Lecture 2 - Kidney, suprarenal gland, ureter, bladder Flashcards
What does the urinary system consist of?
- ) kidneys
- ) ureters
- ) Urinary bladder
- ) Urethra
What is the function of the kidneys?
Urine secretion
What is the function of the ureters?
Ducts collect and transfer urine tot he urinary bladder
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
Retains and stores urine
What is the function of the urethra?
Discharges urine from the body
What is urine and what does it consist of?
yellowish watery fluid that contains nitrogen compounds like urea and other waste substances from the blood by the kidneys. Urine secretion is one of the body’s chief mechanisms of eliminating excess water and salt.
What does the upper urinary tract consist of?
- kidneys
- ureters
What does the lower urinary tract consist of?
- urinary bladder
- urethra
What is a urinary tract infection?
Defined as an infection to any part of the urinary system. Most infections are in the lower urinary tract.
Where can the pain be referred in an Upper UTI?
from the loin to the groin.
What causes an upper UTI?
block of urine flow or an infection in the upper UT.
The kidneys are paired ……peritoneal organs
retroperitoneal
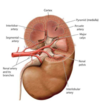
The kidneys are located where and protected by what?
Located lateral to the T12-L3 vertebrae and protected by the 11th and 12th rib. (posteriorly)
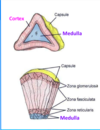
What is the kidney surrounded by?
Perirenal fat
How much does the kidney move during respiration ?
3 cm
Kidney function acronym?
A WET BED
maintaining Acid-bace balance
maintaining Water balance
maintaining Electrolyte balance
removal of Toxins
Blood pressure control - renin
Erythropoietin production
What is perirenal fat and where is it?
surrounds the kidney and is contained within the anterior and posterior renal fascial layers.
perirenal fat is continuous with ?
fat found in the renal sinus
The perirenal fat is …..peritoneal
extraperitoneal (not related to peritoneum)
What is pararenal fat and where is it?
it is external to the posterior layer of the renal fascia. It is associated with the lumbar region
The pararenal fat is …..peritoneal
extra
What are the kinds of renal fascial layers?
- ) anterior renal fascia called Gerota’s fascia
- ) posterior renal fascia called Zuckerandl’s fascia
Gerota’s fascia fuses laterally with?
posterior renal fascia
Where is gerota’s fascia ?
Posterior and parallel to the parietal peritoneum.
Where is zuckerandl’s fascia ?
it is posterior to the kidneys and posterior to the perirenal fat and anterior to the para renal fat.
zuckerandl’s fascia fuses laterally with?
anterior renal fascia
What do collagen bundles do in the renal system?
They come from the fascia and they help keep the renal fat and kidneys in position.
What are the anterior surface relationships of the kidney?