Intro to Motion - Combined Flashcards
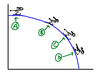
Compare slopes at A and B

Both slopes are large and negative. A has a higher slope.

What would be the net force upon this object?

1 Newton to the right.
m/s SouthEast
Is a unit of?
Velocity
grams x miles/hr
Is a unit of?
Momentum
Describe the Slope

This is a medium constant negative slope.

Describe the velocity at E.

The velocity has decreased until it is amost zero.

Describe the Slope or Steepness.

Medium, Positive, and Constant Slope or Steepness.

Compare slopes at C and D.

Slopes at C and D are both large and negative. The slope at D is larger.

In linear motion, the difference between
-55 mph
and
+55 mph
is?
Direction only
Linear Motion
Motion along a line
What would be the net force upon this object?

10 N to the left.
Describe the Slope of this graph

Begins with a large positive slope.
The slope gradually decreases until the slope is equal to zero.
Acceleration can mean….
Speeding up
Slowing down
or
Turning
(Basically, anything you could feel while you were in a car would indicate acceleration)
Gravitational Field Strength near the Earth’s surface
9.8 newtons/kilogram
The amount of matter in an object.
Mass
Describe the position at D

Positive
Slope or Steepness at A is…..

The slope at A is large and negative

As you go along the curve from A to E, the slope

Decreases
It goes from large negative to zero.

Describe the Slope

This is a medium constant negative slope.

Velocity
Vector Quantity or not?
Vector Quantity
50 mph - North has both magnitude (50) and direction (North).
So, its a vector or vector quantity.
m/s
Is a unit of?
Speed
As you go from A to D, the slope

Increases.
It goes from a slope of zero to a large negative slope.

Describe the Slope

Medium Slope
Negative Slope
Constant Slope

Compare slopes at A and B

Both slopes are large and negative. A has a higher slope.

The slope at C is…

The slope at C is medium and positive

Describe the Steepness

Medium, Constant, Negative Steepness
Describe the Slope

The graph starts with a small positive slope. The slope increases until point “c” Then the slope begins to decrease.
The slope is positive at all times in this graph.

Describe the slope or steepness at B

Small negative slope

Compare slopes at C and D.

Slopes at C and D are both large and negative. The slope at D is larger.

In a motion graph, how do we decide which variable to put on the horizontal axis?
“Time”
Always goes on the horizontal axis for motion graphs in Mr. Bixel’s physical science class.
Describe the Slope

Medium, Constant, Positive.

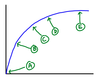
Compare the slopes at points B and C

B has a high positive slope
C has a medium positive slope

Compare the slope of the line at points A and B.

Both have a high positive slope, but A has the highest slope.

How does the slope at point C compare to the slope at point D?

Both are postive slopes, but C has a higher slope.

Inertia
VERY close in meaning to “mass”
BUT
Inertia is usually used when you are talking about stopping a moving object or making a stationary object start moving.
Describe the slope

The graph starts with a large positive slope. The slope decreases to zero. Then, the slope becomes increasingly negative.

Describe the slope or steepness at A.

Zero

Describe the slope at point D

Small positive slope



Describe the position at C

Positive
Compare slopes at C and D.

Slopes at C and D are both large and negative. The slope at D is larger.

Compare the slopes at points B and C

B has a high positive slope
C has a medium positive slope

Displacement
How far you are from where you started, and in what direction.

Describe Slope at C

Slope at C is medium and negative

Describe the steepness or slope at A

Zero

Describe the slope

Negative Slope
Decreasing Slope
(We say the slope is “decreasing” when the “hill” is getting less steep.)

True or False?
This object changes direction.

True!
It started out moving in the positive direction, changed directions at point C, and later moves in the negative direction.

Describe the Slope or Steepness of this graph

Small, Positive and Constant

x
the symbol for position
(X marks the spot)
Any object experiencing zero net force will ALWAYS have _______________
Zero Acceleration
Scaler
A quantity that has a magnitude (size) but no direction.
Examples:
Temperature. 78 degrees tells you how “big” the temperature is, but there is no direction to 78 degrees.
”s” is a unit of
time
”s” means “seconds”
Describe the position at E

Positive
If an object is not accelerating, you can be absolutely positive that it is experiencing ________________.
Zero Net Force
The slope at C is…

The slope at C is medium and positive

The study of motion
Kinematics
The symbol for acceleration
a
“m/s” is a unit of
speed
(Units of speed will always have a distance over a time)
How does the slope at point C compare to the slope at point D?

Both are postive slopes, but C has a higher slope.

The slope(steepness) at D is…

The slope at D is large and positive.

