Introduction to Dermatology Flashcards
(20 cards)
The skin is the largest organ in the body and contains several adnexal structures.
What does this mean and what are these?
Structures adjoining onto an organ
Hair, nails, glands, sensory structures
Identify the labels
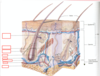

What is the function of the following:
a) Sub-cutis (hypodermis)
b) Dermis
c) Epidermis
Sub-cutis (hypodermis):
- Anchors skin to fascia using fibrous bands
- Fat/energy store & Insulation
Dermis:
- Collagen & elastin matrix
- Mucopolysaccharide gel
- Lots of stuff in it/goes through it
Epidermis:
- Outer layer
- 3 cell types - mostly keratinocytes
What is present in the dermis?
Structures:
- veins & arteries
- hair follicles & associated structures - on diagram
- nerves - i know theyre cells but shut up
- sweat glands
Cells:
- Fibroblasts
- Dermal dendritic cells
- Macrophages
What is the function of melanocytes?
Melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located mainly in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin’s epidermis
Once synthesized, melanin is contained in special organelles called melanosomes which can be transported to nearby keratinocytes where they sit above the nucleus
What are Langerhan’s cells?
Antigen-presenting immune cells
When activated - they move to lymph nodes to induce an immune response
What are the 5 layers (strata) of the epidermis?
(from outermost in)
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
Charlie loves grandmas soggy biscuits xox
Shown is a diagram of the epidermis
For each layer - describe its function
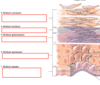
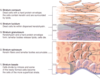
In the diagram below - identify the structures present within each structure
If you want you can relate it to the overall function of the layer(s) its present in

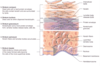
Identify the parts of the nails anatomy
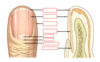
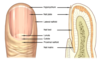
What are the stages of the hair cycle?
Anagen
- Active growing phase
- 80-90% of hair in this stage
Catagen
- Nourishment of growing hair stops - follicle shrinks
- 2nd-3rd week of cycle
Telogen
- resting phase for 1–4 months
- up to 10% of hairs in a normal scalp
What are the functions of the skin?
Thermoregulation:
- Insulation, heat transfer
Skin immune system (SIS):
- Remember all the immune cells in skin
- Innate and adaptive functions
Barrier:
- Protects from chemical, mechanical, UV, microorganisms
- Keeps in water and electrolytes
Sensation:
- Temp, touch, pain
Vit D synthesis
Interpersonal Communication
What are the causes of skin disease?
Causes can be external or internal…
External:
- Infection
- UV
- Trauma
- Chemical (allergen or irritant)
- Temperature
Internal:
- Systemic disease
- Infection
- Genetics
- Drugs
What problem does this patient have?
What usually causes it?

Photosensitivity
Extreme sensitivity to UV light (esp UVA, UVB) which means skin easily damaged
Usually caused by medications
What skin conditions can be caused by cold?
Chilblains
Frostbite
Skin necrosis
Cold urticaria
The following words are used to describe skin lesions - what do they mean?
a) macule
b) patch
c) papule
d) plaque
a) macule - small circumscribed area (usually < 5mm)
b) patch - larger circumscribed area
c) papule - small raised area
d) plaque - larger raised area
The following words are used to describe skin lesions - what do they mean?
a) Vesicle
b) bulla
c) pustule
d) abscess
e) erosion
f) ulcer
a) Vesicle - Small fluid filled
b) Bulla - larger fluid filled
c) pustule - small puss filled
d) abscess - larger puss filled
e) erosion - lesion with loss of epidermis
f) ulcer - lesion with loss of epidermis and dermis
What is urticaria?
AKA Hives
Outbreak of swollen, pale red bumps or plaques (wheals) on the skin that appear suddenly
In response to allergens but also stuff like cold
What are the different investigations available in Dermatology?
For bacterial infection:
- Charcoal swab
- MC&S - Microscopy, culture, sensitivities
For viral:
- Viral swob for PCR (+ swab of bullae etc)
- Can take throat swab in systemic illness
For fungal:
- Skin scraping
- Nair clipping
- Hair sample
- Fungal cultures
General - Skin biopsies (punch biopsies)


