Lecture 5 and 6: Male Tract and Endocrine Control I and II Flashcards
(71 cards)
Testis is an ____ and ____ gland
Exocrine (secretory product = spermatozoa)
Endocrine (secretory product = mainly testosterone)
What is the overall pathway of sperm?
- The testes are where sperm are manufactured in the scrotum.
- The epididymis is a tortuously coiled structure topping the testis, and it receives immature sperm from the testis and stores it several days.
- When ejaculation occurs, sperm is forcefully expelled from the tail of the epididymis into the deferent duct. (v_as deferen_s)
- Sperm then travels through the deferent duct through up the _spermatic cord i_nto the pelvic cavity, over the ureter to the prostate behind the bladder.
- Here, the vas deferens joins with the s_eminal vesicle_ to form the ejaculatory duct, which passes through the prostate and empties into the urethra.
- When ejaculation occurs, rhythmic muscle movements propel the sperm forward.

Describe the cell types in the tests
- Gonocytes
- =Primordial germ cells
- primitive germ cells that become spermatogonia
- Only present in early life- up to minipuberty
- Spermatogonia
- Germ cells
- Deferentiated to produce sperm
- Pre-sperm cells that replicate by mitosis
- Sertoli cells
- Epithelial cells
- Nurse cells- help development of pre-sperm cells.
- Lumen of tubule help developing pre-sperm cells
- Increase in number during minipuberty
- Leydig cells
- Sit outside the Seminiferous tubules
- Main product is androgen
- Myoid cells
- Contractile
What cells in the testes differentiate to become sperm?
Spermatogonia
Germ cells
Deferentiated to produce sperm
What cells in the testes nurse the developing pre-sperm cells?
Sertoli cells
What are the interstitial cells in the testes that produce androgen?
Leydig cells
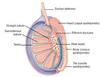
What is this a cross section of?

Seminiferous tubule
Label this cross section of Seminiferous tubule

- leydig
- basement membrane
- spermatognium
- primary spermatocyte
- secondary spermantocyte
- spermatid
- sperm cell or spermatozoon
- lumen of seminiferous tubule

Describe Primordial germ cells
- what they become
- when they’re first seen
- where they’re found
- Primordial germ cells (PGCs) will become either sperm or oocytes
- PGCs are first seen around 3-4 weeks post-conception
- PGCs are first found in the yolk sac of the extraembryonic tissues and migrate to the gonadal ridges (near the developing kidney) via the hind gut.

•Question if an embryo is 21 days post conception what is its gestational age?
5 weeks gestational age
Because conception occurs around 14 days after LMP (last menstrual period)
How do we date pregnancies?
Last Menstrual period (or with ultrasound now)
What is the difference between post-conception age and LMP?
Conception occurs around 14 days after LMP (last menstrual period)
So 5 weeks LMP = 3 weeks post conception.
Describe Germ cell migration.
- Stem cell factor (a growth factor) seems to be important in driving migration and if there is inadequate SCF the PGCs die. So PGCs that wander away from the correct path of migration should be eliminated by apoptosis. (so they only end up in the gonads) (avoid ectopic PGCs).
- While migrating, PGCs follow fine enteric nerves and do not always enter or stop at the testes.
- There are reports of germ cells developing ectopically –e.g. in the pancreas where they form oocytes.
- Ectopic germ cells may be the origin of germ cell tumours outside of the testes.
When the Primordial Gern cells (PGCs) arrive at the gonads, they’re called ______
Gonocytes (eventually turn into sperm)
What forms spermatogonia?
1) Primordial Germ cells arrive in the (male) gonad = now called gonocytes
2) The gonocytes turn into spermatogonia (have different developmental stages as stem cells)- change not just in puberty but earlier on in life

What are Seminiferous Tubules?
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testes, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
The epithelium of the tubuleconsists of a type of sustentacular cells known as Sertoli cells, which are tall, columnar type cells that line the tubule.

Germ cells are thought to arise from _____
These are thought to arise from PGCs (primordial germ cells)
93% of germ cell tumours are found in the testis (4% in the ovaries, others are ectopic)
Describe Leydig cells
- In adults and fetuses testosterone is produced by the Leydig cells
- Initial production by embryonic Leydig cells not dependent on stimulation by Testosterone 7-8 weeks (sex differentiation occurs in ¬7-8 weeks gestation)
- Approximately 1_4 weeks gestatio_n production of testosterone becomes LH (pituitary) /hCG(placenta) dependent
- Embryonic Leydig cells are derived from different progenitors to adult Leydig cells. Adult Leydig cells differentiate from stem cells at puberty.

What occurs at 2 months postpartum?
Mini puberty
Sudden surge in testosterone secretion (then drops off at 3-4 months)
At post-puberty, the leydig cells become responsive to LH and you start to get adult level of testosterone.

Describe the different hormone levels during mini-puberty
- Testosterone (leydig cells)
- AMH and Inhibin (sertoli dependent cells)

What is mini-puberty thought to be important in?
Not certain
- masculinising the neonatal brain
- Promoting Sertoli cell proliferation
- Promoting differentiation of gonocytesinto dark AD-spermatogonia
- This may have implications for the timing of orcidoplexy
Sertoli cells nurse cells that promote _______
Sertoli cells nurse cells that promote post mitotis development of sperm precursors
Describe the Anatomimcal role of the sertoli cells
Sertoli cells nurse cells tha_t promote post mitotis development_ of sperm precursors
Line the inside of the seminiferous tubules
Create the blood testis barrier

Sertoli cells are important for… (4)
- nourishing spermatogonia
- resorbing the e_xcess cytoplasm_ –residual body
- Producing seminiferous tubule fluid
- Maintaining the spermatogonialstem cell niche