Lifestyle factors and disease Flashcards
What are the leading causes of adult deaths n the uk?
- Cardiovascular disease: 24% - Cancer: 21% - Respiratory diseases: 20% - External factors: 4%
What are lifestyle factors that improve health?
Self-management
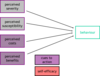
- health-protective behaviours
- screening behaviours
- health risk behaviours
What are 4 key health protective behaviours ?
- smoking - diet - alcohol - activity
What is the significance of the observed dose-response effect?
- increased benefit with more health behaviours being done
What is the magnitude of the benefit of engaging in all health behaviours rather than none?
- 3-3.5x less likely to die if you participate with all the healthy behaviours
What does the IMB model show us about psychological model of health behaviour
- demonstrates the key elements needed for behaviour change

What factor enable people to change unhealthy behaviour?
Motivation - these can be extrinsic or intrinsic factors
How can behaviour changes be better managed?
Having SMART goals? - Specific - Measurable - Achievable - Relevant: links with their motivation (Realistic) - Time-limited
What is motivational interviewing?
- one-on-one approach - overcome ambivalence about behaviour to change - enhance commitment to change - enhance motivation to change - address barriers to change
What are some limitations to models?
- a lot of variation, cannot explain exceptions - can explain efforts to change behaviour but cannot explain maintenance of these changes - there are non-rational factors
What is the dual process model?
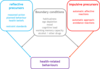
What are reflective precursors?
- reasoned action
- planned behaviour
- health beliefs
- restraint standards
What are boundary conditions?
- habitualness: despite stale popcorn, people will still eat the same amount as if it was fresh
- ego depletion: will-power comes from a limited pool of mental resources that can be used up. when energy for mental activity is low, self-control is low
- mood
- cognitive load: the brain can only process a certain amount of information at one time
- working memory capacity
- alcohol/other drugs
What are impulsive precursors?
- automatic affective reactions
- automatic approach-avoidance reactions
Describe the Health Belief Model