Khan Academy P/S Flash Cards ~Last 9 pages
________ is the way people organize themselves — bunch of people who live together in a specific geographical area, and interact more with each other than outsiders. Share a common culture over time.
Society is the way people organize themselves — bunch of people who live together in a specific geographical area, and interact more with each other than outsiders. Share a common culture over time.

- _________ = rules that guide the way people live, and _________ = structure that provides organization for people.
- _________ includes ____________, ex. family, education, politics, which all meet basic human needs. The hardware on a phone.
- _________ provides guidelines for living, ex. software or apps on a phone, constantly being updated. What makes society run.
-
Culture = rules that guide the way people live, and society = structure that provides organization for people.
- Society includes institutions, ex. family, education, politics, which all meet basic human needs. The hardware on a phone.
- Culture provides guidelines for living, ex. software or apps on a phone, constantly being updated. What makes society run.
- Culture talks about rules and instructions within a society that teach tem how to live.
- Culture refers to ideas and things passed from one generation to the next — language, customes, etc. Varies as we travel around the globe.
- Chinese and Spanish spoken all around the world
- Many like meat and vegetables, while others eat tofu and grasshoppers.
- Ways of greeting differ, ex. In Japan they bow, and the depth of bow is defined by relative status. And in Europe, men and women kiss on both cheeks.
- Culture talks about rules and instructions within a society that teach tem how to live.
- Culture refers to ideas and things passed from one generation to the next — language, customes, etc. Varies as we travel around the globe.
- Chinese and Spanish spoken all around the world
- Many like meat and vegetables, while others eat tofu and grasshoppers.
- Ways of greeting differ, ex. In Japan they bow, and the depth of bow is defined by relative status. And in Europe, men and women kiss on both cheeks.

There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
- _______ _______ _________ ___ _________: all people share culture with others in their society, provides rules and expectations for carryong out daily rituals and interactions.
There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
- People Share Culture in Society: all people share culture with others in their society, provides rules and expectations for carryong out daily rituals and interactions.
There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
- __________ ___ __________ — it evolves over time and is adaptive.
* Normal in hunter/gathers (cooperativity is encouraged) different than today’s information/technology age (individualism/competition)
- __________ ___ __________ — it evolves over time and is adaptive.
There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
-
Culture is Adaptive — it evolves over time and is adaptive.
* Normal in hunter/gathers (cooperativity is encouraged) different than today’s information/technology age (individualism/competition)
-
Culture is Adaptive — it evolves over time and is adaptive.

There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
- ________ _______ __ _______ — creation of culture is ongoing and cumulative, and societies build on existing cultures to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
* Normal values are shaped by your culture. Ex. Putting a baby in a crib is strange in other parts of the world. Culture differs around the world.
- ________ _______ __ _______ — creation of culture is ongoing and cumulative, and societies build on existing cultures to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
-
Culture Builds on Itself — creation of culture is ongoing and cumulative, and societies build on existing cultures to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
* Normal values are shaped by your culture. Ex. Putting a baby in a crib is strange in other parts of the world. Culture differs around the world.
-
Culture Builds on Itself — creation of culture is ongoing and cumulative, and societies build on existing cultures to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.

There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
- _________ ___ ___________ — from one generation to the next. We teach a way of life to the next generation. Humans are only mammals with culture to adapt to environments (to survive on equator and arctic)
There are 4 Main Points of Culture:
- Culture is Transmitted — from one generation to the next. We teach a way of life to the next generation. Humans are only mammals with culture to adapt to environments (to survive on equator and arctic)

______ ________ refers to patterns of experiences and attitudes that exist in the highest class segments of a society. This tends to be associated with wealth and formality.
High culture refers to patterns of experiences and attitudes that exist in the highest class segments of a society. This tends to be associated with wealth and formality.

____________ _________ refers to values and behaviours that are in line with larger societal norms (like avoidance of crime).
Normative Culture refers to values and behaviours that are in line with larger societal norms (like avoidance of crime).
_________ _________ refers to patterns of experiences and attitudes that exist within mainstream normative society - like attending a game or watching a parade.
Popular Culture refers to patterns of experiences and attitudes that exist within mainstream normative society - like attending a game or watching a parade.