When they describe the “top velocity” of a type of airplane, the reference object they would typically use would be what?
The air the plane is flying in.
Describe the velocity at A

High Positive Velocity
(Remember, the slope of a position time graph IS the velocity.)

True or False?
This object changes direction.

True.
The initial velocity of the object is negative. The object changes direction somewhere between C and D, and then moves in the positive direction.

As you go from A to E, the slope…

Decreases

a
The symbol for acceleration
As you go from A to E, the slope…

Decreases

Describe the slope of this graph

Slope is positive and decreases all the way down to zero slope. Then, the slope becomes increasingly negative

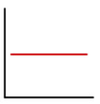
Describe the Slope of the Blue Line

Constant Slope of Zero

The slope at D is….

Large and Negative

Air Friction
The force of friction impeding the motion of an object fighting its way through the air.
(It has to bump the air molecules out of the way)
How does the slope at point C compare to the slope at point D?

Both are postive slopes, but C has a higher slope.

More mass means more ___________.
Inertia
Describe the Slope

Constant
Medium
Positive

Compare slopes at A and B

Both slopes are large and negative. A has a higher slope.

True/False
The entire time between when this cannonball
leaves the cannon until it hits the ground,
the cannonball is in
“Free Fall.”

True.
Once it leaves the cannon, the only force acting upon the cannonball is gravity.
Describe Slope at C

Slope at C is medium and negative

What quantity is this device used to measure?

Time
Objects with bigger mass have more _________
Inertia
Newton’s First Law
Objects in motion stay in motion
Objects at rest stay at rest
If its moving, it will keep moving in a straight line, at the same velocity, FOREVER, unless acted upon by a net force.
Describe the position and velocity at point A

Position is negative
Velocity is large and positive

Describe the Slope

The graph has a Constant Large Negative Slope

Slope at E is….

Zero

Describe the steepness or slope at A

Zero

Describe the Slope

Medium Slope
Negative Slope
Constant Slope

Velocity
The speed and direction an object is travelling.
Describe the position and velocity at point E

Object has reached the reference point and has come to a stop.

What is secret # 4 for understanding these graphs
Secret #4
Just use the word “Steepness” instead of Slope when you write down your description o fthe graph.
Then, go back and erase the word “Steepness” and write in the word slope.
Describe the Slope

Contant zero slope
Position at A is..

High positive

Acceleration = (8 mph) / second
Another way of saying that someone is accelerating in such a fashion that each second they were going 8 mph faster than the second before?
Describe the position at point A

The position at point A is zero. The object is at the reference point.

Compare slopes at C and D

Both are negative slopes
C has a higher slope

Describe the Slope of this graph

Begins with a large positive slope.
The slope gradually decreases until the slope is equal to zero.

cm/day
Is a unit of?
Speed
The position at A is

Zero.
It is at the reference point.

Describe the Slope

Medium, Constant, Positive.

Describe the position at A

Positive
Describe the Slope of the Red Line

The slope is infinite.
Some may describe this as “undefined.”

Describe the Slope of this Graph

Starts with medium positive slope.
Slope gradually increases until it is quite steep.

What would be the net force upon this object?

30 N to the right.
As you go from A to E, the slope…

Decreases

Describe the slope at point E.

Zero

If a graph has a positive steepness, how would you describe the slope
The graph has positive slope.
(Just replace the word steepness with slope)
What would the net force be upon this object?

2 N to the right
Definition of Mass
The amount of matter in an object.
(Each time you add an atom to an object, you add mass)
Three most common types of interaction
Touch
Gravity
Friction
The slope(steepness) at D is…

The slope at D is large and positive.

“hr” is a unit of
time
Compare the slope of the line at points A and B.

Both have a high positive slope, but A has the highest slope.

The slope at B is….

The slope is small and positive at point B

What are these things?

Ball Bearings

Slope at E is….

Zero

m/s - North
Is a unit of?
Velocity
As you go along the curve from A to D, the slope…

Becomes increasingly positive.

As you go along the curve from A to D, the slope…

Becomes increasingly positive.

In linear motion, how will we show the direction an object is travelling?
With a “+” sign or a “-“ sign.
The plus would mean one direction, and the minus would mean in the exact opposite direction.
Describe the velocity at A.

Large Negative Velocity

A letter written smaller and below the rest of the writing.
<span>v</span>t
Here the “ t “ is subscripted
Subscript
Interaction
When two objecst have an effect upon each other.
In order to describe the velocity of an object, you must always refer to a ___________ _____________.
reference object
Position at clock reading = zero
<span>x</span>0
newton
Is a unit of?
Force
Describe the motion of the object at D

At D, the object is moving quite fast in the negative direction.

