Lecture 1- Alcohol metabolism Flashcards
(26 cards)
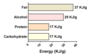
alcohol energy content
29 KJ/g
where does alcohol metabolism happen
most >90% metabolised in the liver
where is the rest excreted
passively in the urine and on the breath
Alcohol is metabolised to
acetate
outline how alcohol –> acetate
Alcohol is oxidised by alcohol dehydrogenase to acetaldehyde and then to acetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase

alcohol dehydrogenase
converts alcohol to acetaldehyde
acetaldehyde is
a toxic metabolite–> accumulation causes a hangover
aldehyde dehydrogenase
converts acetaldehyde –> acetate
acetate is then converted to
acetyl-CoA and used in the kreb cycle or for fatty acid synthesis
small amount of alcohol can be oxidised by
P450 2E1 enzyme (CYP2E1) or by catalase in the brain
recommended limitys
- 14 units/week spread over at least 3 days
one unit of alcohol = g
8g
one unit=
half pint of beer and small glass of wine
rate at which alcohol is eliminated
at a rate of 7g per hour
liver damaged caused by
acetaldehyde toxicity
acetaldehyde toxicity to the liver usually kept to a minimum by
aldehyde dehydrogenase (low Km for acetaldehyde- high affinity)
Prolonged and excessive alcohol consumption can cause
sufficient acetaldehyde accumulation to cause liver damage
Excess NADH and acetyl-CoA from excessive alcohol consumption leads to changes in liver metabolism
- Fatty liver
- Alcoholic hepatitis
- Alcoholic cirrhosis

Disulfiram
for the treatment of alcohol dependence
- Inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase
- If patients drinks alcohol acetaldehyde will accumulate –> hangover symptoms

metabolic results due to alcohol consumption
- lactic acidosis
- urate crystal accumulate in tissues producing gout
- hypoglycaemia
- fatty liver
how does alcohol oxidation lead to lactic acidosis
- decrease in NAD+/NADH ratio
- inadequate NAD+ for conversion of lactate to pyruvate
- lactate accumulates in the blood
- lactic acidosis
how does alcohol oxidation lead to gout
- decrease in NAD+/NADH ratio
- inadequate NAD+ for conversion of lactate to pyruvate
- lactate accumulates in the blood
- kidnesy ability to excrete uric acid reduced
- urate crystals accumulate in tissues producing gout
how does alcohol oxidation lead to hypoglycaemia
- decrease in NAD+/NADH ratio
- inadequate NAD+ for conversion of lactate to pyruvate
- lactate accumulates in the blood
- inadequate NAD+ for glycerol metabolism
- deficit in gluconeogenesis
- hypoglycaemia


