LAB 4: Innominate Flashcards
EVALUATION: Reset hips
Always perform prior to supine evaluation
Have supine patient bend knees, place feet flat on table, lift hips off the table, place hips back down, and extend knees back to a flat supine position

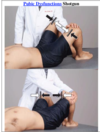
Standing flexion test EVALUATION
Patient standing, physician behind patient with eyes at level of patient’s PSIS
Contact the inferior aspect of the PSIS bilaterally. Ask patient to bend forward with hands towards toes, knees straight. Let your thumbs follow the motion of the PSIS
(+) Test = one PSIS moves farther superiorly
Indicates SI joint dysfunction on the side that elevates first
Standing flexion may be falsely positive if patient has unequal hamstring length. Therefore, treat the hamstrings and then reassess
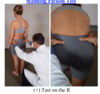
ASIS Compression test EVALUATION
Patient supine. Physician stands with dominant eye closest to the patient’s body.
Contact the ASIS bilaterally. Induce a force through the ASIS, toward the table (posteriorly and medially), alternating between the right and left hands. Note end- feel on each side.
(+) Test = “hard end-feel” or “restriction of motion” on one side
Indicates SI joint dysfunction on the side of restricted motion

PSIS height EVALUATION
Patient prone or standing
Place your thumbs on the inferior aspect of the PSIS bilaterally
Gently push cephalad and note which PSIS is more superior

ASIS height EVALUATION
Patient supine or standing
Place your thumbs on the inferior aspect of the ASIS bilaterally
Gently push cephalad and note which ASIS is more superior

Iliac crest EVALUATION
The physician places his hands on the patient’s iliac crests and evaluates the symmetry of heights of the two crests.
The physician should begin by placing the edges of his index fingers lateral and below the actual iliac crests. Then the physician slides these fingers upward and medially to come into contact with the superior aspect of the iliac crests.

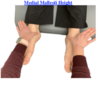
Medial malleoli height EVALUATION
Patient supine
Contact inferior aspect of medial malleoli bilaterally
Note which side is more superior
ASIS to midline EVALUATION
Patient supine
Measure the distance from the ASIS to the xyphoid or umbilicus
Note which side has an increase in distance

Pubic tubercle EVALUATION
Patient supine
Heel of hand starts at the suprapubic area.Palpate inferiorly until pubic tubercles felt on superior aspect of pubic bones. Use thumbs or index fingers to contact each pubic tubercle.
Note asymmetry (right vs left) and/or pain to palpation, assess for superior or inferior tubercle

Anterior Innominate rotation
Standing flexion/pelvic compression + on side of dysfunction
PSIS heights: superior on side of dysfunction
ASIS heights: inferior on side of dysfunction
Malleoli: inferior (long) on side of dysfunction
Iliac crest heights: even

Posterior Innominate rotation SD
Standing flexion/pelvic compression + on side of dysfunction
PSIS heights: inferior on side of dysfunction
ASIS heights: superior on side of dysfunction
Malleoli: superior (short) on side of dysfunction
Iliac crest heights: even

Superior inominate shear SD
Standing flexion/pelvic compression + on side of dysfunction
PSIS heights: superior on side of dysfunction
ASIS heights: superior on side of dysfunction
Malleoli: superior (short) on side of dysfunction
Iliac crest heights: superior on side of dysfunction
Pubic tubercle heights: superior on side of dysfunction

Inferior Innominate shear SD
Standing flexion/pelvic compression + on side of dysfunction
PSIS heights: inferior on side of dysfunction
ASIS heights: inferior on side of dysfunction
Malleoli: inferior (long) on side of dysfunction
Iliac crest heights: inferior on side of dysfunction
Pubic tubercle heights: inferior on side of dysfunction

Outflare of innominate
Standing flexion/pelvic compression + on side of dysfunction
ASIS to midline distance: longer on side of dysfunction

Inflare of innominate SD
Standing flexion/pelvic compression + on side of dysfunction
ASIS to midline distance: shorter on side of dysfunction