Describe the Slope

Contant zero slope

Slope or Steepness at A is…..

The slope at A is large and negative

Force
Vector Quantity or not?
Vector
50 newtons downward has both magnitude (50) and direction (downward).
So, its a vector or vector quantity.
Describe the slope of this graph.

The slope starts out medium and positive and is fairly constant.
Then, the slope rapidly decreases to zero and then becomes increasingly negative.
At the end, the slope is medium, constant and negative.

What quantity is this device used to measure?

Mass
(Note, mass is different than weight)
Scales measure weight
Balances measure mass

Average Speed
A single speed that can be used to represent an object’s speed during a period of time, even if the object is changing speeds.
Sliding Fricition means…
The force of friction impeding the motion of an object sliding across a surface.
“mm/yr” is a unit of
Speed
(Units of speed will always have a distance over a time)
d
the symbol for distance
All of the red lines are ____________ to the red curve.

“Normal”
Describe the slope at point D

Small positive slope

Describe the steepness or slope at A

Zero

In motion along a line, what is the difference between the following two “velocities?”
17 m/s
-17 m/s
The objects are traveling at the same speed, but in opposite directions.
In linear motion, we can use plus and minus to represent different directions.
What can this tell you about mass and weight?

The Earth’s gravity applies a force of
9.8-Newtons to a 1-kg mass

Describe the slope

Negative Slope
Decreasing Slope
(We say the slope is “decreasing” when the “hill” is getting less steep.)

The size of the force of air friction is dependant upon
______________
and
_______________
The size and shape of an object
and
The speed at which the object is moving relative to the air.
In a motion graph, how do we decide which variable to put on the horizontal axis?
“Time”
Always goes on the horizontal axis for motion graphs in Mr. Bixel’s physical science class.
Describe the Slope

The slope is constant and it is zero.
Acceleration
That rate at which you change your velocity.
Example:
Every second, he was going 5mph faster than the second before.
The slope at B is….

The slope is small and positive at point B

The slope at D is….

Large and Negative

Describe the slope or steepness at A.

Zero

Describe the Slope

Zero
(I guess its constant too)

This is called a

Motion Map
Slope at E is….

Zero

Which object is moving faster?
A car going +10 mph
A moped going - 10 mph
Neither.
They are both going the same speed, but in different directions.
Is the following a description of a distance or a displacement?
He travelled 20 miles North.
Displacement
(Magnitude = 20 miles)
(Direction = North)
Describe the Slope

Initially, the slope is large and positive. The slope then decreases until it is small and positive.

Velocity at A is …

At A, the velocity is large and negative.

Compare the slopes at points B and C

B has a high positive slope
C has a medium positive slope

“Free Fall”
When the ONLY force acting upon an object is gravity.
This can be after an object is dropped.
It can also be after an object is thrown up.
It can even be after an object is thrown sideways.
In all these situations, the only force acting upon the object is gravity.
What quantity is this device used to measure?

Volume
True/False
The soccer ball shown in the picture is in “Free Fall.”

True.
It doesn’t matter if the ball is going up, down, or sideways. As long as the only force acting upon the ball is gravity, it is in “Free Fall.”
Tell me about this object at point E.

It is now quite far from the reference point in the negative direction, but the object has come to a stop.

How would you describe the slope (steepness) at point A?

High Positive Slope

Gravity
A force between any two objects with mass
Describe the Slope

The slope is constant and it is zero.
What word can be used in the exact same place as the word slope?
Steepness
Distance
Vector Quantity or not?
Not
25 meters does not have a direction.
No direction, not a vector.
Is “speed” a scaler or a vector?
It is a scaler. Speed has a magnitude (size) but no direction.
Example: 50 mph.
Electrical charges can apply a _________
Force
(Think of static electricity pulling a sock onto your shirt when you take them out of dryer.)
Compare the slopes at points B and C

B has a high positive slope
C has a medium positive slope

The slope at D is….

Large and Negative

v
the symbol for velocity
What is the formula for finding
Average Speed

Is velocity a vector or a scaler?
Velocity is a vector.
It has both magnitude (size) AND direction.
Example:
Her velocity was 30 mph north.
Slope or Steepness at A is…..

The slope at A is large and negative

The angle of a line on a graph
Slope
meter
Is a unit of?
Distance
Why hasn’t Mr. Bixel written my assignments down on the Moodle calendar for the past few days?
Because, something is wrong with the server, and he does not have access to Moodle.
Describe the slope at point E.

Zero

Describe the slope at point E.

Zero

Mass and Weight mean ____________ things.
Different
“m/s North” is a unit of
Velocity
(notice that it has a direction included)
Velocity at clock reading = t
<span>v</span>t
As you go from A to D, the slope

Increases.
It goes from a slope of zero to a large negative slope.