A __________ is culture (ideas) of a _____-______ (medium) sub-community ( small community) that distinguishes itself from the larger dominant culture of larger society/community
- ___________ smaller than a nation but unlike a micro-culture, it is large enough to support people throughout their entire lifespan.
- ___________ affect your life on a longer period than a micro-culture
- _____-_______ = population size falls between micro and macro levels. They are medium sized groups such as communities, organizations, cities, states, clans, and tribes
A subculture is culture (ideas) of a meso-level (medium) sub-community ( small community) that distinguishes itself from the larger dominant culture of larger society/community
-
Subculture smaller than a nation but unlike a micro-culture, it is large enough to support people throughout their entire lifespan.
- Subcultures affect your life on a longer period than a micro-culture
- Meso-level = population size falls between micro and macro levels. They are medium sized groups such as communities, organizations, cities, states, clans, and tribes

A ______-__________ can’t support people throughout their lifespan, refers to groups/organizations only affecting a limited period of one’s life. Ex. Girl Scouts, college sororities, and boarding school.
Subcultures include ethnic groups like Mexicans or orthodox Jews, or groups like the elite upper class. Subculture can cause tension with ____________ ________-which have the power to determine the cultural expectations of society.
A micro-culture can’t support people throughout their lifespan, refers to groups/organizations only affecting a limited period of one’s life. Ex. Girl Scouts, college sororities, and boarding school.
Subcultures include ethnic groups like Mexicans or orthodox Jews, or groups like the elite upper class. Subculture can cause tension with dominant group-which have the power to determine the cultural expectations of society.

When the laws of the dominant society is violated (conflict with larger culture becomes serious), a ______________ ________. ________________: group with expectations and values that strongly disagree with the main values from the larger society. It refers to a subculture that rejects some of the larger culture’s norms and values, and usually develop their own set of norms to live by.
- Ex. Mormons believe in _________. __________ = more than one spouse (broader definition), _________ is more than one wife, __________ — woman has multpile husbands
- Ex. Old Order Amish (PA/OH) reject mainstream ideas and have their own ideas/values, reject technology and consumerism and replace with religious principles (simple lifestyle)
When the laws of the dominant society is violated (conflict with larger culture becomes serious), a counterculture results. Counterculture: group with expectations and values that strongly disagree with the main values from the larger society. It refers to a subculture that rejects some of the larger culture’s norms and values, and usually develop their own set of norms to live by.
- Ex. Mormons believe in polygamy. Polygamy = more than one spouse (broader definition), polygyny is more than one wife, polyandry — woman has multpile husbands
- Ex. Old Order Amish (PA/OH) reject mainstream ideas and have their own ideas/values, reject technology and consumerism and replace with religious principles (simple lifestyle)

Jim Goes to College Subculture
- Within a nation many smaller groups – ethnic, regional, tribal subcultures made of people who identify closely with each other. So subculture is smaller community that distinguishes itself from larger society.
- Different cities states in US may have their own unique subcultures.
- Ex. Jim, grew up in Florida his whole life, but got into university in Washington DC. Notices a lot of differences between the two. Ex. Has to parallel park, and has to pay for parking. Driving in DC not same as in Florida, much more traffic.
Jim Goes to College Subculture
- Within a nation many smaller groups – ethnic, regional, tribal subcultures made of people who identify closely with each other. So subculture is smaller community that distinguishes itself from larger society.
- Different cities states in US may have their own unique subcultures.
- Ex. Jim, grew up in Florida his whole life, but got into university in Washington DC. Notices a lot of differences between the two. Ex. Has to parallel park, and has to pay for parking. Driving in DC not same as in Florida, much more traffic.
__________ _____ is the fact cultures take time to catch up with technological innovations, resulting in social problems. Common in societies because ___________ ________ changes rapidly, while ___________ ________ resists change.
- __________ __________ refers to physical and technological aspects of our daily lives, like food and houses, and ___________ ___________ doesn’t include physical objects, like ideas/beliefs/values, which resist change.
- Example: when cars first invented, there were no laws to govern driving (no speed limits, lanes, etc). Very dangerous but laws were soon written to fix the problem. Or invention of computer and emails.
Culture Lag is the fact cultures take time to catch up with technological innovations, resulting in social problems. Common in societies because material culture changes rapidly, while nonmaterial culture resists change.
- Material Culture refers to physical and technological aspects of our daily lives, like food and houses, and non-material culture doesn’t include physical objects, like ideas/beliefs/values, which resist change.
- Example: when cars first invented, there were no laws to govern driving (no speed limits, lanes, etc). Very dangerous but laws were soon written to fix the problem. Or invention of computer and emails.

