Liver Flashcards
(43 cards)
what is portal venous timing for the liver?
70 sec
How does in an out of phase imaging work?
The water and fat are summed in the in phase images and subtracted in the out of phase images.
Why does iron load cause loss of signal on the in phase images?
Because iron causes longer TE which allows a longer dephasing time, exaggerated T2* effect and loss of signal
Where does focal fat occur? Three places…
Gallbladder fossa Subcapsular (along falciform) Periportal (bonus throughout the liver)
What does amyloid look like in the liver?
Can cause abnormal extracellular deposition causing focal or diffuse areas of decreased attenuation.
What does Wilsons disease do to the liver? What are three other common features?
Wilson disease causes high level of Copper to accumulate in the liver which can be hyperattenuating on Ct with multiple nodules, leading to hepatomegaly and cirrhosis. Also accumulates in the basal ganglia and cornea. AR gene defect.
Diagnosis?

Echinoccal disease
Hepatic echinococcosis is caused by ingestion of the eggs of echinoccus granulosus (edemic in Mediteranean basin) with sheep herding
Echinoccal eggs develop into hydatid cysts which on CT loo like a well-defined hypoattenuating mass with a floating membrane or daughter cyst. Peripheral calcifications are possible
Iorn overloaded liver has what signal on all MRI signals? What is the internal control?
Hypointense on all signals. Paraspinal muscles are the control.
DDx of hypoattenuating liver lesion?
Hepatic steatosis (Most common)
Hepatic amyloid (less likely and can be focal or diffuse)
Definition and DDx of hyperattenuating liver lesions?
Definition: HU >75
DDX: Iorn overload (most common)
Medications (amoidarone, gold, methotrexate)
Copper overload (Wilson disease)
Gylcogen excess
Dx?

Candidasis
Systemic fungal infection that may seed the liver and the spleen
CT shows multiple tiny hypoattenuating microabscesses in the liver and the spleen which can be rim-enhancing
DDX for hypoattenuating liver lesions: metastatic disease, lymphoma, biliary hamartomas or Caroli disease
Early signs of cirrhosis (3)
Expansion of perportal space
Atrophy of the medial segment of the left hepatic lobe causes increaed fat anterior to the right main portal vien
Features of HCC on T2?
Classically T2 hyperintense to surrounding liver
Renerative nodules are usually T2 dark
“Nodule within a nodule” is concerning and describes a central bright T2 nodule with a T2 dark border
Hypervascular hepatic mets? (name 5)
- Neuroendocrine (including pancreatic neuroendocrine and carcinoid)
- RCC
- Thyroid carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Sarcoma
Hypovascular hepatic mets?
Colorectal cancer and pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Calcified hepatic mets?
Colorectal tumors
Ovarian serous tumors
(usually means a better prognosis)
Dx?

Pseudocirrhosis
Macronodular liver contour from multiple scirrhous hepatic metastases (mimic cirrhosis)
MCC is treated breast cancer
Capsular retraction is charactersitic when present
Metastatic hepatic lesion appearance on MRI?
Hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2
(except blood products or melanin (melanoma) are T1 hyperintense)
Dx?
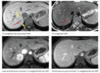
FNH
Arterial enhancement with quick wasout
Scar is T2 hyperintense. Delayed enhancement of the scar is not shown here
Dx?

Hemangioma
Note the two areas of nonehnacement on the delayed images consistent with cystic degeneration
Causes of Budd Chiari?
Caused by venous outflow obstruction which can be thrombotic or non-thrombotic (often a hypercoagulable state such as OCPs, pregnancy, hematologic disorder, malignancy, infection or trauma)
Dx?

Budd-Chiari
Massive enlargement of the caudate lobe with atrophy of the left lobe and right anterior segments of the liver
Collateral venous drainage is visualized within the periphery
Acute Budd Chiari presentation Triad:
Hepatomegaly
Ascites
Abdominal Pain
What is the MDCT hepatic trauma staging by AAST?



