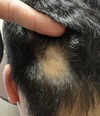
ITE 2018 Flashcards
(93 cards)
What lessens the severity of OSA and reduces blood pressure and offers further benefit beyond that of traditional diuretics?
Aldosterone antagonist (Spironolactone). Resistant hypertension is common in OSA and is associated with higher levels of aldosterone, which can lead to secondary pharyngeal edema, increasing airway obstruction.
What is hypertensive emergency?
SBP >180 or DBP >110 with end organ damage.
symptomatic HCM, what drug to use?
BB. If they are unable to tolerate BB, use verapmil.
HTN medications in AA
Use Thiazides and CCB
Murmur increases with Valsalva
Think HCM
What needs to be considered when starting or adjusting the dosage of novel anticoagulants (NOACs)?
Renal Function novel anticoagulants include apixaban (eliquis), dabigatran (Pradaxa), edoxaban (Savaysa) and rivaroxaban (Xarelto).
What is used to adjust warfarin dosing and what is used to adjust heparin dosing?
INR for warfarin PTT for heparin
What should be initiated in patients with DM, HTN and microalbuminuria?
Ace inhibitors for renal protection Reduce decline in renal function.
In patients with marfan’s what would the cardiac examination reveal? What occurs in 80-100% of affected individuals
aortic regurgitation murmur or a murmur of mitral valve prolapse. Aortic root dilation
What should be obtained in patients presenting with acute atrial fibrillation?
TSH level Patients with hyperthyroidism have threefold risk of developing AFIB.
In patients undergoing or vascular or high risk surgeries such as joint replacement, what is recommended to decrease risk of CVD and perioperative mortality?
statins
The use of gadolinium contrast has been associated with? In what types of patients should we avoid this with?
development of nephrogenic systemic sclerosis. Avoid in patients with GFR <30, as well as patients with renal failure.
What is the most appropriate pharmacological therapy for anticoagulation in pregnant patients?
Enoxaparin (lovenox)
What antihypertensive drug may reduce the severity of sleep apnea?
Spironolactone OSA causes resistant HTN, which is associated with higher levels of aldosterone, which can lead to secondary pharyngeal edema, increasing airway obstruction.
In patients who with HTN that do not have DM, therapy may be started with?
ACEI, Thiazide, Diuretics, or CCB.
What is the preferred test to confirm legionnaire’s disease? What is the gold standard?
Urine test for legionella pneumophilia antigen. Rapid test. Gold standard is sputum cx. Takes 48-72 hours.
What should be avoided in patients with IBS?
Lactulose -Osmotic laxative, it should be avoided in patients with IBS because it is broken down by colonic flora and produces excessive gas.
What is FDA approved for short term treatment in adults and children with occasional constipation and in patients with IBS?
Polyethylene glycol (Miralax), a long-chain polymer of ethylene oxide, is a large molecule that causes water to be retained in the colon, which softens the stool and increases the number of bowel movement.
Test of choice for patients in patients with suspected distal biceps tendon rupture?
MRI
For DM patients, what is the goal HbA1c goal? What is recommended first line as long as there are no contradictions? What if goal is not met or HbA1c is > or = to 9?
7 Metformin Add another agent to metformin.
How do you recognize nephrotic syndrome?
peripheral edema, heavy proteinuria, and hypoalbuminemia, Hyperlipidemia
How do you diagnosis nephrotic syndrome?
protein/cr ratio >3.0-3.5mg OR 24 hour urine collection showing >3.0-3.5 of protein.
IV versus IM versus PO immediate release opioids peak time
morphine, oxycodone, hydromoprhine Oral takes one hour IV takes 10 minutes IM takes 20 mins
What is the only proven therapy for pulmonary hypertension related to COPD patients?
Supplemental oxygen Supplemental oxygen should be recommended when the PaO2 is <60 mmHg, because it has been shown to improve mortality by lowering pulmonary arterial pressures. Do not use PAH drugs such as nifedipine, sildenafil, bosentan because they cause V/Q mismatch.