Lecture 6: Cardiac Rhythm Disturbances (Atrial, Junctional, Ventricular) Flashcards
What is your interpretation?

Sinus Arrhythmia
What is Sinus Arrythmia due to?
Normal, but minimal, increase in HR during inspiration and decrease in HR during exhalation

Bile salt accumulation in obstructive jaundice can have an affect on the SA node and lead to what type of HR?
Bradycardia
What is the effect of hyperkalemia on HR?
Bradycardia
List some drugs that can cause bradycardia?
- Quinidine
- Digitalis
- HTN drugs –> clonidine, methyldop, and reserpine
- Beta-blockers —> propranolol and metoprolol
Sinus bradycardia is a common finding with what type of MI?
Acute inferior MI (increased vagal tone, N/V)
Sick sinus syndrome has what effect on HR?
Bradycardia
Which HR is considered bradycardia?
HR < 60/min
What are characteristic ECG findings of someone with Sick Sinus Syndrome?
- Periods of inappropriate, and often, severe bradycardia
- Sinus pauses, arrest, and sinoatrial (SA) exit block with, and often without, appropriate atrial and junctional escape rhythms
- Alternating bradycardia and atrial tachyarrhythmias

For each of these parameters, pO2, pCO2, pH, and BP, use (↑↓) to describe which is associated with bradycardia
- ↓pO2
- ↑pCO2
- ↓pH
- ↑BP
What is the most common cause of unexplained pause on an EKG tracing?
Nonconducted PAC

What is the tx of choice for pt with sinus bradycardia, if HR <45-50 with hemodynamic compromise/unstable acute situations?
Use caution in which pt’s?
- Atropine
- Use caution in glaucoma –> can ↑ IOP
If atropine is given to someone with hemodynamically unstable sinus bradycardia and fails to work, what are the next 3 options for tx?
- Epinephrine
- Isoproterenol
- Pacemaker
Define automaticity in regards to cardiac cells
Property of cardiac cells to depolarize spontaneously during phase 4 of AP/leads to generation of an impulse
What characteristics are used to determine if a PAB is present and to help differentiate it from something more serious?
- Appears early in the cycle
- Morphologically distinct from the previous P waves

What is the characteristic finding on an EKG of a PAB with aberrant ventricular conduction?
Wide QRS following PAB

What is this known as?

Atrial Bigeminy

Interpret the tracing in A and B

- A) 1st degree AV block w/ non-conducted PAC
- B) 1st degree AV block w/ non-conducted PAC occurring in trigeminal rhythm

Interpret this EKG

Non-conducted PAC in Bigeminal rhythm

What is the tx for PAC’s if symptomatic?
- Reverse causes (i.e., coffee, alcohol, other contributors)
- Beta-blocker —> Metoprolol
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia has a sudden onset and what is the HR?
Rate = 150-250/min

What are the criteria for paroxysmal atrial tachycardia with AV block?
What should you suspect as underlying cause?
- Greater than one P’ wave per QRS complex; 2 P’ waves for each QRS
- Rapid rate with spike P’ waves
- Suspect digitalis toxicitiy

Interpret this EKG

Atrial Tachycardia with 2:1 AV block

Interpret this EKG

Atrial Tachycardia w/ 2:1 AV block

What are the criteria for Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (i.e., morphology, rate/rhythm, intervals)?
- 3 or more DIFFERENT P waves
- P-R interval varies
- Irregular ventricular rhythm
- Atrial rate >100

List 5 etiologies for Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
- Lung disease (COPD, pneumonia, ventilator theophylline)
- Beta agonists
- Electrolyte abnormalities (↓K+ and ↓Mg)
- Digitialis toxicitiy
- Sepsis
Which EKG abnormality will almost exclusively been seen in COPD patients on ventilator theophylline?
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia

Interpret this EKG

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia

Interpret this EKG

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia

Interpret this pt’s EKG

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia

What are the Tx options for Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia?
- CCB –> nondihydropyridine = Dilitiazem or Verapamil via IV
- MgSO4 via IV then Amiodarone/Adenosine
What is the atrial rate in Atrial Fibrillation and what are the other characteristics on the EKG (baseline, rhythm, and intervals)?
- Atrial rate >350-600/min
- Undulating baseline w/ no discernible P waves
- Irregular RR interval; “irregularly irregular” ventricular rhythm

Interpret this EKG

Atrial Fibrillation w/ Complete AV block

Interpret this EKG

Atrial Fibrillation

What is the diagnosis based on this EKG?

Atrial Fibrillation w/ controlled ventricular response

What is the characteristic appearance of Atrial Flutter and in which leads is it seen best?
- “Saw tooth appearance”
- Leads II, III, and aVF

Interpret this EKG

Atrial Flutter

Interpret this EKG

- Acute Pericarditis w/ Atrial Flutter
- Pericardiits will show diffuse ST elevations in multiple leads
- Atrial flutter is best seen in leads II, III, and aVF

Interpret this EKG

Atrial Flutter w/ 2:1 AV block

Interpret this EKG

- Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV block
- Notice every other p wave is NOT followed by a QRS

If you see a premature QRS complex that is slightly widened you should consider that it may be due to what?
Premature Junctional (or atrial) beat with aberrant ventricular conduction

A junctional automaticity focus may cause retrograde atrial depolarization and how will the premature P’ wave appear?
Inverted P’ wave in leads with upright QRS

Interpret this EKG

(AV) Junctional Bigeminy

Interpret this EKG

(AV) junctional trigeminy

What is the rate for paroxysmal junctional tachycardia and how will the P wave appear?
- Rate = 150-250/min
- P wav may be lost (buried), inverted BEFORE or AFTER each QRS

What is the dx of his 12 lead EKG?

