L15, 16 & 17: Fertilisation and Embryology Flashcards
Embryo vs Fetal period?
Embryo = first 8 weeks
Fetal = 9 weeks to birth
What is a teratogen?
Agents which upset embryological development, e.g. chemical agents, radiation, viruses
Describe the process of fertilisation?
Occurs in the ampulla of the uterine tube.
- Acrosome reaction: Sperm penetrates zona pellucida via action of proteolytic enzymes. Sperm fuses with oocyte.
- Fusion triggers calcium waves. Blocks polyspermy. Calcium waves cause release of cortical granules that release enzymes that:
- Digest binding sites on oocyte
- Make zona resistant to proteolytic enzymes
What are the results of fertilisation?
- Zygote formed
- Sex determined
- Diploidy destored
- Initiation of cleavage (mitosis) to form blastomere stage.
Describe the process of cleavage.
Occurs after fertilisation.
Zygote undergoes a series of mitotic divisions as it travels towards the uterus.
After 96 hours, the morula is formed - a compact ball of cells.
After 6 days, the implanted blastocyst is formed.

What is the function of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump in the blastocyst?
Pump brings Na+ into the blastocyst, which draws in water causing it to swell.
Two regions form:
Outer trophoblast - forms the foetal part of placenta
Inner cell mass (ICM) - forms the embryo
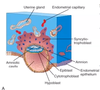
Describe the process of implantation.
Blastocyst makes contact with endometrium (uterus lining).
Blastocyst membrane and endometrium membrane merge to form syncytiotrophoblast. This functions to:
- Secrete hCG (maintains pregnancy by producing progesterone)
hCG is the hormonal basis of the pregnancy test.
The embryo is gradually absorbed by the endometrium, until about 10 days in when it is fully implanted.
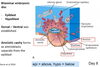
Describe the formation of the bilaminar embryonic disc.
By day 8, the inner cell mass differentiates into two layers, known as the bilaminary embryonic disc.
- Epiblast (dorsal surface)
- Hypoblast (ventral surface)
The amniotic cavity forms as the amnioblasts separate from the epiblast.
What does the hypoblast form right after the formation of the bilaminar embryonic disc?
Hypoblast forms the primary umbilical vesicle (AKA yolk sac) and later, the secondary umbilical vesicle.
The hypoblast also forms the extraembryonic mesoderm, which creates spaces that form the chorionic cavity. The embryonic disc is suspended in the chorionic cavity by a connecting stalk of extraembryonic mesoderm.
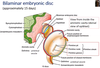
Describe the formation of the primitive streak.
Forms within the amniotic cavity.
The primite streak forms, and is composed of:
- Primitive pit
- Primitive node
- Primitive groove
What are the two little dips that form anove and below the primitive streak?
Two grooves form - the future position of the oropharyngeal and cloacal membranes.
Which body axes does the primitive streak define?
- Cranial-caudal
- Medial-lateral
- Left-right
Describe the process of gastrulation.
Gastrulation is the migration of epiblast cells through the primitive streak to form new layer of cells (Day 14).
The new layer is called the endoderm.
Around Day 16, migrating epiblast cells form the mesoderm.
Then, the remaining epiblast cells form the ectoderm.
We now have a three primary germ cell layers, made of ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.

Describe the formation of the notochord.
AS cells pass through the primitive streak to form the mesoderm, they migrate laterally and cranially in and condense in a structure to form the notochord.
The notochord stimulates:
- Formation of nervous tissue
- Formation of vertebral bodies

List some adult tissue derivatives of the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Ectoderm - Neural tube, epidermis of skin
Mesoderm - Muscular, CT of body
Endoderm - Epithelial lining of the organs