Java Flashcards
Diagram of the exception hierarchy
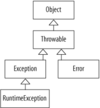
What are the 3 categories for exceptions and errors
CUE
- Checked Exceptions - Checked at compile time.
- Unchecked Exceptions - Usually programmer error. RuntimeException and subclasses.
- Errors - Not checked at compile time, but can be caught. E.g., AssertionError, ExceptionInInitializeError, OutOfMemoryError
What is a required when you create a try block?
A try block must have at least one catch or finally block
Describe the 4 different access modifiers
- public
- protected - subclass and package
- *default (package) - *package only
- private
What are the two ways to create a thread?
Either by extending java.lang.Thread or by implementing java.lang.Runnable
How do you create a thread using java.util.Thread
class Comet extends Thread {
public void run( ) {
System.out.println("Orbiting");
orbit( );
}
}
Comet halley = new Comet( );
How an example of implementing the Runnable interface
class Asteroid implements Runnable {
public void run( ) {
System.out.println("Orbiting");
orbit( );
}
}
Asteroid maja = new Asteroid( ); Thread majaThread = new Thread(maja);
Name the 6 thread states
NEW - A thread that is created but not started
RUNNABLE - A thread that is available to run
BLOCKED - An “alive” thread that is blocked waiting for a monitor lock
WAITING - An “alive” thread that calls its own wait( ) or join( ) while waiting on another thread
TIMED_WAITING - An “alive” thread that is waiting on another thread for a specified period of time; sleeping
TERMINATED - A thread that has completed
Describe thread priorities
The valid range of priority values is typically 1 through 10, with a default value of 5.
Lower priority threads yield to higher priority threads.


