Lecture 12 Flashcards
(25 cards)
Gluconeogenesis def
new production of glucose. Important to maintain sugar levels (why we don’t wake up hypoglycemic) The source of excess sugar in blood in diabetes
Gluconeogenesis done in
the liver and the kidney
Gluconeogenesis Bypass steps 1/3
conversion of pyr to two different things
pyruvate → OAA → PEP
(3 c → 4 c → 3c)
- pyruvate carboxylase
- PEP Carboxylase
- Pyruvate kinase
during last step, Glu-6P hydrolysed into glucose
Gluconeogenesis vs. Glycolysios
Glycolysis: Carbon loss during Krebs. All tussies do glycolysis.
Gluconeogenesis: no loss of carbon, which means we can use. Happens in specific structures under specific conditions. Only in LIVER and KIDNEY
Regulated differently
How does the liver decide between doing glycolysis or gluconeogenesis?
Levels of glucose!
Big impacts from: insulin and glucagon
PEPCK
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
often rate limiting step in gluconeogenesis
Enzyme: bypass 1

Pyruvate carboxylase
bypass second enzyme

first bypass, second step.
*important rate limiting step of gluconeogenesis
bypass, third enzyme
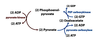
first bypass,
Glu-6P is getting hydrolyzed into glucose
Fructose 2,6-biphosphate as glucose indicator
acts as a regulator of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
↑ glucose= ↑Fru 2,6bp
↓gluc = ↓ Fru 2,6bp

Fructose 2,6 biphosphate
↑ glucose triggers
relase on insulin (to absorb glucose and lower it in the blood)
glucagon produced when
blood glucose is low (produced by α cells)
glucagon activates ______ inhibits_____
activates gluconeogenesis
inhibits glycolysis
insulin activates _____ inhibits _____
activates glycolysis
inhibits gluconeogenesis
what controls the levels on Fru 2,6 bp??
separate distinct enzyme activities

we want _____ active when glucose in abundant
PFK-2
we want _____ active when glucose is low (gone)
FBPase-2
_____(hormone) activates PFK-2
instulin
_____ (hormone) activates
FBP-ase-2
Carbon sources for gluconeogenesis
-Lactate: converted back to pyr & made into glu through the bypass steps
-Glycerol: phosphorylated then oxidized & enter gluconeogenic cycle
-Amino Acids: enters krebs at 4c levels , which produces intermediates (that are interchangable) that can produce glucose
Glycoxilate cycle overview
is an anabolic pathway that converts Ac-CoA → succinate to synthesize carbohydrates
-a way around carbon loss from Krebs
*Cycle exclusive to plants, fungi and protists
Can humans use Fatty acids for gluconeogenesis via glycoxilate cycle?
NO!
Humans don’t have glycoxilate cycle and can’t convert fat to sugar.
Every time you put in an acetate two CO2 come out. Can’t get net profit. Spending as much as you put in.
glycoxilate cycle: an end around carbon loss
very similar to krebs, fat converted separate organelles, succinate comes off then converted to OAA to make glucose
2Acetyl-CoA + NAD+ → succinate + NADH + H+
No carbon loss!!