Describe the steepness or slope at A

Zero

Compare the slope of the line at points A and B.

Both have a high positive slope, but A has the highest slope.

Describe the Slope

Starts with a small positive slope. The slope increases until it is medium and positive.



Compare slopes at C and D

Both are negative slopes
C has a higher slope

What word can be used in the exact same place as the word slope?
Steepness
miles East
Is a unit of?
Displacement
<span>v</span>0
Velocity at clock reading = zero
A force is a
Push or a Pull
Describe the Steepness

Medium, Constant, Negative Steepness
Distance
How far you have travelled.

Describe the Steepness

Constant Medium Positive Steepness (Slope)
In which direction would the net force be upon this object?

To the left.

the symbol for position
x
Describe the slope at point E.

Zero

The slope at B is….

The slope is small and positive at point B

Describe the steepness

Negative Steepness
Decreasing Steepness
(We say the slope is “decreasing” when the “hill” is getting less steep.)

Describe the slope at point D

Small positive slope

As you go from A to D, the slope

Increases.
It goes from a slope of zero to a large negative slope.

What would be the net force upon this object?

30 N to the right
Mass means pretty much the same thing as ________
Inertia
An object in motion will stay in motion in a straight line, forever, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
Half of Newton’s First Law
Constant Speed
Not speeding up or slowing down
Time
Vector Quantity or not?
Not
3 seconds does not have a direction.
No direction, not a vector.
Velocity at A?

High Positive.
(Its a velocity graph!!!)

The slope at C is…

The slope at C is medium and positive

Describe position and velocity at pont A

The object is at the reference point and has not yet started to move.

A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Example:
Forces are vectors because if you push or pull on something, there is a magnitude (size) of your push, and there is always a direction of your push.
Vector
An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
The other half of Newton’s First Law
The slope at C is…

The slope at C is medium and positive

Describe the slope of this graph

Slope is positive and decreases all the way down to zero slope. Then, the slope becomes increasingly negative

“miles” is a unit of
distance
Velocity at clock reading = zero
<span>v</span>0
Inertia means almost the same thing as __________
Mass
Compare slopes at A and B

Both slopes are large and negative. A has a higher slope.

Describe the slope at point D

Small positive slope

You can reduce the friction between to sliding surfaces by coating the surfaces with a ______________.
Lubricant
(oil, grease. etc)
Position at clock reading = “t”
<span>x</span>t
30 meters is a distance, so its a scalar quantity.
If you add a direction so it reads
30 meters north, then it becomes
_______________ which is a ______________
If you add a direction so it reads
30 meters north, then it becomes
displacement which is a vector.
Describe the motion of the object at D.

The object is slowing down, and has almost stopped. It is still moving slowly in the negative direction.

Magnetism can apply a __________
Force
Describe the Slope

Slope = Infinity
or
The slope is undefined.

Describe the velocity at D

At D, the object is moving quite fast and in the positive direction.

Describe the Slope

Starts with a small positive slope. The slope increases until it is medium and positive.

Two definitions of acceleration
Change in speed or direction
or
Change in Velociy
Describe the Slope of the Red Line

The slope is infinite.
Some may describe this as “undefined.”

miles/hr - West
Is a unit of?
Velocity
If you took this thingy to the moon and looked at it, the mass would _______________?

Stay the same.
The 1-kg label on th object will still say 1-kg, and it will still be correct.

Describe the Slope

Slope = Infinity
or
The slope is undefined.

Describe the Slope or Steepness.

Medium, Positive, and Constant Slope or Steepness.

Velocity
Vector or Scaler?
Vector
<span>x</span>t
Position at clock reading = “t”
Describe the position of this object at point A.

HOGWASH!!!!!
This is a velocity graph. It tells me nothing about position!!!!!

Describe the slope or steepness at A.

Zero

Describe the Slope

The slope is zero
The slope is constant

Describe the slope at point D

Small positive slope

Normal
Perpendicular
Change in Momentum
Impulse
Compare slopes at C and D.

Slopes at C and D are both large and negative. The slope at D is larger.

Look carefully at the following graph. Does this show and object that is moving or standing still.

“m” is a unit of
distance
Speed
Vector Quantity or not?
Not
50 mph does not have a direction.
No direction, not a vector.
Distance
Vector or Scaler?
Scaler
(Distance has magnitude only)
Velocity at C

Negative velocity

How can you determine the direction in which friction acts upon a moving object
Friction will act in the direction opposite of the motion of the object.
inch
Is a unit of?
Distance
Describe the steepness or slope at A

Zero

If objects in motion tend to stay in motion, forever, unless acted upon by a net force, why do we seem to always see objects slowing down on their own?
Friction
(This is the force usually slowing down objects, and it is hard to actually see where the friction is coming from)
How does the slope at point C compare to the slope at point D?