_________ ________ — feelings of disorientation, uncertainty, and even fear when they encounter unfamiliar culture practices. Ex. Moving countries or travels to another type of life (urban to rural).
- In foreign places, business is conducted differently, and food completely different.
- As a result of culture shock may feel homesick, lonely, etc.
- Sometimes see things frowned upon in own culture.
Culture Shock — feelings of disorientation, uncertainty, and even fear when they encounter unfamiliar culture practices. Ex. Moving countries or travels to another type of life (urban to rural).
- In foreign places, business is conducted differently, and food completely different.
- As a result of culture shock may feel homesick, lonely, etc.
- Sometimes see things frowned upon in own culture.

- __________ is the spread of an invention or discovery from one place to another, ex. Capitalism, democracy, and religious beliefs. Even technology and software has made a difference in how people connect with others across the globe.
- Can occur in many ways.
- Exploration, military conquest, missionary work, mass media, tourism, and the internet.
- Ex. Food in America seen all around the world — McDonalds in Asia. Spanish is one of the fastest growing languages. Or the ALS ice bucket challenge
- Diffusion is the spread of an invention or discovery from one place to another, ex. Capitalism, democracy, and religious beliefs. Even technology and software has made a difference in how people connect with others across the globe.
- Can occur in many ways.
- Exploration, military conquest, missionary work, mass media, tourism, and the internet.
- Ex. Food in America seen all around the world — McDonalds in Asia. Spanish is one of the fastest growing languages. Or the ALS ice bucket challenge

_______ _______ = dissemination of information, and how information is transmitted within a culture. Includes print media (books, music, newspaper and magazines) and digital media (TV, media, radio, and the internet). How it’s consumed changes across cultures in each group. (Ex. Older people might get their info via TV and newspaper while younger people can get it via the internet).
Mass Media = dissemination of information, and how information is transmitted within a culture. Includes print media (books, music, newspaper and magazines) and digital media (TV, media, radio, and the internet). How it’s consumed changes across cultures in each group. (Ex. Older people might get their info via TV and newspaper while younger people can get it via the internet).

According to the _____________ ___________, mass media’s main role is to provide _____________. _______________ also say mass media can act as an agent of socialization (ex. ____________ ___________ of watching Olympics on TV, and ___________ ____________ — entire internet communities) and act as an _________ ___ ________ ________.
- Also tells us what society expects of us through rewards and punishment, ex. Seeing criminals. But can also glorify behaviours that are wrong in society, like intense physical violence.
- Also functions as a promoter of consumer culture. At the turn of century average US child saw 20000 commercials a year on TV. Only increased from there, and not clear what impact this may have on next generation.
According to the functionalist perspective, mass media’s main role is to provide entertainment. Functionalists also say mass media can act as an agent of socialization (ex. Collective Experience of watching Olympics on TV, and Community Building — entire internet communities) and act as an enforcer of social norms.
- Also tells us what society expects of us through rewards and punishment, ex. Seeing criminals. But can also glorify behaviours that are wrong in society, like intense physical violence.
- Also functions as a promoter of consumer culture. At the turn of century average US child saw 20000 commercials a year on TV. Only increased from there, and not clear what impact this may have on next generation.

- The __________ ____________ on Mass Media focuses on how the media portrays and reflects and exacerbates __________ that exist in society, ex. Race/social class
- Conflict Theorists use the term _____________ to describe the process by which a small number of people and corporations control what information is presented on the media, and how they move through a series of gates before they reach the public. In some countries, this is decided by the government, in others decided by large media corporations.
- _______________ has more effect on some media than others, ex. Lots of control on big movies, but little overhead control on what’s posted online.
- Also describes how mass media reflects the dominant ideology. Often limits other views. People who make the choice – the gatekeepers are predominantly white, male, and wealthy.
- Portrayal of minorities can be stereotyped. And attempts to fix this can wrongly result in __________.
- The Conflict Perspective on Mass Media focuses on how the media portrays and reflects and exacerbates divisions that exist in society, ex. Race/social class
- Conflict Theorists use the term gatekeeping to describe the process by which a small number of people and corporations control what information is presented on the media, and how they move through a series of gates before they reach the public. In some countries, this is decided by the government, in others decided by large media corporations.
- Gatekeeping has more effect on some media than others, ex. Lots of control on big movies, but little overhead control on what’s posted online.
- Also describes how mass media reflects the dominant ideology. Often limits other views. People who make the choice – the gatekeepers are predominantly white, male, and wealthy.
- Portrayal of minorities can be stereotyped. And attempts to fix this can wrongly result in tokenism.

