L3 Financial Options Flashcards
What is a Call Option?
A contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to BUY the underlying security at a pre-specified price within a respecified period of time. Pre-spec also known as strike or exercise price.
What is a Put Option?
A contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to SELL the underlying security at a pre-specified price within a respecified period of time. Pre-spec also known as strike or exercise price.
What is the different between European and American Options?
EU can only be exercised at the expiration date of the option, but American may be exercised at any time prior to expiration date of the option.
What is the Strike/Exercise Price?
The price of the option @ the time of sale.
What is the difference between an option Buyer/Holder and an option Seller/Writer?
Buyer/Holder holds the right to exercise the option and has a LONG position in the contract. Seller/Writer sells/writes the option and has a SHORT position in the contract. Note: the buy has to pay them a premium as the long side has the option to exercise but short side has an obligation to fulfil the contract if it is exercised. i.e. insurance.
What is “At the Money”?
=
exercise price = current stock price
What is “In the Money”?
(+) An option whose value if immediately exercised would be POSITIVE.
What is “Out of the Money”?
(-) An option whose value if immediately exercised would be NEGATIVE.
Why do we use Options? (2)
Hedge: To reduce the risk by holding contracts or securities whose payoffs are (-)ively correlated with some rise exposure
Spectulate(Gamble): When investors use contracts or securities to place a bet on the direction in which they believe the market is likely to move.
Buy Call Option Payoff Diagram

Sell Call Option Payoff Diagram

Call Option Profit to Buyer
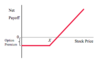
Call Option Profit to Seller
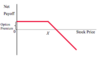
Long Put Option Payoff Diagram
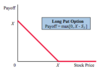
Short Put Option Payoff Diagram

Put Option Profit to Buyer

Put Option Profit to Seller

What is a Put-Call Parity
A principal that defines the relationship between the $ of European put and call options of the same class (same underlying asset, strike price and expiration date. States that simultaneously holding a short European put and long European call of the same class will deliver the same return as holding one forward contract on the same underlying asset, with the same expiration and a forward price equal to the option’s strike price. If the prices of the put and call options diverge so that this relationship does not hold, an arbitrage opportunity exists, meaning that sophisticated traders can earn a theoretically risk-free profit. Such opportunities are uncommon and short-lived in liquid market
Put-Call Parity Equation
C = P + S - PV(K)
helloo
Put-Call Parity Equation w/ DIV
C = P + S - PV(K) - PV(DIV)

What are the factors affecting Strike Price and Stock Price?
- value of a call option inc. as stock inc. All other things held constant.
- value of put option inc. as stock price dec. All other things held constant.
The longer you hold an American Option, the more valueble the option. True/False? Is this the same with European.
This is true, an american option with a later exercise date cannot be worth less than an otherwise identical american option with an earlier date.
For European this is not tru as a later exercise date can be worth less than an otherwise identical European option with an earlier exercise date.
Note that American Options cannot be worth less than its European counterpart, the may have equal value.
5 things.
What are some limitations (I guess) or features of options.
- Put option cannot be worth more than its strike price
- Call option cannot be worth more than its stock price
- American Options cannot be worth less than its European counterpart, the may have equal value.
- American option cannot be worth less than its intrinsic value
- American option cannot have a negative time value i.e. diff bet option $ and intrinsic value.
Does the value of an option generally increase with the volativity of the stock?
Yes :)