Both are postive slopes, but C has a higher slope.

What happens between B and C?

The object turns around.
(It was going in the negative direction, now it is going in the positive direction.

Describe the Slope or Steepness of this graph

Small, Positive and Constant

As you go along the curve from A to D, the slope…

Becomes increasingly positive.

t
The symbol for time
As you go along the curve from A to D, the slope…

Becomes increasingly positive.

Gravity can apply a ___________
Force
Speed
Vector or Scaler?
Scaler
(has only magnitude)
If you say a ball is 30 feet up, what would typically be your reference point.
The ground below the ball.
(The ball would be 30 feet away from the reference point or ground in this case)
What would be the net force upon this object?

10 Newtons to the left.
Describe the Slope

The slope of a vertical line is infinity
(Some would say the slope is “undefined”)

In Newton’s Third Law, which happens first, the action or the reaction.
Neither!
The “action” and “reaction” forces always happen at the exact same time.
The slope(steepness) at D is…

The slope at D is large and positive.

kilogram
Is a unit of?
Mass
Describe the Slope of this Graph

Positive and Increasing

Describe the position and velocity at point D.

The object is moving quite fast in the negative direction and is far from the reference point.

Describe the position at A

High positive position

Describe the Slope

The slope is medium, positive, and constant.

Describe the steepness

Negative Steepness
Decreasing Steepness
(We say the slope is “decreasing” when the “hill” is getting less steep.)

Describe the Slope of the Purple Line

Medium Positive Constant Slope

Describe the slope at point D

Small positive slope

Describe the velocity at A.

The velocity at A is large and positive.
(Check the Axes!!)

How does the slope at point C compare to the slope at point D?

Both are postive slopes, but C has a higher slope.

What is this object doing at point A?

This object is at the reference point and is moving quite fast in the negative direction.

Describe the slope or steepness at B

Small negative slope

As you go along the curve from A to E, the slope

Decreases
It goes from large negative to zero.

Reference object
An object that can be used as a reference for both position and for velocity.
Describe the slope at point E.
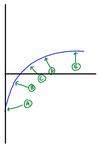
Zero

Describe the slope of this graph

positive and increasing

The word slope means ______________
Steepness
The slope at B is….

The slope is small and positive at point B

As you go along the curve from A to E, the slope

Decreases
It goes from large negative to zero.

Slope or Steepness at A is…..

The slope at A is large and negative

Air Friction
The force impeding the motion of an object traveling through the air.
Describe the motion of the object at E.

The object is moving quite fast in the negative direction.

The slope at D is….

Large and Negative

As you go from A to E, the slope…

Decreases

Acceleration
Vector Quantity or not?
Vector
- 5 m/s2 has both magnitude (5) and direction (negative).
So, its a vector or vector quantity.
Describe the Slope

The slope is constant and zero

As you go from A to D, the slope

Increases.
It goes from a slope of zero to a large negative slope.

Instantaneous Speed
How fast an object is going at an instant in time. It is what is shown on the speedometer of a car.
What can this thingy tell you about weight?

Weight is a force.

The word slope means ______________
Steepness
Net Force
The overall force acting upon an object.
Describe the overall motion of this object.

Starts at rest in a negative position. It speeds up in the positive direction and passes the reference point.

What quantity is this device used to measure?

Length
Describe the slope or steepness at A.

Zero

m/s2
Is a unit of?
Acceleration
The slope at C is…

The slope at C is medium and positive

Compare the slope of the line at points A and B.

Both have a high positive slope, but A has the highest slope.

What would happen to your weight if you left Earth and went to Jupiter?
Your weight would go up.
Jupiter has a much stronger gravitational field than the Earth. Weight is the pull of gravity upon an object.
What is this thing?
(scroll down and look at entire picture)

Your secret weapon to get 4 questions right on the upcoming test.

The word “static” means….
at rest
Describe the steepness of this graph

positive and increasing

the symbol for velocity
v
Normal Force means a force ___________ to a surface
Perpendicular
As you go along the curve from A to D, the slope…

Becomes increasingly positive.

A point or exact location that can be used to help describe the location of some other point or object.
Reference Point
Compare slopes at C and D

Both are negative slopes
C has a higher slope

Describe the slope or steepness at B

Small negative slope

The slope(steepness) at D is…

The slope at D is large and positive.