- Rate is around 220/min
- Supraventricular Tachycardia, and w/ no p waves is a junctional AVNRT

What is the tx for SVT (AVNRT)?
Adenosine

Interpret this EKG

AVNRT or SVT

Interpret this EKG

Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia

What are the ECG characteristics of Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVC’s)?
- Premature + bizarre + wide QRS
- No preceding P wave; may produce retrograde P wave in ST segment
- ST-T wave moves in opposite direction of QRS
- Usually full compensatory pause!

Interpret this EKG

- Multifocal PVCs
- Multiple, irritable ventricular foci producing their own unique PVC upon firing

Interpret this EKG

- Ventricular Bigeminy
- Every other beat has a PVC

Interpret this EKG

R on T Phenomena

Interpret this EKG; when would you see this?

- Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm (AIVR)
- Seen after giving pt a clot bluster (fibrinolytic) and represents reperfusion of a previously ischemic area

Interpret this EKG

Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm (AIVR) w/ increasing fusion beats

Which drug is used for symptomatic PVC’s or in setting of ACS?
Metoprolol IV
If pt is unstable and has PVC’s what drugs can be used?
- Amiodarone
- Lidocaine
- Procainamide
Interpret this pt’s EKG

PVC’s; borderline sinus tachy

In regards to QRS complexes, ventricular rate, and morphology what characterized Ventricular Tachycardia?
- 3 or more consecutive bizarre QRS complexes
- Ventriuclar rate = 120-200 (100-250)
- Usually regular, wide QRS (> 0.12 sec)

For ventricular tachycardia or any irregularity to be considered sustained how long must it last for?
>30 seconds

Interpret this EKG

Ventricular Tachycardia

Interpret this EKG and what would you do?

- Sustained Ventricular Tachycardia
- Cardioversion (ie., shock the heart back into rhythm)
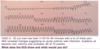
Interpret this EKG

Ventricular Fibrillation

Interpret this EKG

Ventricular Fibrillation

What is your interpretation and what do you do?

- Ventricular fibrillation
- CPR —> Defibrillation

What is the rate of ventricular flutter and how can you tell it apart from fibrillation?
- Rate = 250-350/min
- Smooth, sine waves
- Fibrillation will be more irregular

Interpret this EKG and how do you know?

- Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia
- There are narrow, normal looking QRS’s, so it could not have originated in an irritable ventricular focus; therefore is supraventricular

Interpret this EKG
Torsades de Pointes
What are 3 treatment options for Torsades de Pointes?
- MgSO4 IV bolus
- Overdrive pacing
- Isoproteronol (beta-agonist)

What are 3 characteristic findings of Hypokalemia on an EKG?
- “U” waves
- ↑ QT interval
- Flat or inverted T wave

Interpret this EKG

Hypokalemia

Interpret the abnormalities

- Hypokalemia
- Prominent “U” wave
What are the major EKG features of Hyperkalemia?
- Peaked “T” wave = most prominent feature
- Wide QRS
- ↑ PR interval
- Loss of P wave

What is wrong with this patient, based off the EKG?

Hyperkalemia (peaked T waves and wide QRS)
Which abnormality is responsible for this?

HYPERkalemia
What is the characteristic finding on an EKG with HYPOcalcemia vs. HYPERcalcemia?
- Hypocalcemia = prolongation of QT interval
- Hypercalcemia = short QT interval; short ST segment
What is the quick and dirty way of determining hypocalcemia from an EKG?
- Measure the R-R interval and measure the Q-T interval
- If Q-T interval is >1/2 the R-R than its likely hypocalcemia

What is the underlying abnormality?

Hypocalcemia

Which electrolyte disturbance does this represent?

Hypercalcemia

Characteristic EKG findings of hypomagnesemia?
- Prolonged PR and QT
- Wide QRS
- Everything is slowed down

Which electrolyte abnormality is represented here?

Hyperkalemia

What is the characteristic rate and finding on the EKG for hypothermia?
- Bradycardia
- J wave (Osborne wave)

What is the status of the pt based on this EKG?

Hypothermia

A patient presents with sudden dyspnea, but the lungs are clear and the XR is normal, what should you suspect?
Pulmonary embolism
What is the most common rate on an EKG and characteristic findings of pulmonary embolism?
Associated with what kind of block?
- Sinus tachycardia
- S1; Q3; inverted T3 (rhymes)
- Transient RBBB

What is seen in leads V1-V4 with a pulmonary embolism?
- T wave inversion
- Transient RBBB

Patient presents with sudden dyspnea and has this EKG, what do you suspect?

Pulmonary Embolism (S1; Q3; T3)
What will be seen on EKG of someone with Cerebral Hemorrhage?
Impressive ST-T changes

What underlying pathology would produce an EKG like this?

Cerebral hemorrhage

Whenever you see widespread flattening or mild inversion of T waves without associated ST segment displacement + low voltage QRS, you should always think about what underlying problem?
Hypothyroidism

What are the characteristic EKG findings in Brugada Syndrome?
RBBB w/ ST elevation in V1-V3

A 21 yo male presents to the ED following an episode of syncope. He feels fine now and wants to go home. His EKG looks like this. What is your interpretation?

- Brugada Syndrome
- At risk for sudden death; needs implanted ICD

What are the characteristic EKG findings in Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome?
- Short P-R interval
- Slurred upstroke (delta wave) of QRS
- Accessory AV conduction pathway (Bundle of Kent)

What is your interpretation of this EKG?

Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome



