
Cell Markers: CD33, CD 13, CD34 (dropping off)

Myeloblast

Nucleus: Round to oval, reddish blue, 1-3 nucleoli, finely reticular chromatin with no clumping
Cytoplasm: Scant, basophilic, NO GRANULES
Cell Markers: CD33, CD 13, CD34 (dropping off)

Myeloblast

Nucleus: Round to oval, reddish blue, 1-3 nucleoli, finely reticular chromatin with no clumping
Cytoplasm: Scant, basophilic, NO GRANULES
Cell Markers: CD33, CD 13, CD34 (dropping off)

Myeloblast

Nucleus: Round to oval, light reddish blue, 1-2 nucleoli, fine meshwork chromatin
Cytoplasm: Basophilic with azurophilic (primary), nonspecific granules
Contains myeloperoxidase (for intracellular kill)

Promyelocyte

Nucleus: Round to oval, light reddish blue, 1-2 nucleoli, fine meshwork chromatin
Cytoplasm: Basophilic with azurophilic (primary), nonspecific granules
Contains myeloperoxidase (for intracellular kill)

Promyelocyte

Nucleus: Round to oval, red-blue, variable nucleoli, with fine, clumping chromatin
Cytoplasm: moderate blue to pink, azurophilic (primary) granules, secondary granules (specific, LAP, lysozyme)
Golgi apparatus and “Dawn of Neutophilia”

Myelocyte

Nucleus: Round to oval, red-blue, variable nucleoli, with fine, clumping chromatin
Cytoplasm: moderate blue to pink, azurophilic (primary) granules, secondary granules (specific, LAP, lysozyme)
Golgi apparatus and “Dawn of Neutophilia”


Nucleus: Indented (kidney), light blue to purple, no nucleoli and clumped basophilic cytoplasm
Cytoplasm: moderate clear pink, Tertiary granules (specific) contaning gelatinase, lysozyme, and acetyle transferase.
Doesn’t respond to chemotaxins

Metamyelocyte

Nucleus: Indented (kidney), light blue to purple, no nucleoli and clumped basophilic cytoplasm
Cytoplasm: moderate clear pink, Tertiary granules (specific) contaning gelatinase, lysozyme, and acetyle transferase.
Doesn’t respond to chemotaxins

Metamyelocyte

Nucleus: Elongated horseshoe, purple-red with no nucleoli, clumped and granular chromatin
Cytoplasm: Abundant, pink, with specific violet granules


Nucleus: 2-5 lobes, purple-red, no nucloli, clumped and granular
Cytoplasm: Abundant, pink, specific violet granules
Phagocytosis/pinocytosis, Margination/diapedises