“mm/yr East” is a unit of
Velocity
(notice that it has a direction included)
What is the formula for calculating momentum?
Momentum = Mass x Velocity
Slope = rise/run
The formula for calculating the slope of a line.
When we make a motion graph, what variable will ALWAYS be on the horizontal axis?
Time
(Even if time is the dependent variable, we will always put it on the horizontal axis in motion graphs.)
The force of gravity upon an object
weight
You walk all the way around a typical high school track. Its about 400 meters.
Your Distance = ___________
Your Displacement = _____________
Your Distance = ___\_400-m______\_
Your Displacement = ___\__0-m\________
Distance is how far you travel.
Displacement is how far you end up from the starting point.
How would you describe the slope (steepness) at point A?

High Positive Slope

The slope at D is….

Large and Negative

How would you describe the slope (steepness) at point A?

High Positive Slope

Describe the Slope of this Graph

Positive and Increasing

Newton’s Third Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Describe the Slope

The slope is medium, positive, and constant.

Describe the velocity of the object at E.

At E, the object has stopped, so it has zero velocity.

Describe the Slope

The slope is constant and zero

What is secret # 4 for understanding these graphs
Secret #4
Just use the word “Steepness” instead of Slope when you write down your description o fthe graph.
Then, go back and erase the word “Steepness” and write in the word slope.
Another way to say perpendicular
Normal
In order to describe the position of an object, you must always refer to a ___________ _____________.
Reference Point
(or reference object)
Compare the slope of the line at points A and B.

Both have a high positive slope, but A has the highest slope.

“days” is a unit of
“inches / day2“ is a unit of
acceleration
(notice the the units on the bottom is days squared)
Mass
How much “stuff” there is in an object.
(or how much matter)
(each added atom or molecule adds mass)
acceleration / time graph
A motion graph with time on the horizontal axis and acceleration on the vertical axis.
Describe the Slope

Medium
Constant
Negative

The symbol for time
t
Compare slopes at C and D.

Slopes at C and D are both large and negative. The slope at D is larger.

Describe the slope or steepness at A.

Zero

If all the forces on an object are balanced, then there is no net force. In this case, we say the object is in ____________
Equilibrium
That rate at which you change your velocity.
Example:
Every second, he was going 5mph faster than the second before.
Acceleration
Slope at E is….

Zero

Position
The location of an object in relation to some “reference point”
Describe the Slope of the Purple Line

Medium Positive Constant Slope

Describe the slope

Initial large positive slope.
Slope
You are about to go outside to take measurements necessary to calculate your top running speed. What measurments would you need to take.
Distance
and
Time
(because S = d/t )
Another way of saying that someone is accelerating in such a fashion that each second they were going 7 meters per second faster than the second before?
Acceleration = (7 m/s) / s
or
7m/s2
Compare the slopes at points B and C

B has a high positive slope
C has a medium positive slope

Compare slopes at C and D.

Slopes at C and D are both large and negative. The slope at D is larger.

Compare slopes at C and D

Both are negative slopes
C has a higher slope

Describe the Steepness

Constant Medium Positive Steepness (Slope)
m / s2 is a unit of
acceleration
(notice the the units on the bottom is seconds squared)
Describe the Slope

Zero
(I guess its constant too)

Slope or Steepness at A is…..

The slope at A is large and negative

As you go along the curve from A to E, the slope

Decreases
It goes from large negative to zero.

Describe the Slope

Medium
Constant
Negative

kg m/sec
Is a unit of?
Momentum
Vector
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Example:
Forces are vectors because if you push or pull on something, there is a magnitude (size) of your push, and there is always a direction of your push.
Describe the slope

The graph starts with a large positive slope. The slope decreases to zero. Then, the slope becomes increasingly negative.

Subscript
A letter written smaller and below the rest of the writing.
<span>v</span>t
Here the “ t “ is subscripted
Which object is moving the fastest?

A
The steepest line on a position/time graph represent the fastest moving object.
(A is moving the opposite direction from B and D)
What would happen to your mass if you left Earth and went to Jupiter?
Nothing.
Mass is a measure of how much “stuff” or matter there is in an object.
Describe Slope at C

Slope at C is medium and negative
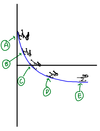
Slope or Steepness at A is…..

The slope at A is large and negative

Describe the velocity of the object at A.

The velocity of the object at point A is zero.

Describe the slope

Initial large positive slope.
Slope
Compare slopes at C and D

Both are negative slopes
C has a higher slope

Slope
The angle of a line on a graph
Describe the general motion of this object.

This object starts out “at rest.” It then gradually picks up speed as it passes the reference point moving in the negative direction.