__________ _________ are similar to conflict theory, in that mass media misrepresents society towards the dominant ideology. Specifically, message about men and women are represented in the media. Depictions of men and women are often stereotyped, emphasizing traditional sex roles.
Feminist Theories are similar to conflict theory, in that mass media misrepresents society towards the dominant ideology. Specifically, message about men and women are represented in the media. Depictions of men and women are often stereotyped, emphasizing traditional sex roles.

____________ ___________ looks at mass media on micro-level to see how it shapes day to day behavior. How mass media blurs line between solidary and group activities – ex. watching a movie (can be watching with other people but because of societal norms/theater rules you can’t talk about it with those who you are watching with). Looks at how we connect with others using media changes over time (email/text message instead of phone, or online dating increase).
Interactionist Perspective looks at mass media on micro-level to see how it shapes day to day behavior. How mass media blurs line between solidary and group activities – ex. watching a movie (can be watching with other people but because of societal norms/theater rules you can’t talk about it with those who you are watching with). Looks at how we connect with others using media changes over time (email/text message instead of phone, or online dating increase).

Culture is typically learned through ___________, ____________, and the _____________ proponent (shaped through _____________).
Culture is typically learned through observation, interactions, and the biological proponent (shaped through evolution).

Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution — both __________ ________ and ___________ can be selected for if they contribute to the success of the species.
- Ex. For behaviours, all cultures have ways of dealing with illness/medicine/healing. Or wedding/funeral ceremonies. Language. Indicates they were selected for as human species evolved.
Charles Darwin’s Theory of Evolution — both physical traits and behaviours can be selected for if they contribute to the success of the species.
- Ex. For behaviours, all cultures have ways of dealing with illness/medicine/healing. Or wedding/funeral ceremonies. Language. Indicates they were selected for as human species evolved.

- Evolution can shape culture, but can also think of how culture can shape human evolution.
- Ex. Hunter-gatherer society vs. farming society, people moved less, and populations grew. Because of this people were more exposed to outbreaks of disease. Since only those that survived weren’t killed off, these societies have shaped our immune systems.
- Or lactose intolerance, first year of life most humans get nutrition from milk, but switched after children are weaned. But Northern Europeans which reared cattle, don’t have this effect – their lactase gene doesn’t turn off. So those able to digest milk more likely to survive.
- Evolution can shape culture, but can also think of how culture can shape human evolution.
- Ex. Hunter-gatherer society vs. farming society, people moved less, and populations grew. Because of this people were more exposed to outbreaks of disease. Since only those that survived weren’t killed off, these societies have shaped our immune systems.
- Or lactose intolerance, first year of life most humans get nutrition from milk, but switched after children are weaned. But Northern Europeans which reared cattle, don’t have this effect – their lactase gene doesn’t turn off. So those able to digest milk more likely to survive.
The resources in society are unevenly distributed. Ex. Wealth un the U.S, top 20% have 72% of the wealth of the country and bottom 20% only control 3%.
- Upper, middle, and lower class. based incomes.
- As you go up the social ladder, have better access to education, healthcare, and housing.
The resources in society are unevenly distributed. Ex. Wealth un the U.S, top 20% have 72% of the wealth of the country and bottom 20% only control 3%.
- Upper, middle, and lower class. based incomes.
- As you go up the social ladder, have better access to education, healthcare, and housing.

Overview of Social Inequality
- There are groups of population that are disproportionally affected by social inequality — _______/______ _____________ have greater degrees of inequality as manifested by lower incomes, lower education, and reduced access to healthcare.
- Those in poverty also face considerable barriers to obtaining the same healthcare, education, and other resources as others.
Overview of Social Inequality
- There are groups of population that are disproportionally affected by social inequality — ethnic/racial minorities have greater degrees of inequality as manifested by lower incomes, lower education, and reduced access to healthcare.
- Those in poverty also face considerable barriers to obtaining the same healthcare, education, and other resources as others.

