Lecture 9: Migraine Pharmacology Flashcards
Which 2 medication classes are used to treat the prodrome effect of a migraine?
- Triptans
- Ergot alkaloids

Which 4 drug types may be used as preventative agents to limit the frequency and severity of migraine attacks, working in the prodrome stage?
- β blockers
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Anticonvulsants
- Ca2+ channel blockers

Which is the treatment modality of choice for patients >18 yo who suffer from chronic migraines?
Botox

What are the 2 Ergot Alkaloids used in the treatment/prevention of migraines?
- Dihydroergotamine (DHE)
- Ergotamine + Caffeine
What 2 β-blockers may be used as preventative agents to limit the frequency and severity of migraine attacks?
- Propranolol
- Timolol
What are the 2 Tricyclic Antidepressants used as preventative agents to limit the frequency and severity of migraine attacks?
1) Amitriptyline
2) Imipramine
Which 2 anticonvulsants may be used as preventative agents to limit the frequency and severity of migraine attacks?
- Topirimate
- Valporate
Which Ca2+ channel blocker may be used as a preventative agent to limit the frequency and severity of migraine attacks?
Verapamil
Neural events result in ______ of blood vessels resulting in pain and further nerve activation —–> headaches/migraines
Dilation
The meninges are innervated by which axons?
What occurs when stimulated by vasodilation?
- Trigeminal axons
- When stimulated by vasodilation they generate throbbing unilateral migraine-like pain

Which fibers release Calcitonin-Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) and Substance P/Neurokinin A?
Has what effect?
- CGRP is released by Ad-fibers –> increases dural vessel vasodilation
- Substance P and neurokinin A from C-fibers –> increases dural vessel permeability
Neuropeptides leading to dilation of cranial blood vessels causing sensitization of nerves to pain which spreads in what direction?
Sensitization spreads from periphery to the brain
What used to treat coronary artery disease can provoke migraine?
Organic nitrates (NO)

What does Cortical Spreading Depression (CSD) lead to?
Accompanied by?
- Leads to cerebral vasoconstriction
- Accompanied by H+, K+, and NO discharge from neurons

Electrolytes (H+ and K+) along with NO discharge from neurons as a result of cortical spreading depression (CSD) lead to what 2 events?
- Dilate cranial arteries
- Depolarize perivascular trigeminal terminals

Release of what promotes neurogenic inflammation?
CGRP and neuropeptides (substance P) act together to produce painful dural inflammation

What elicits the release of CGRP in the pathophysiology of migraines?
Nitric Oxide (NO)
In neurogenic inflammation as a wave of electrical activity and H+/K+ pass through nerve cells they stimulate the release of what?
- Neuropeptides (CGRP and substance P)
- Inflammatory mediators (NO, histamine, and prostaglandins)
What type of serotonin receptors are found on cranial vessels?
Peripheral neurons?
Central neurons?
- Cranial vessels = 5HT-1B
- Peripheral neuron = 5HT-1D
- Central neuron = 5HT-1B/1D

Triptans are selective agonists of which receptors?
5HT-1B/1D

What is the effect of triptans binding to 5HT-1D receptors on presynaptic nerve terminals?
Inhibit presynaptic release of CGRP and other neuropeptides from the peripheral end of the trigeminal nerve
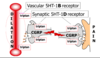
What is the effect of triptans binding to 5HT-1B receptors on vascular smooth muscle?
Stimulates vasoconstriction of dilated meningeal, dural, and pial blood vessels

What are the 2 effects of triptans binding to 5HT-1D receptors on the trigeminal nucleus in the brainstem?
- Modulates incoming painful sensory information from periphery
- Inhibits upward transmission of painful sensory information to the thalamus and higher brain centers where pain is perceived
What 2 triptans can be formulated as nasal spray and when would this be a good option in a clinical setting?
- Sumatriptan and Zolmitriptan
- Effective with nausea/vomiting, simple, works quickly




