javascript Flashcards
(81 cards)
how node treat module files
node never process the .js file directly, it wraps the module as a function and pass it to the chrome v8 engine
what’s the global object in node.js
global
what’s the global object in chrome
window; document
naming convention for class
ClassName
same folder path in require; parent folder path in require statement
same folder ./xxx(.js) parent folder ../xxx(.js)
how to load a module
require(‘’)
EMACscript 6 fancy string function is called?
Template String
the node.js built in packages
path os fs http events ( class: EventEmitter; methods: emit & on )
Since events package provides an EventEmitter class (not an instance), what needs to be paid attention when working on the events?
the actual registering event and emit event action need to be based
what makes the function become the special constructor function inside a class defination
give the function name as ‘constructor’, then it will work with the new key word
what the class sytax sugar does
- generating the function that 1) has the name of the class given and 2) coding block as the constructor method - attach all other attributes to the .prototype attribute of the function with class name
is most of the javascript keyword little cap
yes (new, function, class, cnst…)
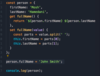
how to inheriant from another class when defining an class
using ‘extends’ keyword
singular module returning object
module.exports =
is module global?
it is actual a local variable that node.js passed into the wrapped function of the module
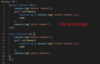
how to see the wrapped function of the module
set a syntax error in the very 1st line of a module like ‘var =;’ and then require it somewhere else
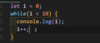
how to set async spin over certain time interval
- return a new Promise 2. Inside the promise, define another async function 3. Inside the function, if goal reached, then resolved; if not, use setTimeout to sell the call again. (*** The async function is within the ‘new Promise’, so whenever it resolved, the same promise instance resolved) 4. Call the async function manuallyafter defination
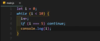
how to set parameter’s default value
constructor ({ keyId, secretKey, paper = true, bucketPct = 0.25 }) { … }
var scope situation
var only socpe to either functional scope or global scope (window or global object)
let and const sope
they scope to the block scope (curly brackets)
what is Hoisting in JS
variable can be used before the definition. (hoisting means moving all declarations to the top of the current scope
what is a primitive type in JS
it is not an object and has no methods
primitive types are immutable, how to approve it
you can not use an string method to alter e.g. toUpperCase the data itself (on the other side, the array method e.g. push can alter the array); the string method can then only manipulate the return value
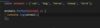
what is Symbol in JS
Symbols are often used to identify object properties.Often to avoid name clashing between properties, since no symbol is equal to another; No two symbols are the same ‘===’