ISLM, PDV, Risk, Money Supply, Interest Rates Flashcards
Show an increase in interest rates on the Keynesian Cross Diagram
Convert this onto an IS curve

How does an increase in taxes affect the IS curve?
An increase in taxes shifts the IS curve to the left.
As the IS curve is downward sloping, equilibrium in the goods market implies that an increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in output.
Shifting the IS curve: Changes in factors that decrease (increase) the demand for goods given the interest rate shift the IS curve to the left (right).

Explain the terms, money supply and money demand?
The money supply is controlled by the central bank, the central bank can choose to adjust the interest rate to set the money supply or adjust the money supply (by selling bonds) to set the interest rate, in modern day we pretty much only see the first option.
Money demand is the demand for central banks money by the other banks for their reserves.
Real money supply = real money demand
What is the difference between nominal money supply and real money supply?
The nominal money supply is the supply of money controlled by the central bank before it has been deflated by P to account for inflation.
The real money supply has been deflated by price level P.

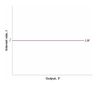
What is the LM curve?
A flat curve, showing the equilibrium in financial markets, it varies directly with the interest rate.
What is the equation for Money supply = money demand?
M = $Y L(i)
State the equation for “real money supply = real money demand”?
M/P = YLi
L(i) = Interest Rate
Y = Real Income
This is reached by dividing both sides of the nominal equation by P.
$Y/P = Y (I think the dollar sign just shows it’s nominal)
What is the equation for the IS relation?
IS Relation:
Y = C(Y-T) + I(Y,i) + G
What is the equation for the LM relation?

What can you find when you put the IS and LM relations together on a graph?
What does each line represent?
- The LM curve represents equilibrium in financial markets
- The IS curve represents equilibrium in the goods market
- Where they cross is output and the current interest rate
This can be used to analyse the effects of changed in policy or exogenous variables:
- Does it shift the IS curve and/or the LM curve?
- What does this do to equilibrium output and the equilibrium interest rate?

What is the purpose of the ISLM model?
To link goods markets with financial markets via interest rates
How will an increase in taxes affect the ISLM graph?
An increase in taxes shifts the IS curve to the left. This leads to a decrease in the equilibrium level of output.
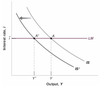
Define monetary expansion and contraction, how will these affect the ISLM graph?
Monetary expansion is an increase in investment
Monetary contraction is an increase in “i” and a decrease in “M” (also called monetary tightening)

What is the drawback of this theoretical ISLM model currently?
How can we adjust for this?
The economy is slow to adjust to policy changes, the model doesn’t show how long it takes to go from one equilibrium to the next.
Y = Actual Output
Y*= Theoretical Equilibrium Output

Explain a second drawback of the ISLM model?
Needs another way of linking financial and goods markets (another “channel”)
- In reality, there is more than just interest rates affecting this relationship
- In order to see these extra things we must look at:
- The value of an asset
- The role of financial assets
- Nominal vs real interest rates
- Risk and Risk Premia