Overview of Social Inequality
- Gender does too. Females experience differences in pay (_______-___ ____), and the _______ _______ _______ (poorly represented in higher positions in companies)
- People may feel increasingly ________ ________, live in ____________ ____________, and feel _____________ ______________.
- Can lead to civil unrest, and tempt people into criminal activities.
Overview of Social Inequality
- Gender does too. Females experience differences in pay (gender-pay gap), and the glass ceiling effect (poorly represented in higher positions in companies)
- People may feel increasingly socially excluded, live in segregated neighborhoods, and feel politically disempowered.
- Can lead to civil unrest, and tempt people into criminal activities.

Overview of Social Inequality
- Ways to help: __________ ________ (ex. Food Stamps), improve _______ ___ _________/___________, and figure out social interventions that allow ___________ ___ __________.
- Health disparity: difference in health outcome that is closely related to social and economic factors. Social inequality causes the difference, not a iological one.
Overview of Social Inequality
- Ways to help: government schemes (ex. Food Stamps), improve access to education/healthcare, and figure out social interventions that allow integration to society.
- Health disparity: difference in health outcome that is closely related to social and economic factors. Social inequality causes the difference, not a iological one.

- We have a number of of ways to break down society into social layers, ex. Classes.
- Lower class — manual work, labour, low-paying jobs.
- Middle class — professionals, better paying jobs.
- Upper Class — very wealthy businessmen and family wealth
- Correlates to amount of income.
- We have a number of of ways to break down society into social layers, ex. Classes.
- Lower class — manual work, labour, low-paying jobs.
- Middle class — professionals, better paying jobs.
- Upper Class — very wealthy businessmen and family wealth
- Correlates to amount of income.

- When we think of ________ ___________, can there be movement? Yes. Various ways.
- Individual can move ____________/___________ mobility — move within the same class. Ex. Accountant switches job to different accounting company.
- ________ ____________ / mobility — move up or down the social hierarchy. Ex. Manager at restaurant becomes CEO of fast food restuarant. But if he gets demoted to serving food, he falls downward.
- When we think of social positions, can there be movement? Yes. Various ways.
- Individual can move horizontally/horizontal mobility — move within the same class. Ex. Accountant switches job to different accounting company.
- Verical movement / mobility — move up or down the social hierarchy. Ex. Manager at restaurant becomes CEO of fast food restuarant. But if he gets demoted to serving food, he falls downward.

There are various types of social constructs that allow for social mobility.
- _______ ________ — very little social mobility, becuase your role is determined entirely by background you are born to and who you’re married to. A lot of social stability. Ex. The Hindu Caste system.
There are various types of social constructs that allow for social mobility.
- Caste System — very little social mobility, becuase your role is determined entirely by background you are born to and who you’re married to. A lot of social stability. Ex. The Hindu Caste system.
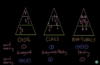
There are various types of social constructs that allow for social mobility.
- _______ ________ — allows for degree of social mobility, combination of background and movement, often by education. Less stability.
There are various types of social constructs that allow for social mobility.
- Class System — allows for degree of social mobility, combination of background and movement, often by education. Less stability.

There are various types of social constructs that allow for social mobility.
- ____________ — concept that people achieve social position soley based on ability and achievements. Highly idealized. Birth/parental background doesn’t matter. Extreme social mobility.
- Social rewards, status, position are awarded to individuals based on their own ability to work (_______). In order for a _____________ to operate, everyone within the society would need the same opportunity to succeed, so that rewards are actually based (primarily) on _______.”
There are various types of social constructs that allow for social mobility.
-
Meritocracy — concept that people achieve social position soley based on ability and achievements. Highly idealized. Birth/parental background doesn’t matter. Extreme social mobility.
- Social rewards, status, position are awarded to individuals based on their own ability to work (merit). In order for a meritocracy to operate, everyone within the society would need the same opportunity to succeed, so that rewards are actually based (primarily) on merit.”

If a change in social class happens in a person’s own lifetime – ______________ _________.
If a change in social class happens in a person’s own lifetime – intragenerational mobility

________________ ________ — change in social class between generations, ex. Parent is working class and son is working class.
Intergenerational Mobility — change in social class between generations, ex. Parent is working class and son is working class.