Describe the slope or steepness at B

Small negative slope

Describe the velocity at E

Velocity at E is zero.
(the slope of a position/time graph IS the velocity)

In linear motion, the “+” and the “-“ symbols are used to show what?
Direction
Slope at E is….

Zero

Describe Slope at C

Slope at C is medium and negative

When we refer to the “trace” on a graph, we are talking about …
The best fit line or curve on the graph.
Compare slopes at C and D

Both are negative slopes
C has a higher slope

As you go along the curve from A to D, the slope…

Becomes increasingly positive.

Kinematics
The study of motion
Tension
A force exerted by a string or rope.
How would you describe the slope (steepness) at point A?

High Positive Slope

As you go from A to D, the slope

Increases.
It goes from a slope of zero to a large negative slope.

“miles North” is a unit of
Displacement
(Displacement is a vector, so it has both magintude and direction.)
Describe the Slope

The slope of a vertical line is infinity
(Some would say the slope is “undefined”)

The formula for calculating the slope of a line.
Slope = rise/run
The slope at B is….

The slope is small and positive at point B

Describe the position at point A

At point A, the object is:
- Far from the reference point.
- In a negative position

Describe the Slope

The graph starts with a small positive slope. The slope increases until point “c” Then the slope begins to decrease.
The slope is positive at all times in this graph.

Describe Slope at C

Slope at C is medium and negative

Definition of Weight
The force of gravity upon an object.
<span>v</span>t
Velocity at clock reading = t
If there is no air friction, which would experience a greater acceleration when dropped off a cliff, a large rock or a small rock?
Neither, both would accelerate at the same rate, and both would reach the ground at the same time.
Describe the slope at point E.

Zero

Magnitude
How big something is.
Describe the Slope

Zero

True or False
This motorcycle rider is in “Free Fall.”

True.
Once he goes off the jump, the only force acting upon him is the force of gravity. (Until he lands of course)
Describe the Slope

The slope is zero
The slope is constant

Position/Time graph
A motion graph with “time” on the horizontal axis and “position” on the vertical axis.
This graph shows the motion of 4 objects.

Describe the Slope

Initially, the slope is large and positive. The slope then decreases until it is small and positive.

Describe the Slope of the Blue Line

Constant Slope of Zero

Describe the general motion of this object over the period of time graphed.

This object starts with a very high initial positve velocity, and a negative position. It slows down as it passes the reference point and eventually comes to rest at point E.

If a graph has a positive steepness, how would you describe the slope
The graph has positive slope.
(Just replace the word steepness with slope)
The slope(steepness) at D is…

The slope at D is large and positive.

Compare the slope of the line at points A and B.

Both have a high positive slope, but A has the highest slope.

Formula for finding Weight
Weight = ___________ x ____________
Weight = mass x gravity
If an object is experiencing an unbalanced force, we know that the _________ _____________ is not zero.
Net Force
Is displacement a vector or a scalar?
Displacement is a vector. It has both magnitude and a direction.
Describe the steepness or slope at A

Zero
miles/hr
Is a unit of?
Speed
Describe the slope or steepness at A.

Zero

Another way of saying that someone is accelerating in such a fashion that each second they were going 8 mph faster than the second before?
Acceleration = (8 mph) / second
Describe the steepness of this graph

positive and increasing

True/False
This fighter jet is in “Free Fall.”

False.
This fighter jet has more forces acting upon it than just gravity. It is experiencing the following forces:
- Gravity
- “Lift” (from the air on the wings)
- “Thrust” (generated by the afterburners)
“cm/day” is a unit of
speed
(Units of speed will always have a distance over a time)
milliNewtons
Is a unit of?
Force
Speed
How fast an object is traveling.
(Direction is not important)
Touch
Gravity
Friction
The three things we often think about when we are looking for forces.
If you took this thingy to the moon and looked at it, the weight would _______________?

Go down.
The moon has less gravity, so the red needle would only point to about 2.

Formula for acceleration
Accleration =
Acceleration = change in velocity/change in time
can also be written as:
a = Δv / Δt
Velocity at A

Zero
(remember, the slope of a position/time graph IS the velocity)

How fast an object is traveling.
(Direction is not important)
Speed
How would you describe the slope (steepness) at point A?

High Positive Slope

As you go along the curve from A to E, the slope

Decreases
It goes from large negative to zero.

Pounds
Is a unit of?
Force
The location of an object in relation to some “reference point”
Position
As you go from A to E, the slope…

Decreases

The slope at D is….

Large and Negative

“cm/hr West” is a unit of
Velocity
(notice that it has a direction included)
Another name for Newton’s First Law
Law of Inertia
The slope at B is….

The slope is small and positive at point B

What can you tell about this object at point A?

