Lecture 13: Fetal Heart Monitoring Flashcards
(28 cards)
What is considered an acceleration of FHR at ≥ 32 weeks and at <32 weeks gestation?
- ≥ 32 weeks: HR ≥ 15 bpm above baseline for 15 sec or more (but <2 mins)
- <32 weeks: HR ≥ 10 bpm above baselines for 10 sec or more (but <2 mins)

What is the normal amount of variability in amplitude with FHR?
Moderate (normal) = range of 6-25 bpm

What is the pH of fetal scalp blood that is considered abnormal (fetal acidosis)?
pH <7.20
How do late decelerations appear on fetal heart monitor?
Lowest point of deceleration occurs after peak of the contraction

When monitoring FHR, at what point on the strip do you assess?
Between contractions

What are the goals and management of category II, tachysystole, if seen on fetal heart monitoring?
- GOAL: to reduce uterine activity
- Lateral positioning + IV bolus + ↓ oxytocin rate or discontinue
- If no response, give uterine tocolytic (Terbutaline SQ or IV)

What is the cause of early deceleration of FHR and how are they seen on monitor?
- Occur 2’ to head compression; fetal autonomic response to ↑ ICP —> ↓ in HR
- NOT assoc. with fetal distress
- The lowest point of deceleration occur at the same time as the peak of contraction = “mirror image“

What are the goals and management for category II, recurrent variable decelerations (>50% of contractions)?
- GOAL: alleviate cord compression
- Repositioning amnioinfusion (1st stage of labor)
- Modify pushing efforts: have Mom push w/ every other CTX

What are 2 potential causes of late decelerations?
- Excessive uterine activity
- Maternal supine HYPOtension

What kind of variability, accelerations, and decelerations may be seen in category I interpretation of FHR pattern?
- Moderate variability
- NO late or variable decelerations
- Accelerations and early decelerations may or may not be present

What is the pressure sensitive tocodynanmometer transducer useful for measuring?
Measures frequency of contractons; but NOT the strength

What is the most common cause of fetal tachycardia?
Fetal infections –> Chorioamnionitis

What is considered a prolonged acceleration of FHR and how long is considered a change in baseline?
- Prolonged acceleration = ≥ 2 mins
- Change in baseline = ≥ 10 mins

What is decreased baseline variability of the FHR an indicator of and when is it an ominous sign?
- Sign of fetal stress, is assoc. w/ hypoxia and acidemia
- Is ominous sign with persistent late decelerations

When are prolonged decelerations commonly seen on monitor?
During maternal pushing

What is the cause of late decelerations on fetal heart monitoring; why are they a bad sign?
- Caused by uterine placental insufficiency (UPI)
- Most ominous type –> repetitive decelerations usually indicate fetal metabolic acidosis and low arterial pH

How do variable decelerations of FHR appear on monitor; what is the criteria?
- Abrupt ↓ in FHR ≥ 15 bpm lasting ≥ 15 sec and <2 min (looks like big ‘V’)
- Can occur before, during, or after the contraction

How do you measure Montevideo units; what do they indicate; what is normal?
- Measure the strength of contractions in a 10 minute period (summed together)
- >200 MVU’s is adequate

What is a normal FHR, tachycardia, and bradycardia?
- Normal = 110-160 bpm
- Tachy = >160 bpm
- Brady = <110 bpm

When would you do fetal scalp stimulation and what is a normal response?
- Useful to differentiate fetal sleep from acidosis, when fetal tracing shows reduced variability but no decelerations
- When scalp stimulated: acceleration of 15 bpm lasting 15 sec occurs then the fetal pH value almost always is 7.2 or greater

When is a sinusoidal pattern seen on fetal heart monitoring?
Seen w/ fetal anemia

Which FHR is an early sign and which is a late sign of fetal hypoxia?
- Tachycardia is an early sign of hypoxia
- Bradycardia is a late sign of hypoxia

What is your evaluation of the uterus based on this strip?
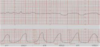
Tachysystole

Using a fetal scalp electrode for internal monitoring should be avoided in which patients?
HIV patients






