Intro to Opthalmology Flashcards
(42 cards)
Anatomy of the eye
Emmetropia is the refractive state of an eye in which parallel rays of light entering the eye are focused on the retina, creating an image that is perceived as crisp and in focus. Myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism are abnormalities of this desired condition.

In an emmetropic eye the light should come to focus on the macula which is the centre of the retina.
Refractive errors
In people with refractive erroes, either long-sightedness or short-sightedness. The images come into focus either in front of the retina such as in myopia (short sight) or hypertropia (long sightedness) where a short eyeball causes the images to come into focus behind the retina.

Think of the eye as being in the eye socket or orbit:
6 muscles
7 orbital bones

Extraocular muscles
Any misalignment of the visual axis will lead to double vision in adults when good vision has been obtained in each eye.
If the visual axis is misaligned in a child this will lead to suppression of the second image, one lazy eye.

Inflammation in the eye socket:
Will lead to bulging of the eye and possibly compression of the optic nerve. Similarly a tumour in a bony box=proptosis/exopthalmos

On the other hand, what happens with an orbital fracture?
=This leads to in sinking-enophthalmos of the eye and sometimes eye movement restriction if the extra ocular eye muscles are trapped.
In this case-cant look up with left eye as IR is trapped.
Embryology of the eye:
Facial development happens 4-8 weeks of development of the embryo. If things don’t fuse according to plan it can lead to varying clefting syndromes.
The optic vesicle develops as an outpouching of the forebrain from about 4 weeks onwards and tends to invaginate to a form which looks like the eyeball and similarly the structures of the eye form alongside it. Any disturbance of this process will lead to colobomas
The optic vesicle develops as an outpouching of the forebrain from about 4 weeks onwards and tends to invaginate to a form which looks like the eyeball and similarly the structures of the eye form alongside it. Any disturbance of this process will lead to…
…colobomas
Given that the fusion line is inferior, these leads to the typical colobomas defects in the iris and in the retina.

Visual milestones-newborns
So best toy for a child isnt a flully animal but actually a chessboard since they can actually see it

Visual milestones-5 to 8 months

9 months-1 year

The crucial first 7 years
If this process is disrupted in the first 7 years, often irreversible lazy eye (s) can result, which cannot be remedied later on.

Blindness definition
Blindness is the inability to see. The leading causes of chronic blindness include cataract, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration, corneal opacities, diabetic retinopathy, trachoma, and eye conditions in children (e.g. caused by vitamin A deficiency). Age-related blindness is increasing throughout the world, as is blindness due to uncontrolled diabetes. On the other hand, blindness caused by infection is decreasing, as a result of public health action. Three-quarters of all blindness can be prevented or treated.

There are four levels of visual function:
1 normal vision
2 moderate visual impairment
3 severe visual impairment
4 blindness
Most common cause of visual impairment:
=cataract and not having the correct glasses
Cataract is also most common cause of blindness

Causes of blindness
Globally, the leading causes of blindness, in order of frequency, are:
- cataract (a clouding of the lens of the eye that impedes the passage of light),
- uncorrected refractive errors (near-sightedness, far-sightedness or astigmatism),
- glaucoma (a group of diseases that result in damage of the optic nerve),
- age-related macular degeneration (which involves the loss of a person’s central field of vision).
Other major causes include corneal opacities (eye diseases that scar the cornea), diabetic retinopathy (associated with diabetes), blinding trachoma, and eye conditions in children such as cataract, retinopathy of prematurity (an eye disorder of premature infants), and vitamin A deficiency
Trachoma:
Slippery slope to blindness
Strategy: SAFE
Surgery-to rotate the eyelashes out so they don’t wear away at the eye
Antibiotics to treat the infection
Facewashing
Education and environment

Visual impairment in our community
Significant impact on qol and comorbidities

Age related macular degeneration
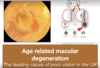
The retina which is the light sensitive film of the eye develops changes which affects vision and bleeding and scarring happens as a result.
In wet type, the visual loss is accelerated.
Age Related macular degeneration (AMD)
‘Dry’ and ‘wet’ .1/3 of those over 75y will have dry AMD changes 2.2% of UK population >65y is blind in 1 or both eyes from AMD. Treatment options: Anti VEGF treatments via intravitreal injections

Wet AMD:

Prevention of wet AMD

Wet AMD treatment options
-Anti-vascular endothelial growth factors which can stabilise the vision in 95%

How is the treatment for wet AMD given?
- The injection is given directly inside the eyeball through the pars plana (safe place)

What does the treatment for wet AMD do?
It reverses the changes. See bleeding and exudation on left and on right changes have been reversed.

Another condition which causes bleeding in the back of the eye is…
…diabetic retinopathy
National service framework

What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic Retinopathy is a microvascular complication of diabetes. The severity is due to the duration and control of diabetes. All patients over the age of 12 have to attend annual screening and are referred to the eye department if the disease exceeds nationally set criteria. Treatment is with laser, a destructive modality which can control progression but cannot restore vision.