It is “at rest” and it is quite far from the reference point. Its position is negative.

The blue line could also be consider to be ______________ to the red surface

“Normal”
“cm West” is a unit of
Impulse
Change in Momentum
Describe the position at B.

Positive

What control or controls in a car is often used to cause the car to accelerate?
Gas Pedal
Brakes
Steering Wheel
(Remember, an acceleration can mean speeding up, slowing down, or turning)
How big something is.
Magnitude
Describe the slope or steepness at B

Small negative slope

“cm” is a unit of
distance
When you describe the velocity of a car, your typical reference object would be what?
The surface of the road beneath the car.
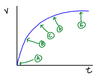
As you go from A to E, the slope…
Decreases

Compare slopes at A and B

Both slopes are large and negative. A has a higher slope.

A single speed that can be used to represent an object’s speed during a period of time, even if the object is changing speeds.
Average Speed
Position at E is….

The position at E is almost zero
(it is very slightly positive)

Describe the overall motion of this object.

Starts in a positive position with a high negative velocity. It passes the reference point while gradually slowing to a stop.

Newton’s Second Law
A = F/M
(Acceleration = Force divided by Mass)
Describe the Slope

Slope = 0 at the start.
Abruptly changes to constant negative medium slope.
Abruptly changes back to a slope of zero.

Compare the slopes at points B and C

B has a high positive slope
C has a medium positive slope

The definition of “Displacement” is “how far you are from the reference point and in what direction.”
Displacement can also often be thought of as:
How far you are from where you started. (and in what direction)
The slope at C is…

The slope at C is medium and positive

m/(s x s)
Is a unit of?
Acceleration
<span>x</span>0
Position at clock reading = zero
Describe the slope of this graph

positive and increasing

A quantity that has a magnitude (size) but no direction.
Examples:
Temperature. 78 degrees tells you how “big” the temperature is, but there is no direction to 78 degrees.
Scaler
Describe the velocity at point A

The velocity at point A is zero.
(This is a velocity graph!)

The slope(steepness) at D is…

The slope at D is large and positive.

How would you describe the slope (steepness) at point A?

High Positive Slope

Velocity/Time graph
A motion graph with time on the horizontal axis and velocity on the vertical axis.

Describe the Slope

The graph has a Constant Large Negative Slope

Static Friction means
The force of friction preventing a motionless object from moving.
Describe Slope at C

Slope at C is medium and negative

Temperature
Vector Quantity or not?
Not
37 degrees does not have a direction.
No direction, not a vector.
As you go from A to D, the slope

Increases.
It goes from a slope of zero to a large negative slope.

Describe the slope of this graph.

The slope starts out medium and positive and is fairly constant.
Then, the slope rapidly decreases to zero and then becomes increasingly negative.
At the end, the slope is medium, constant and negative.

How does the slope at point C compare to the slope at point D?

Both are postive slopes, but C has a higher slope.

Describe the velocity at point E.

The velocity at point E is high and positive.
(Its a velocity graph!!!)
kiloNewtons
Is a unit of?
Force
Reference Point
A point or exact location that can be used to help describe the location of some other point or object.
What is meant by the acronym:
A.U.T.O.graph
When we look at graphs, we will always think about:
A - the axes
U - the units
T - the trace
O - the origin
What would be the net force upon this object?

100 Newtons upward

Describe the Slope

Slope = 0 at the start.
Abruptly changes to constant negative medium slope.
Abruptly changes back to a slope of zero.

Which object is not moving?

C
True or false.
This object is moving at a constant speed.

False

Slope at E is….

Zero

“in” is a unit of
distance
the symbol for distance
d
Describe the Slope of this Graph

Starts with medium positive slope.
Slope gradually increases until it is quite steep.

What is happening at point D

The object has reached quite a high positive velocity and is about to blow past the reference point.

Describe the Slope

Zero

Displacement
Vector or Scaler?
Vector
As you go along the curve from A to E, the slope

Decreases
It goes from large negative to zero.

Describe the slope or steepness at B

Small negative slope

What mathematical calculation would you do to determine the net force upon the skydiver shown here?

Net Force = (Force of Gravity) - (Force of Air Friction)
Is the following a description of a distance or a displacement?
He traveled 30 meters.
Distance
It has no direction, so it cannot be a displacement.
Describe the Slope

Constant
Medium
Positive

Compare slopes at A and B

Both slopes are large and negative. A has a higher slope.

How fast an object is going at an instant in time. It is what is shown on the speedometer of a car.
Instantaneous Speed
“Uniform Linear Motion”
is just a physicsy way of saying….
“Moving in a straight line at a steady speed.”


