Lecture 10: Antiepileptic Agents Flashcards
List the 9 antiepileptic drugs which work as pre-synaptic voltage-gated Na+ channels blockers via enhanced fast inactivation.
1) Carbamazepine
2) Oxcarbazepine
3) Lamotrigine
4) Phenytoin
5) Rufinamide
6) Topiramate
7) Valproic acid
8) Zonisamide
9) Lacosamide

Which AED is unique in its ability to prolong fast inactivation of Nav ion channels and also enhance slow inactivation of Nav channels?
Lacosamide

Which 2 antiepileptic drugs are AMPA-receptor antagonists?
MOA?
- Topiramate
- Perampanel
MOA = bind AMPA receptor and block glutamate binding; channel doesn’t open –> AP does not propogate downstream

Which antiepileptic drug is an NMDA-receptor antagonist?
Felbamate
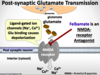
The pharmacological activity of AED Nav channel blockers is _______ and ________-dependent
State and Use-dependent

AED’s binding site is at the _________ side Nav channel ‘pore’
Interior

Which gate must be open for AED’s to access the pore of Nav channels?
Which states can this occur?
- Activation gate
- Open state and Fast-inactivated state

The probability of Nav blockade is proportional to what?
FREQUENCY of Nav channel opening and dose

Why do the AED’s that are Nav blockers act preferentially on the neurons involved in epileptic seizures?
The neurons involved will be firing at higher freqeuncy than normal, allowing more chances for these drugs to slip right in and bind
What is the water-soluble pro-drug of phenytoin which is given via IV and is an Nav channel blocker used as an antiepileptic?
Fosphenytoin
Which AED acts as a Nav channel blocker (fast inactivation), AMPA-receptor antagonist, and GABAA agonist?
Topiramate

What occurs when the post-synaptic GABAA receptor becomes occupied by GABA?
- Cl- channel opens
- Hyperpolarization occurs blunting AP propogation

What is the MOA of the AED, Tiagabine?
- Blocks pre-synaptic reuptake of GABA by blocking the GABA transporter, GAT-1
- Causes GABA to go post-synaptically, bind GABAA receptor leading to hyperpolarization and decreased AP propogation

What are the 3 MOA’s of Valproic acid used as a AED at the pre-synaptic GABA terminal?
1) Increase activity of glutamic acid decarboxylase, leading to increased GABA presynaptically
2) Inhibit GABA-T, which typically metabolizes GABA
3) Inhibit Succinic Semialdehyde Decarboxylase (SSD), which typically metabolized GABA

Which 2 AED’s inhibit the metabolism of GABA through the inhibition of GABA-T?
- Vigabatrin
- Valproic acid

Which drug in the barbiturate family gets metabolized to phenobarbital in the body?
Primidone

Where do Benzodiazepines bind the GABAA receptor and what effects does this have?
- Bind to a distinct site –> Allosteric change potentiate GABA binding
- Cl- channel opens with greater frequency

Where do Barbiturates bind the GABAA receptor and what is their effect?
- Bind a distinct site
- Increases the duration of Cl- channel opening
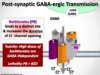
Of the GABAA receptor agonists used as AED’s which is more lethal at higher doses and why?
- Barbituates are more lethal due to being GABA INdependent
- Benzodiazepines are GABA-dependent

What are the 7 AED’s which act post-synaptically to potentiate GABAA-receptor Cl- currents?
1) Phenobarbital
2) Primidone
3) Clonazepam
4) Lorazepam
5) Diazepam
6) Clobazam
7) Topiramate

Which type of ion channel mediates the 3-Hz spike and wave activity in the thalamus which is the hallmark of absence (petit mal) seizures?
T-type Ca2+ channels
Which narrow spectrum drug is only used for absence seizures and only limits excitation (Ca2+ channels)?
Ethosuximide

Which 3 AED’s are antagonists of T-type Ca2+ channels?
- Ethosuximide (narrow spectrum)
- Valproic acid (also GABA-T inhibitor and prolongs fast inactivation of Nav channels)
- Zonisamide (also prolongs fast inactivation of Nav channels)

What is a complication of using Zonisamide as an AED in some patients?
Is a sulfonamide and people may have allergies
Which 2 AED’s act as both antagonists of T-type Ca2+ channels and prolong fast inactivation of Nav channels?
- Valproic acid (also GABA-T inhibition)
- Zonisamide
Which AED blocks synaptic vesicle 2A protein on the presynaptic terminal of glutamate neuron?
Levetiracetam

