Lab final now son! Flashcards
(182 cards)

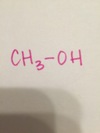
methyl alcohol
What should you do if something gets in your eye?
Remember that the first aid you give yourself is critical. Every second counts dont forget to help your neighbor- your neighbor cant see! Hold the eyelid open while flushing the eye with water from the eyewash for about 15 minutes and then see a doctor immediately.
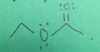
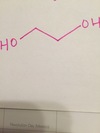
draw structure
Biphenyl
neutral

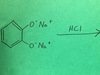
What are the inorganic compounds used in the solubility experiment?
Water - H2O
what is the formula to calculate molality?
m=moles of solute/kg of solvent

trans-cinnamic acid
weak acid
Who should be called immediately for assistance in case of an accident or injury in the laboratory?
The lab instructor. If for some reason the laboratory instructor is away then the laboratory assistant or a staff member.



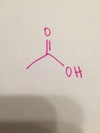
salicylic acid
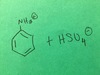
draw structure
Hexane
base


succinic acid
How can you eliminate the possibility of your Bunsen burner becoming a fire hazard?
It should be burning only when it is being used. It should be carefully positioned so that the flame will not burn overhanging shelves, books, paper, or its own tubing. No flammable chemicals should be in the vicinity

cyclohexene

acetanilide
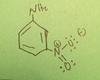
draw structure
3-nitrophthalic acid
weak acid

what ORGANIC material was used in the Distillation Lab?
Isopropyl Alcohol
n-Butyl Alcohol
Methyl Alcohol
Sec-Butyl Alcohol
n-Amyl Alcohol
n-Hexyl Alcohol
What is the melting point range of a pure sample?
a pure sample exhibits a melting point range of a one to three degree difference between the point at which the first crystal begins to melt, and the temperature at which the last crystal is completely melted.
draw structure
o-xylene

Describe how to distinguish an open fire in the laboratory.
Discharge small fire extinguisher at base of flames slowly and systematically moving from one side to the other to avoid flashback while calling for assistance. If not immediately brought under control have fire department called while using larger back-up extinguishers and evacuating nonparticipants. Do not stay in the laboratory if fire continues to spread.

carbon disulfide
When does boiling occur?
when vapor pressure and atmospheric pressure are equal
Define Azeotrope.
a constant boiling mixture of two or more components with a definite composion usually boiling below the lowest boiling point or sometimes above the highest boilng point but never inbetween
draw structure
ethyl acetate