Lesson 16 - Vertebral Pathology Flashcards
When imaging the vertebral artery it is imporant to include ________ in your image
Transverse Processes of the vertebrae
So people will believe it’s the vertebral artery
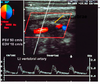
Where is the doppler beam sent when imaging the Vertebral Artery?
Between the transverse processes
Imaging techniques for a normal vertebral artery

- Anterior window
- line up on mid to distal CCA
- Angle lateral and look for shadow (angle & tip)
- Velocity - PSV (EDV optional)
- Waveform morphology
- Direction, ex: waveform is inverted above the baseline, going away from the TD, toward the head, correct for vertebral
- Sometimes straight steer of color and/or spectral works better btwn small disc space
- Some machines have alternate 20deg angle rather than 30
- Check direction with spectral – may be vertebral vein too
- Vertebral vein may be pulsatile

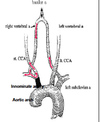
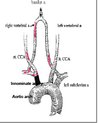
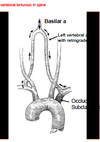
Where is the obstruction when a Lt. Vertebral steal occurs?
Lt. Subclavian proximal to vertebral
- Reversed flow in ipsilateral vertebral
- Increased velocity in contralateral vertebral
How does the disease progress in Lt. Vertebral Steal?
- Early systolic deceleration
- Partial steal (incomplete, transitional, to & fro)
- Complete steal
*More steal when arms are in use
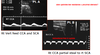
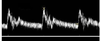
Describe the waveform changes with advancing vertebral and subclavian steal
NORMAL: continuous forward flow
EARLY STEAL: peak begins to invert during systole
PROGRESSION OF SUBCLAVIAN DISEASE: increasing systolic peak inversion until the peak reverses below the baseline. To and fro patterns are seen when the systolic peak falls below the baseline while the diastolic flow continues in the forward direction.
FINAL STAGES: entire waveform shows continuous flow reversal

Describe the waveform of an early subclavian steal
- Continuous forward flow
- Systolic peak inversion
*mild steal = mild occlusion

What is an early sign of subclavian stenosis?
Early systolic deceleration (ESD) after peak systole

What is the “bunny rabbit”?
Early Systolic Deceleration (ESD)
- happens in the vertebral on the side of the occluded subclavian
- changing pressure patterns in left arm in the presence of proximal subclavian srtery stenosis affect the vertebral waveforms

What exacerbates ESD?
progression of subclavian disease
What is the stress study?
When is it done?
- Stress pts effected arm to increase perfusion
- when partial steal is detected
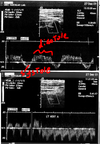
How is a stress study performed?
1) Isometric exercise, doppler while doing it and you’ll see full reversal start (using arms may turn partial steal into severe) *look at diseased arm
2) Inflate cuff above systolic pressure for 2-3 minutes (causes vasodialtion)
3) Doppler upon release of cuff and you’ll see full reversal
*flow will be normal when cuff is inflated b/c no blood is getting to the arm - will reverse when cuff is released. **same side as subclavian. as it get’s worse, you lose the bunnies ear

What is done during the isometric exercise of the stress study?
Pt clench fist for 3 seconds
Upon release of fist the flow will reverse
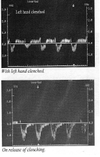
What happens to the flow in the vertebral when the pt clenches and releases fist?
flow will reverse upon release of fist
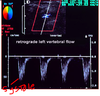
Retrograde flow in the vertebral artery throughout systole and diastole is a sign of _______________
Severe subclavian stenosis or occlusion
*flow towards the arm the entire time
*complete steal