Labor & Delivery Flashcards
Review fetal presentation, stages of labor, procedures during labor, pain control, and complications.
What is fetal presentation?
The position of the fetus in the uterus.
What is breech presentation?
The buttox or feet are the presenting part in the client’s pelvis.

What is vertex presentation?
The back of the head (occipital) is the presenting part in the client’s pelvis.

What is face presentation?
The front of the head (mento) is the presenting part in the client’s pelvis.

What is shoulder presentation?
The shoulder is the presenting part in the client’s pelvis.

Fetal presentation has 3 letters in it.
Q: What does the first letter indicate?
The first letter of a fetal presentation can be L or R.
- This means that the presenting part in the mom’s pelvis can be facing the left or right.
Fetal presentation has 3 letters in it.
Q: What does the second letter indicate?
The second letter of a fetal presentation can be O, M, or S.
This means that the presenting part in the mom’s pelvis can be the:
- O: occipital - the back of the baby’s head
- M: mento - the face
- S: sacrum - the buttox
Fetal presentation has 3 letters in it.
Q: What does the third letter indicate?
The third letter of a fetal presentation can be A, P or T.
This means that the presenting part in the mom’s pelvis can be:
- anterior: facing the front of the mom’s body
- posterior: facing the back of the mom’s body
- transverse: facing either side of the mom’s body
What fetal presentation is this?

Right occipitoposterior or ROP

The back of the head (occipito) is in the right side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the back of the mom’s body (posterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Left occipitoposterior or LOP

The back of the head (occipito) is in the left side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the back of the mom’s body (posterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Right occipitoanterior or ROA

The back of the head (occipito) is in the right side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the front of the mom’s body (anterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Left occipitoanterior or LOA

The back of the head (occipito) is in the left side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the front of the mom’s body (anterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Left mentoanterior or LMA

The face (mento) is in the left side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the front of the mom’s body (anterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Right mentoposterior or RMP

The face (mento) is in the right side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the back of the mom’s body (posterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Left sacrum anterior or LSA

The sacrum is in the left side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the front of the mom’s body (anterior).
What fetal presentation is this?

Left sacrum posterior or LSP
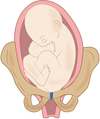
The sacrum is in the left side of the mom’s pelvis and is facing the back of the mom’s body (posterior).
What is the most common and desirable fetal presentation for delivery?
LOA = left occipital anterior
This is the easiest position for delivery of baby.

Where should the fetoscope be placed to hear fetal heart tones best?

On the upper back of the baby.

What is fetal station?
Fetal station is how many centimeters the fetus is above or below the ischial spines.

What is true labor?
- contractions are regular
- contractions are getting more frequent and closer together
- cervical dilation is progressing
What is false labor?
- contractions are irregular
- contractions go away when walking or drinking water
False labor contractions are also called Braxton-Hick contractions.
What is a normal fetal heart rate?
110 - 160 beats/minute
What is fetal bradycardia?
< 110 beats/minute for at least 10 minutes.
What is fetal tachycardia?
> 160 beats/minute for at least 10 minutes or longer.
Interventions:
Fetal bradycardia or tachycardia
- position mom on left side
- give 7 - 10 liters of oxygen by face mask
- get vital signs
- call HCP
What are the 4 stages of labor?
- labor
- pushing and birth of baby
- delivery of placenta
- recovery
What are the 3 parts of the first stage of labor?
- Latent stage
- Active stage
- Transition stage
What is the latent stage of labor?
- mild intensity
- cervical dilation of 1 - 4 cm
- contractions are every 15 - 30 minutes and last 15 - 30 seconds
What is the active stage of labor?
- moderate intensity
- cervical dilation of 4 - 7 cm
- contraction are every 3 - 5 minutes
- contractions last for 30 - 60 seconds
What is the transition stage of labor?
- severe intensity
- cervical dilation of 8 - 10 cm
- contractions are every 2 - 3 minutes
- contractions last for 45 - 90 seconds
How long does the recovery stage last for?
Recovery stage lasts for 1 - 4 hours.
What are the general interventions for all the stages of labor?
- maternal and fetal vital signs
- IV fluids
- contraction monitoring
- basic comfort and pain control
Why would local anesthesia be used during labor?
Local anesthesia would be used in the perineal area if the laboring client has to get an episiotomy.

What is an episiotomy?
An episiotomy is a surgical cut of the perineum to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through.

What are the interventions after an episiotomy?

-
decrease swelling and discomfort
- apply ice packs
- sitz baths
- analgesic spray or ointment
- prevent constipation
-
take showers instead of baths
- baths increase the risk of infection
What is a lumbar epidural block?
When a catheter is placed in the lumbar region to deliver pain meds continuously during labor.

Interventions:
Lumbar epidural block

- monitor for hypotension
- increase IVF for hypotension
- monitor for bladder distention
The nerve that controls blood pressure and bladder control may get blocked.
What is a subarachnoid spinal block?
Pain medication is administered once in the spine with a needle right before birth.
Interventions:
Subarachnoid spinal block
-
lie flat 8 - 12 hours after injection
- to prevent leakage of fluid and headache
-
monitor for hypotension
- increase IVF for hypotension
The nerve that controls blood pressure may get blocked.
What opioid pain medicines can be given to a laboring woman?
- hydromorphone
- meperidine
- fentanyl
Side effects and nursing considerations:
Opioid pain meds during labor
- assess for decreased respirations and hypotension
- don’t give to client with history of opioid dependence
- antidote is naloxone
What is induction?
Induction is medications that are given to quicken the laboring process.
What classifications of meds would be given for induction?
- Prostaglandins - misoprostol
- Uterine stimulants - oxytocin
What is an amniotomy?
An amniotomy is when the amniotic membranes are ruptured using a hook to quicken the labor process.

