Lab Nine Flashcards
(21 cards)
How are the testes suspended within the scrotum?
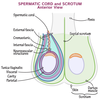
The testes are suspended by the spermatic cord within the scrotum.
Where do the testes pass through as they descend?
The testes pass through the inguinal canal of the abdominal wall as they descend.

How does connective tissues divide a testicle?
Connective tissue divides a testicle into lobules which contain seminiferous tubules.

What is the name of the highly coiled tube located on the surface of the testicle?
The epididymis.

Where can you find the dartos muscle and what is its function?
The dartos muscle can be found in the wall of the scrotum. Its main function is to regulate the temperature of the testicles by expanding or contracting to wrinkle the scrotal skin. Contraction reduces the surface area available for heat loss, thus reducing heat loss and warming the testicles.

What is the sensitive, cone-shaped end of the penis called?
The glans penis.

Describe the function of the corpora cavernosa?

The corpora cavernosa are a pair of dorsal erectile bodies that make up most of the penis. Their proximal ends form the crura of the penis. Each crus is surrounded by an ischiocavernous muscle and anchors the penis to the pubic arch of the bony pelvis. The corpora cavernosa extend distally along the length of the penis as far as the glans.

Which cells found in the epithelial lining of seminiferous tubules give rise to sperm cells?
Spermatogenic (stem) cells give rise to sperm cells.

What are undifferentiated sperm cells called?
Undifferentiated sperm cells are called spermatogonia.

What is the name of the process by which sperm are formed?
Spermatogenesis.

How many chromosomes are normally present in sperm cells?
Normally there are 23 chromosomes present in sperm.

When do sperm cells undergo maturation?
Sperm cells undergo maturation when they are stored in the epididymis.

How many chromosomes are found in secondary spermatocytes and spermatozoa?
There are 23 chromosomes found in both spermatocytes and spermatozoa.

What is the function of Sertoli cells in seminiferous tubules?
Sertoli cells have five main functions:
- Maintenance of the blood-testis barrier
- Support of spermatogenesis (formation of sperm cells)
- Support of spermiogenesis (maturation of spermatids into sperm cells)
- Secretion of inhibin
- Secretion of androgen-binding protein

What is the function of interstitial Leydig cells?
Loose areolar connective tissue fills the external spaces around the seminiferous tubules and within this space are blood vessels and large interstitial cells of Leydig. These cells produce male sex hormones, the most abundant and important being testosterone.

What kind of epithelium lines the epididymis?
The epididymis is lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells, Some of these columnar cells exhibit long, non-motile stereocilia on their apical surface. These structures absorb excess testicular fluid and pass nutrients to the sperm that are found in the lumen of the tubules.

What is the function of the epididymis?
The epididymis has three main functions:
- Monitors and adjusts the composition of the fluid within the tube
- Acts as a recycling centre for damaged spermatozoa
- Stores spermatozoa and facilitates their functional maturation

Describe the anatomical relationships between the ampulla of the ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, and the prostate gland.
Just before the ductus deferens reaches the prostate gland, it becomes enlarged and the expanded portion is called the ampulla. The ampulla joins the duct draining the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct. This short duct penetrates the muscular wall of the prostate gland and empties into the prostatic urethra.

Describe the function of the seminal vesicles.
These glands contribute to approximately 60% of the volume of semen. The secretion is a yellowish, viscous alkaline fluid. It contains a lot of fructose which is metabolized by spermatozoa to produce ATP. Thus, the spermatozoa become mobile. The secretion also contains ascorbic acid, coagulating enzymes (clotting proteins), and prostaglandins.

Describe the function of the prostate gland.
The prostate gland produces a weakly acidic secretion that contributes to approximately 20-30% of the volume of semen. This fluid is milky and is a nutrient source (citrate) that also contains enzymes. Thus, the secretions of this gland also play a role in activating the sperm. The enzymes are important regarding the internal environment of the vagina. The secretion contains seminalplasmin, an antibiotic.

Describe the function of the bulbourethral or Cowper’s glands.
These glands secrete a clear, thick, sticky alkaline mucus that helps to neutralize any urinary acids that may be remaining in the urethra. This secretion also provides lubrication of the urethra for the passage of semen for the tip of the penis during intercourse.