Which 2 AED’s block the α2δ1 Ca2+ channel on the presynaptic terminal of the glutamate neuron?
1) Gabapentin
2) Pregabalin
Which 5 AED’s are used as first-line treatment of both simple and complex partial onset seizures?
- Lamotrigine
- Oxcarbazepine
- Perampanel
- Primidone
- Lacosamide
Which 3 AED’s are used for absence (petit mal) seizures?
1) Ethosuximide
2) Clonazepam
3) Valproic acid
Which AED is used for myoclonic seizures?
Clonazepam
Which 2 AED’s are used for Tonic/Clonic seizures?
- Primidone
- Phenytoin
Which 4 AED’s are broad spectrum (i.e., partial onset and generalized onset, minus absence)?
1) Carbamazepine
2) Phenobarbital
3) Topiramate
4) Valproic acid
Which 6 AED’s are used for Lennox-Gastaut seizures?
- Rufinamide
- Topiramate
- Clobazam
- Clonazepam
- Lamotrigine
- Felbamate
Which 6 AED’s are used for Status Epilepticus seizures?
- Lorazepam
- Diazepam
- Phenobarbital
- Phenytoin
- Valproic acid
- Levetiracetam
The abrupt withdrawl of any antiepileptic medication may precipitate?
May lead to what type of behavior?
- Precipitate status epilepticus
- Suicidal behavior and ideation
Which AED follows zero-order (saturable) pharmacokinetics?
Phenytoin

Due to the pharmacokinetics of Phenytoin, what serum drug level must be monitored and maintained?
10-20 mcg/mL

Phenytoin is a well-known inducer of?
CYP-450 enzymes
*Frequent drug-drug interactions
What are 2 toxicities associated with the AED, Phenytoin?
- Gingival hyperplasia
- Hypocalcemia/Vit. D deficit/Osteoporosis
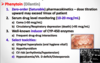
Osteopenia/Osteoporosis is a side effect associated with chronic administration of which 4 AED’s?
What do these drugs induce?
- Carbamazepine
- Phenytoin
- Phenobarbital
- Valproic acid
*These drugs induce CYP450-dependent vitamin D catabolism

What are some of the issues associated with the AED, Carbamazepine (i.e., serum drug level, inducer of, toxicities)?
- Serum drug level monitoring (4-12 mcg/mL) = narrow window
- Inducer of CYP-450 enzymes
- Induces auto-induction (self-metabolism)
- Hematological toxicities: leukopenia/neutropenia/thrombocytopenia
Which AED induces its own metabolism?
Also occurs to a lesser extent with what other AED drug?
What may occur because of this?
- Carbamazepine induces own metabolism
- Also, to lesser extent (25%), with lamotrigine
*This may lead to a potential loss of efficacy and recurrence of seizures

Before administering which AED is a CBC required as this drug has potential side effects including leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia?
Carbamazepine
What analogue of carbamazepine was formulated which has fewer CNS/hematological SE’s and is a less-potent CYP450 inducer?
Oxcarbazepine
What are some of the issues associated with the AED, Phenobarbital?
- Need serum drug level monitoring (10-40 mcg/mL)
- Well known inducer of CYP-450 enzymes (frequent drug-drug interactions)
- Toxicities: hypocalcemia/Vit. D deficit/Osteoporosis

Which AED is only prescribe-able via REMS program; why?
- Vigabatrin
- May cause progressive, permanent, bilateral, concentric vision loss

Which 4 AED’s are associated with hepatic CYP450 induction?
- Carbamazepine
- Phenytoin
- Phenobarbital
- Valproate
What are 3 major AED-drug interactions associated with the CYP450 inducers?
- Increased clearance of oral contraceptives –> 2-4 fold rise in OHC failure rate; risk for unplanned pregnancy
- Increase clearance of warfarin –> less anticoagulation; elevated risk for arterial/venous thrombosis
- Increase clearance of HIV meds –> elevated risk for HIV replication
Which 2 AED’s inhibit conjugation of drugs by UGT causing accumulation of parent drug (esp. each other when used together)?
Valproic acid and Lamotrigine

Which 3 AED’s induce conjugation of drugs by UGT causing a reduction of parent drug (i.e., when given with valproic acid will decrease levels of valproic acid)?
1) Phenytoin
2) Carbamazepine
3) Phenobarbital

Which 6 AED’s require us to look at the renal function (i.e., serum creatinine/creatinine clearance); why?
- Levetiracetam / Topiramate / Oxcarbazepine / Gabapentin / Pregabalin / Vigabatrin
- 65-100% renal clearance; renal insufficiency requires dose adjustment

What are some of the example causes of Status Epilepticus?
- Abrupt withdrawl of AED’s, BZD’s, Opioid’s, Alcohol
- Brain mass/trauma
- Infection
- Fever
What is the initial therapy for convulsive status epilepticus (i.e., the first IV, alternative drug, and if no IV access)?
- In first IV:
- Lorazepam
- Alternative
- Diazepam
*Wait 1 minute for response then additional lorazepam PRN
- If no IV access:
- Midazolam via IM injection

If treating convulsive status epilepticus adult and first IV treatment does not work, what are the AED’s used in the second IV treatment?
- Fosphenytoin
- Phenyotin
- Valproic acid
- Levetiracetam