What are the assessments after an amniotomy?

- assess for prolapsed cord
- assess for meconium-stained fluid
- assess for bloody fluid
- may indicate abruptio placenta or fetal trauma
- assess for bad odor
- may indicate infection
What is external rotation?
External rotation is manipulating the fetal position by pressing on the mom’s abdomen.
It is done to get the baby in a more favorable position for labor.
What is a cesarean delivery?
Cesarean delivery is an abdominal incision is made through the uterus to deliver the baby.
What are the interventions before a Cesarean delivery?
- informed consent is signed
- maternal and fetal vital sign monitoring
- start IV fluids
- insert foley
What are the interventions after a Cesarean delivery?
- assess for bleeding and infection
- encourage ambulation to prevent DVT
- encourage turning, coughing and deep breathing to prevent pneumonia
- pain control
- promote bonding
What is PROM?
PROM is premature rupture of the membranes before 37 weeks’ gestation.
Client will report continuous vaginal wetness. Have her report to hospital as soon as possible for delivery.
Interventions:
PROM
- check nitrazine test to see if it’s positive for amniotic fluid
- no vaginal exams - increases the risk of infection
Immediate complication
What is a prolapsed umbilical cord?
A prolapsed umbilical cord is when the umbilical cord drops through the open cervix into the vagina ahead of the baby.

The cord can then become trapped against the baby’s body during delivery.
Interventions:
Prolapsed umbilical cord
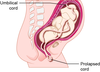
- elevate any parts that are lying on the cord with a gloved hand
- put mom in extreme Trendelenburg position
- give oxygen 8 - 10 L/minute by mask
- prepare for immediate birth
What is placenta previa?
Placenta previa is when the placenta has grown over the cervix.

What are the characteristic signs of placenta previa?

painless, bright red bleeding
Interventions:
Placenta previa

- maternal vital signs and fetal monitoring if there is excessive bleeding
- no vaginal exams
- bed rest
Immediate complication
What is abruptio placenta?
Abruptio placenta is when the placenta has separated off the uterine wall.

What are the characteristic signs and symptoms of abruptio placenta?

- severe pain and dark red blood
- rigid and tender uterus that doesn’t fully relax between contractions
Interventions:
Abruptio placenta
- cesarean delivery if baby is not coming out immediately
- blood transfusion to mom
Describe:
Vena cava syndrome
Vena cava syndrome is is another word for supine hypotension syndrome.
It is not a medical emergency, but interventions are required. It is when the mom is laying on the vena cava and cutting off circulation to the baby.
What are the characteristic signs and symptoms of vena cava syndrome?
- hypotension
- lightheadedness
Interventions:
Vena cava syndrome
- put mom on left side
- or put mom with a pillow under one side of the hips
This position gets pressure off the vena cava.
What is the gestational age of preterm labor?
Between 20 - 37 weeks of gestation
Medications:
Preterm labor
-
give tocolytics to prevent labor
- magnesium sulfate
-
give steroids to increase production of surfactant to fetal lungs
- betamethasone or dexamethasone
Describe:
Dystocia
Dystocia is a difficult labor that is prolonged or painful.
It is caused by a large fetus, position of fetus or the mom’s pelvis shape.
Describe:
Amniotic fluid embolism
Immediate complication
Amniotic fluid embolism is when an embolism can lead to respiratory failure and bleeding.
Interventions:
Amniotic fluid embolism
- give oxygen, possible intubation, and ventilator
- cesarean delivery once the mom is stabilized
Signs and symptoms:
Fetal distress
Immediate complication
- fetal heart rate is < 110 or > 160 beats/minute
- meconium-stained amniotic fluids
- fetal hypo or hyperactivity
- severe variable or late decelerations
Describe:
Intrauterine fetal demise
Intrauterine fetal demise is when the baby dies in utero.
Interventions:
Intrauterine fetal demise
- assess mom for DIC (bleeding and clotting disorder)
- emotional support
What is “VEAL CHOP”?
VEAL CHOP is an acronym to remember fetal heart rate pattern changes.
The order of the letters in VEAL correlates to accelerations or decelerations and the letters in CHOP help you remember the cause of each fetal heart rate change.
What do the letters “VEAL CHOP” stand for?
-
Variable decelerations in baseline fetal heart rate
- Cord is compressed
-
Early decelerations of fetal heart rate
- Head is compressed
-
Accelerations of fetal heart rate
- O: everything is OK
-
Late decelerations:
- Placenta is compressed
What type of fetal heart rate decelerations are these?

Variable decelerations caused by cord compression.
There is an abrupt decrease in fetal heart rate. They have a U, V or W shape. Can occur at any time during contraction cycle. Can be an emergency if fetal heart rate declines to less than 70 beats/minute.
What type of fetal heart rate decelerations are these?

Early decelerations caused by head compression.
There is a gradual decrease in fetal heart rate and a return to baseline associated with contraction. This is a normal finding.
Immediate complication
What type of fetal heart rate decelerations are these?

Late decelerations caused by placenta compression.
There is a gradual decrease in fetal heart rate. The lowest heart rate occurs after the contraction peak.
Immediate complication
What are the general interventions if the mom or baby is having life-threatening distress during labor?
- put mom in Trendelenburg position
- give oxygen 8-10 liters by mask
- give IV fluids
- blood transfusion if needed
- prepare for cesarean delivery
What is a fetal scalp electrode?
A fetal scalp electrode is a spiral wire placed directly on the fetal scalp or presenting part used to measure and record a very accurate fetal heart rate.
They are placed when there is a non-reassuring fetal heart rate.


