Lecture 9: Developmental Origins of Vascular Dysfunction Flashcards
(24 cards)
What is the blood vessel structure?
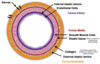
What does tunica adventitia merge with?
Connective tissue
What responds to vasoconstrictors/dilators?
Smooth muscle
What produces vasoconstrictors/dilators?
Endothelium
What is the NO pathway of relaxation?
Ach binds to receptor - eNOS increased - NO - cGMP - relaxation
What is the PGI2 pathway of relaxation?
ACh - COX - PGI2 - cAMP - relaxation
What is the EDHF pathway of relaxation?
ACh - increase Ca - hyperpolarization (change in potassium) - relaxation
What do smaller arteries become and what relaxation pathways do they rely on?
Resistance arteries - rely on all three pathways
What relaxation pathway do bigger vessels rely on?
NO
What does ACh affect?
Endothelium
What does nitroglycerin do?
Acts on vascular smooth muscle
What are the changes to ACh and nitroglycerin in babies born small?
Reduced response to ACh (reduced relaxation - reduced endothelial function) No change to nitroglycerin response - no damage to smooth muscle
What happens to carotid artery stiffness in babies born small?
Increased
What is wire myography?
Measure ability of blood vessels to constrict/dilate in response to a particular drug
What happens to BP when mothers have a 30% reduction in total diet?
Increase in MAP - initially more present in males but females catch up
What does phenolephrin do?
Reduces sensitivity to U4 (thromboxane) - good because it reduces constriction but this response disappears with age
What does thromboxane (U4) do?
Causes constriction - born to mum with restricted diet - increased sensitivity to U4 - bad - more constriction
What happens if a mother reduces protein intake by 30%?
Dysfunction in endothelium (reduced ACh response) and dysfunction in vascular smooth muscle (SNP)
What does SNP do?
Increases relaxation - acts on smooth muscle
What happens to SNP affect with IUGR?
Curve shifted to right - smooth muscle disfunction- less vasodilator action (reduced cGMP pathway)
What is the effect of alcohol?
Higher systolic BP, aorta is relaxing less
What are mechanical wall properties?
Disable vascular smooth muscle and assess structure of vessel and its ability to stretch
What do collagen and elastin cause?
Collagen – stiffness Elastin – compliance
What is the stress strain curve and how is this affected by alcohol and IUGR?
Measure of how stiff the vessel is. IUGR and alcohol - curve is shifted to left - coronary artery is stiffer


