Lecture 9: GI Bleeds and GI/Abdominal Emergencies Flashcards
Herniations or saclike protrusions of the mucosa through the muscularis at points of nutrient artery penetration defines what?
Diverticulosis
Periumbilical pain out of proportion to tenderness (i.e., pt is writhing in pain, but PE isn’t impressive) is characteristic of what GI problem?
Acute Mesenteric Ischemia
What will abdominal XR show in patient with Acute Mesenteric Ischemia?
Characteristic sign?
- Bowel distention and Air-fluid levels
- Thumb-printing (submucosal edema)

What is the diagnostic study of choice for Acute Mesenteric Ischemia?
Early celiac and mesenteric ________ is recommended?
- CT angiography = study of choice
- Early celiac and mesenteric arteriography is recommended
Which procedure is indicated in Acute Mesenteric Ischemia to restore intestinal blood flow obstructed by embolus or thrombosis or to resect necrotic bowel?
Laparotomy
Ischemic colitis is characterized by what symptoms and signs?
Severe lower abdominal pain followed by rectal bleeding
Abdominal XR of ischemic colitis will show what?
- Colonic dilation
- Thumb-printing
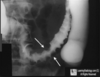
Differentiate acute mesenteric ischemia from ischemic colitis?
- AMI = periumbilical pain out of proportion to tenderness
- IC = severe LOWER abdominal pain followed by rectal bleeding
Although iron-deficiency anemia is associated with occult GI blood loss, why is it also a common finding in pre-menopausal women?
- Menstruation
- Pregnancy-associated iron loss
Most common cause of Acute Liver Failure?
Acetaminophen
Toxic Megacolon carries a high risk for what complication?
Treated how?
- Perforation
- Treatment w/ surgery
Perforated Viscus refers to what?
Significant why?
- Any hollow organ (esophagus, stomach, intestine, uterus, bladder) perforation
- EMERGENCY SURGERY!
Perforated viscus is visualized with what imaging modality?
What is seen?
- CT or plain XR
- Free air under diaphragm or air in mediastinum (Pneumoperitoneum = below diaphragm and Pneumomediastinum = above diaphragm)
Low grade fever is typical of appendicitis, but what is a high-grade fever or rigors (chills) suggestive of?
- Appendiceal perforation
- Septic thrombophlebitis (pylephlebitis) = rare
Psoas sign vs. Obturator sign for Appendicitis?
Psoas sign - pain on passive extension of the right hip
Obturator sign - pain w/ passive flexion and IR of the right hip
Moderate ________ with _______ is a common lab finding in appendicitis
Moderate leukocytosis with neutrophilia is a common lab finding in appendicitis
What are 2 useful imaging modalities for the diganosis of appendicits?
- Ultrasound
- CT
What are the most common symptoms/signs of Intestinal Obstruction?
- Colicky abdominal pain
- N/V –> Feculent vomiting (common)
- Abdominal distention
- Absence of flatus or stooling



