L.10 Alcohols Flashcards
Sections 1.2, 5.1 - 5.3 Organic Chemistry
Alcohols
General Form
Pka
Group
Suffix
Prefix
Priority
- ROH
- pKa = 16
- Group = hydroxyl (-OH)
- Suffix = -ol
- Prefix = Hydroxy-
- Higher priority than double or triple bonds and alkanes
- Diols = Two hydroxyls, geminal same carbon -or- vicinal if on adjacent
Structure of a PHENOL
Benzene Rings with Hydroxyl Groups

How are Phenols Named?
Phenols are named by their relative position of the hydroxyl groups with any other attached molecule.
ortho- ADJACENT
meta- SEPARATED BY 1 CARBON
para- ON OPPOSITE SIDES OF THE RING

Physical Properties of Alcohols & Phenols
Alcohols; hydrogen bonding ( F O N ) raises their boiling/melting points relative to there corresponding alkanes. Also increases solubility.
Phenols; hydrogen on the phenol is more acidic b/c the electron on the oxygen is resonance stabilized by the benzene ring. (Aromatic ring can delocalize the charge of the conjugate base)
Electron-donating groups like alkyl groups decrease acidity because they destabilize negative charges. Electron-donating groups, such as electronegative atoms and aromatic rings, increase acidity because they stabilize negative charges
Oxidation Reactions of 1°ALCOHOLS
1° Alcohols
PCC (mild oxidant) = Aldehyde
Chromium (strong) = Carboxylic Acid
Jones Oxidation CrO3 + H2SO4 + Acetone (strong) = Carboxylic Acid
Oxidation Reactions of 2º ALCOHOLS
2º Alcohols
PCC (mild) = Ketones
K/Na2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 (stong) = Ketones
CrO3 + H2SO4 + Acetone (strong) = Ketones
Oxidation Reactions of 3º Alcohols
Cannot be further oxidized
What are Mesylates & Tosylates?
Alcohols can be converted to mesylates and tosylates to make them better-leaving groups for nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Mesylates contain the functional group -SO3CH3, which is derived from methanesulfonic acid.
Tosylates contains the functional group -SOC6H4CH3, which is derrived from toluenesulfonic acid.
Explain the conversion of alcohols into protecting groups.
- Two equivalents of alcohol or a dialcohol can be reacted
with the carbonyl of an aldehyde or ketone to
form an ACETAL or KETAL respectively.
- Then, other groups in the compound can be reacted (especially by reduction with Lithium aluminum hydride ) without affecting the newly formed acetal or ketal.
- The acetal or ketal can be regenerated back to carbonyls with
catalytic acid, which is called deprotection.
How are QUINONES produced?
- Phenol + Oxidizing Agents = Quinones
- Quinones are resonance-stabilized electrophiles
- Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) & K1 (menaquinone) are examples of biochemically relevant quinones.
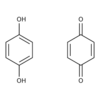
(photosynthesis + carboxylation of blood clotting factors)
What is UBIQUINONE? & How is it useful?
Ubiquinone, also known as COENZYME Q is a biologically active quinone that acts as an electron acceptor in complexes I II & III of the electron transport chain.
Thus,
It is reduced to UBIQUINOL, which is an electron carrier within the phospholipid bilayer (long alkyl chain = lipid soluble)

Can Quinones be further oxidized?
Yes, they are further oxidized to form HYDROXYQUINONES.
- Used for the synthesis of medications
- Two carbonyls + HYDROXYL GROUP
- Less electrophilic, but still very reactive
2-HYDROXY-1,4-BENZOQUINONE
(If more than one hydroxyl group then, di-, tri-, etc.)



