Janis Notes Flashcards
(436 cards)
Define Maffucci’s syndrome.
Enchondromatosis associated with multiple cutaneous hemangiomas.
Indications for Mohs micrographic surgery (5).
- Recurrent
- Cosmetically sensitive (periorbital, periauricular, perinasal)
- Morpheaform and sclerosing or aggressive features
- Poorly delineated margins in scar tissue
- Other tumor types: SCC with perineural involvement, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, microcystic adnexal carcinoma.
Define Nevus of Ota.
Nevus of Ota: Onset at birth or less than 1 year and around puberty. Found more commonly in blacks and Asians. Blue-brown, unilatreal, periocular macula. Size varies from few cm to covering half the face. Areas follow distribution of V1 and V2.
Describe Tessier Cleft Number 5.
Tessier Cleft Number 5.
One liner: Cleft begins lateral to the canine and courses lateral to infraorbital foramen terminating in the lateral aspect of lower eyelid and orbital floor.
Soft tissue:
- Begins medial to oral commisure and courses along the cheek lateral to the nasal ala
- Terminates in the lateral half of the lower eyelid
Skeletal involvement:
- Begins lateral to the canine.
- Courses lateral to infraorbital forarmen
- Terminates in the lateral aspect of the orbital floor and rim.
- Lateral orbital wall possibly thickened and greater wing of sphenoid abnormal.

Risk of malignant transformation with congenitcal nevocytic nevi.
- Small (<1.5 cm^2): 1-5% lifetime risk (rarely before puberty).
- Medium (1.5 - 20 cm^2): uncertain (rarely before puberty).
- Giant (> 20 cm^2): 5-10% result in melanoma with 50% arising between the age of 3-5 years old.
Risk factors (11) for recurrence of BCC and SCC.
- Location/size: >20 mm on trunk/extremities; >10mm cheek, forehead, scalp, neck; >6mm central face, genitalia, hands, feet.
- Poorly defined borders.
- Recurrent lesion.
- Immunopsuppresion
- Previous radiotherapy.
- Pathology: morpheaform, sclerosing, micronodular, mixed infiltrative, adenoid, desmoplastic
- Perineural involvement
- Lymphovascular invasion
- Radpidly growing
- Depth: >2mm, Clark IV and V
- Poorly differentiated
Timing of normal suture fusion.
- Metopic: 6-8 months.
- Sagittal: 22 years.
- Coronal: 24 years.
- Lambdoidal: 26 years.
Risk factors for tetanus (5).
- Time since injury (>6 hours)
- Depth of injury (>1 cm)
- Mechanism of injury (crush, burn, GSW, puncture)
- Presence of devitalized tissue
- Contamination (grass, soil, saliva, retained foreign body)
Treatment of phenol burns.
Irrigate and treat with polyethylene glycol.
Define Parkes Weber syndrome.
- Similar to Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome (patchy port-win stain on an extremity overlying a deeper venous and lymphatic malformation with associated skeletal hypertrophy).
- Distinguished by the prescence of an arteriovenous fistula.
Steps to PIP contracture release after Dupuytren’s disease excision and continued stiffness.
- Chein rein ligament release.
- Volar capsulomtomy.
- Collateral ligament release.

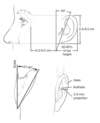
Name two otoplasty techniques for addressing lower third prominence.
- Modified fishtail excision of lobule (Wood-Smith)
- Inferior conchal mastoid sutures

Horizontal (5) and vertical buttresses (4) of the face.
HORIZONTAL BUTRESSES
- Frontal bar
- Inferior orbital rim / upper transverse maxillary
- Maxillary alveolar and hard palate / lower transverse maxillary
- Mandibular alveolar / upper transverse mandibular
- Inferior border of mandible / lower transverse mandibular
VERTICAL BUTTRESSES
- Zygomaticomaxillary / lateral maxillary / lateral buttress
- Nasomaxillary / medial maxillary / medial buttress
- Pterygomaxillary / posterior maxillary / deep buttress
- Vertical mandible / posterior verticle

Describe ‘Stahl’s ear’.
The presence of the third and/or horizontal superior crus with a pointed upper helix. Results in upper and middle third prominence.

Describe the intracranial, cranial, orbit, midface, and extremity findings in Apert syndrome.
- Intracranial: elevated ICP.
- Cranial: bicoronal synostoses with turribrachycephaly, enlarged anterior fontanel, bitemporal widening, occipital flattening.
- Orbits: exorbitism, downslanting palpebral fissures, and mild hypertelorism.
- Midface: hypoplasia, parrot beak deformity, high arch or cleft palate, anterior open bite, class III malocclusion.
- Extremity: Complex syndactyly of hands and feet.

Treatment of hydroflouric acid burns.
Calcium gluconate.
Surgical management of trigonocephaly (metopic synostosis).
Overcorrection of frontal dysmorphology and bitemporal contriction with bifrontal craniotomy, frontal reshaping and expansion of frontoorbital bar and frontal bone flaps with interpositional bone graft, wedge osteotomies, bone grafting.
Alkali burns cause what time of injury.
Liquefactive necrosis.
Where is Stenson’s duct located intraorally?
Opposite the second maxillary molar.
Describe the cranial, extremity, and other findings of Muenke syndrome.
- Cranial: uni or bicoronal synostosis.
- Midface: typically no hypoplasia.
- Extremities: Thimble like hypoplasia.
- Other: sensorineural hearing loss.
Describe Tessier Cleft Number 30.
Tessier Cleft Number 30
One liner: Mandibular cleft originating between the central incisors and extending inferiorly, yielding notching of the lower lip and a bifid tongue.
Soft tissue:
- Notch in lower lip
- Bifid anterior tongue with attachment to mandible by dense fibrous band.
Skeletal involvement:
- Cleft between central incisors extending into mandibular synthesis
- Hyoid bone may be absent
- Thyroid cartilage incompletely formed

Surgical management of lambdoid synostosis.
Biparietal-occipital craniotomies, occipital switch, and contouring.
Formula to estimate caloric needs in burns.
Curreri formula.
Caloric needs = [25 kcal/kg/day] + [40 kcal/%TBSA/day]
Caloric needs per day = [25 kcal]*[weight in kg] + [40 kcal]*[%TBSA]
Compared with nasal ideals for whites, describe the characteristic differences of black and middle eastern noses?
Blacks
- Wide, low nasal dorsum
- Descreased nasal length and tip projection
- Poor nasal tip definition
- Acute columellar-labial angle
- Alar flaring
Middle Eastern
- Wide nasal bones
- Thick, sebaceous skin
- Ill-defined bulbous tip
- High dorsum and over projecting radix
- Acute columellar-labial angle
- Slight alar flaring