Lecture 3 Flashcards
(23 cards)
Calcium Excitation-Contraction Coupling
In the 1960s Calcium Was Found to be the Intracellular Messenger That Activates Contraction in Response to Excitation of the Plasma Membrane
Calcium Excitation-Contraction Coupling
In the 1960s Calcium Was Found to be the Intracellular Messenger That Activates Contraction in Response to Excitation of the Plasma Membrane
Ionized Ca2+ concentration in extracellular space and intracellular stores is…
> 1 mM
Ionized Ca2+ concentration in cytosol of resting monocytes is…
The heart contracts when calcium…
enters the cytosol from the extracellular space and intracellular stores by passive diffusion down this >1,000 fold gradient
The heart relaxes when calcium…
is removed from the cytosol by active transport
Chemical signals: Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane…
initiates a chemical signal when the cation binds to intracellular high affinity Ca2+ binding (E-F Hand) proteins
Electrical signals: Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane generates…
an “inward” (depolarizing) current because the cation carries positive charge into the cell
Primitive monocytes
*Contractions are weak, tension develops slowly *only a small amount of calcium is needed to activate contraction *diffusion of Ca from the extracellular fluid into the cytosol is sufficiently rapid examples: embryonic muscle and adult smooth muscle

Adult skeletal and cardiac myocytes
*contractions are strong, tension develops rapidly *a large amount of calcium is needed to activate contraction *diffusion of calcium from the extracellular fluid is much too slow example: striated muscle

T-tubules
these tubules open to communicate freely with the extra cellular space, filled with calcium that can enter the cytosol when the calcium channels open. Rapidly propagate action potentials into the cell interior
Ionized Ca2+ concentration in extracellular space and intracellular stores is…
> 1 mM
Ionized Ca2+ concentration in cytosol of resting monocytes is…
The heart contracts when calcium…
enters the cytosol from the extracellular space and intracellular stores by passive diffusion down this >1,000 fold gradient
The heart relaxes when calcium…
is removed from the cytosol by active transport
Chemical signals: Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane…
initiates a chemical signal when the cation binds to intracellular high affinity Ca2+ binding (E-F Hand) proteins
Electrical signals: Ca2+ influx across the plasma membrane generates…
an “inward” (depolarizing) current because the cation carries positive charge into the cell
Primitive monocytes
*Contractions are weak, tension develops slowly *only a small amount of calcium is needed to activate contraction *diffusion of Ca from the extracellular fluid into the cytosol is sufficiently rapid examples: embryonic muscle and adult smooth muscle
Sarcotubular network
Pumps calcium out of the cytosol into the SR

Adult skeletal and cardiac myocytes
*contractions are strong, tension develops rapidly *a large amount of calcium is needed to activate contraction *diffusion of calcium from the extracellular fluid is much too slow example: striated muscle
Subsarcolemmal cisternae
Contains structures that release calcium into the cytosol

T-tubules
these tubules open to communicate freely with the extra cellular space, filled with caliu
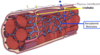
Dyad
Composite structures formed by the membranes of the t-tubules and the subsarcolemmal cisternae of the SR
Mediate the ability of an action potential at the cell surface to trigger the release of activator calcium from the sarcotubular network within the cell



