Lab (Areas of the Brain) Flashcards
(11 cards)
Dura
Outermost layer of the meninges; intracanial dura mater is attached to the crainum; spinal dura mater forms a sac

Arachnoid
Thin meningial layer that lines and is attached to dura mater; interconnected with with pia mater by arachnoid trabeculea

Pia
Innermost/thinnest layer of meninges; attached to surface of CNS and arachnoid trabeculea

Falx Cerebri
sickle shaped dural septum between the two cerebral hemispheres

Falx Cerebelli
the smaller of the two folds of dura mater separating the hemispheres of the brain that lies between the lateral lobes of the cerebellum

Tentorium Cerebelli
Dural septum between cerebellum and the inferior sufaces of the occipital lobe and temporal lobes

Diaphragma sellae
Small dural septum that covers the pituitary fossa

Superior Sagittal Sinus
A prominent venous sinus in the attached edge of the flax cerebri
Venous blood traveling posteriorly in this sinus meets up with blood from the straight sinus at the confluence of the sinuses

Longitudinal Fissure
Extensive vertical cleft, oriented sagittally and occupied by the falx cerebri, separating the two hemispheres around the margin of the undivided corpus collosum
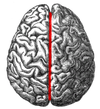
Central sulcus
Boundary between frontal and pariental lobes
Begins just medial to the superior border of the hemisphere, proceeding over its superior margin, descending obliquely forward almost to the lateral sulcus

Lateral sulcus
also called the Sylvian Fissure
Long, deep sulcus on the lateral aspect of each cerebral hemisphere resulting from downward and foward expansion of the temporal lobe during fetal development



